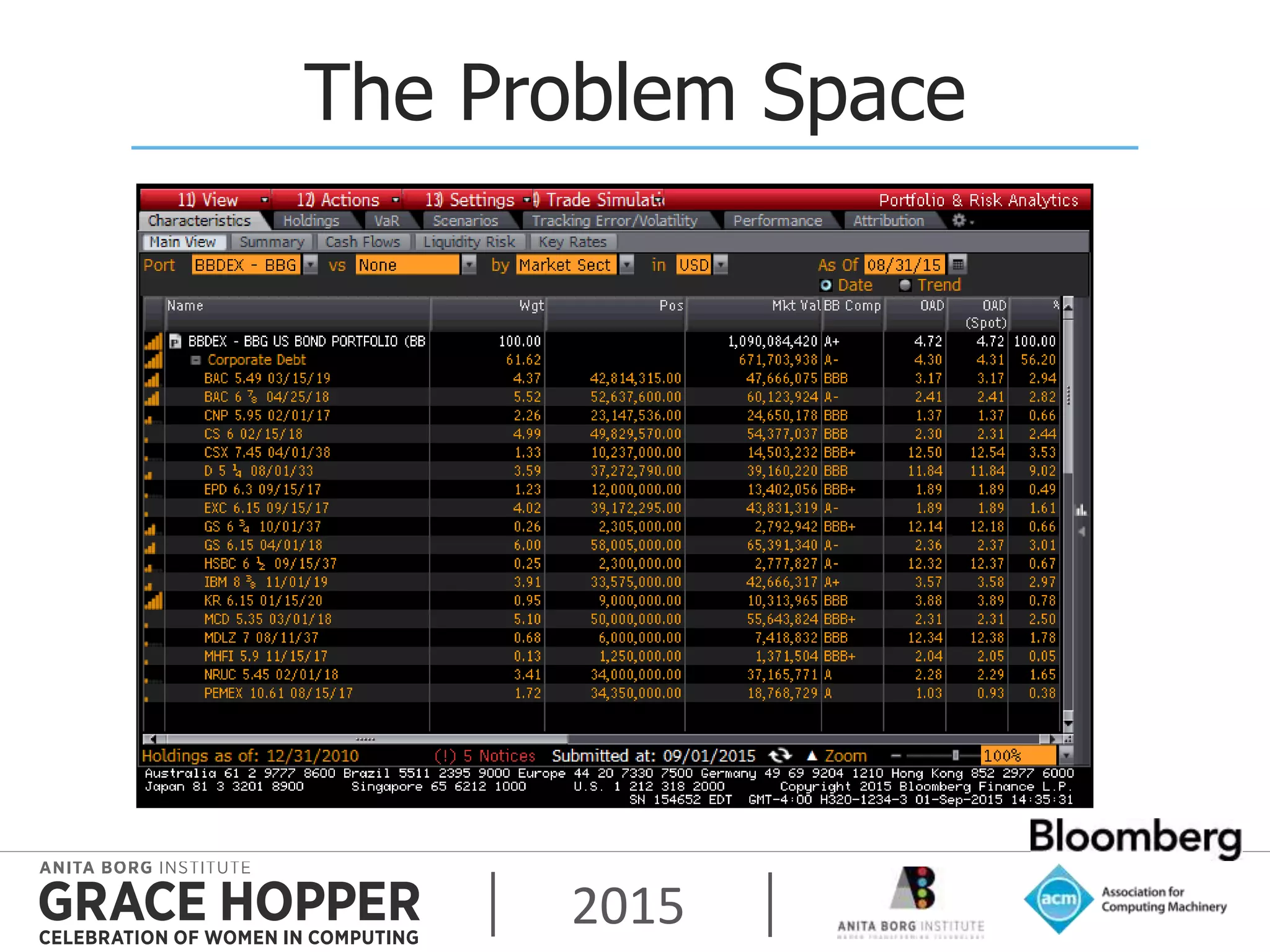
