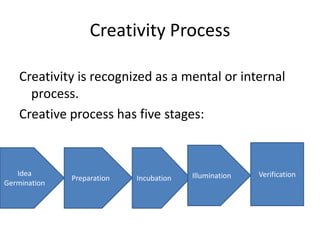
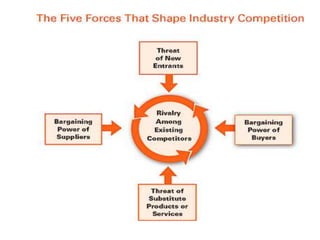
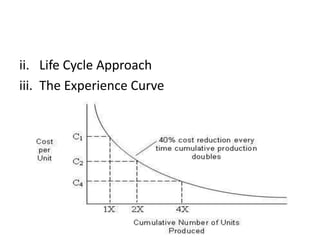
This document discusses creativity and entrepreneurship, outlining key aspects of developing a creative plan and project. It covers stages of creativity like idea generation and incubation. It also discusses identifying project opportunities through tools like SWOT analysis and monitoring trends. Project planning involves defining objectives, scheduling, and designing controls. The stages of project formulation include feasibility, economic, technical, input, financial, and social cost-benefit analyses. Market and demand analysis and financial analysis are also important parts of evaluating a potential project.