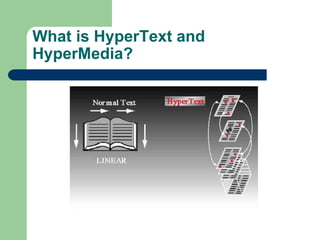
This document defines multimedia and discusses its applications. Multimedia is defined as using more than one medium, such as text, graphics, sound, animation and video. It is digitized to allow computer manipulation. Examples of multimedia applications include the World Wide Web, interactive TV, computer games and virtual reality. Multimedia can be linear or nonlinear. It is important for learning as it engages multiple senses. Careers in multimedia include positions in management, production, art, content and support.