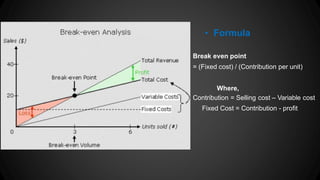
The document outlines the key components of a feasibility study, including market analysis, technical analysis, financial analysis, economic analysis, and legal/administrative considerations. It discusses the importance of feasibility studies in determining the viability of a proposed project or initiative. Specifically, the document provides details on how market analysis and financial analysis are conducted as important dimensions of feasibility that help evaluate opportunities, costs, and potential profitability.