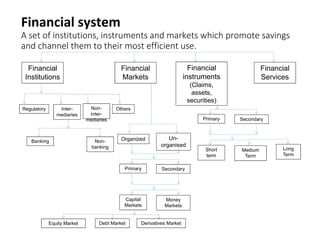
This document defines key terms in finance and describes various financial institutions and markets. It begins by defining finance, money, and credit. It then discusses two main classifications of finance - public and private. Next, it examines different types of financial institutions like banks, investment companies, insurance companies, and credit unions. It also explores various financial markets and instruments. In closing, the document emphasizes the relationship between financial institutions and markets.