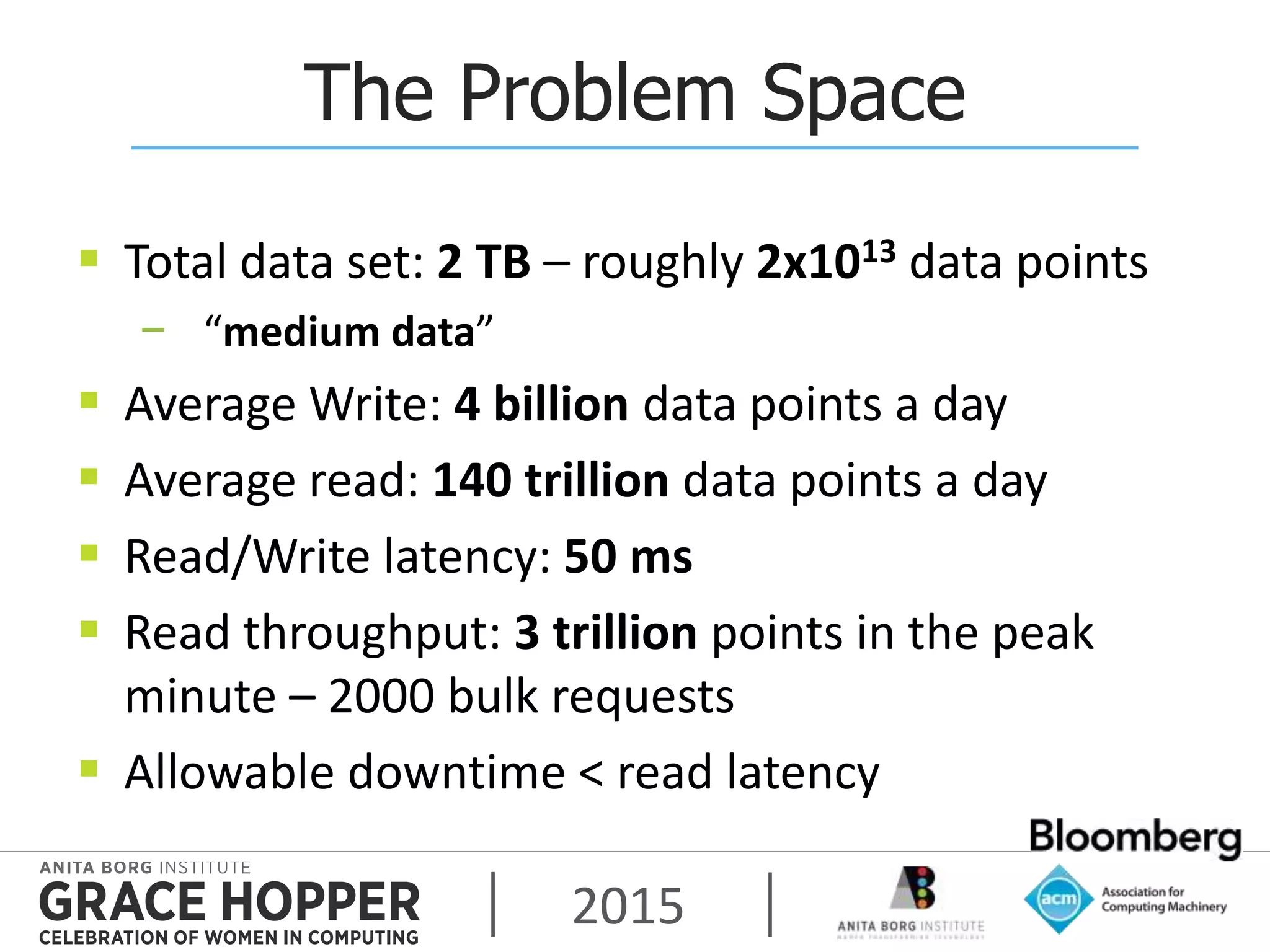
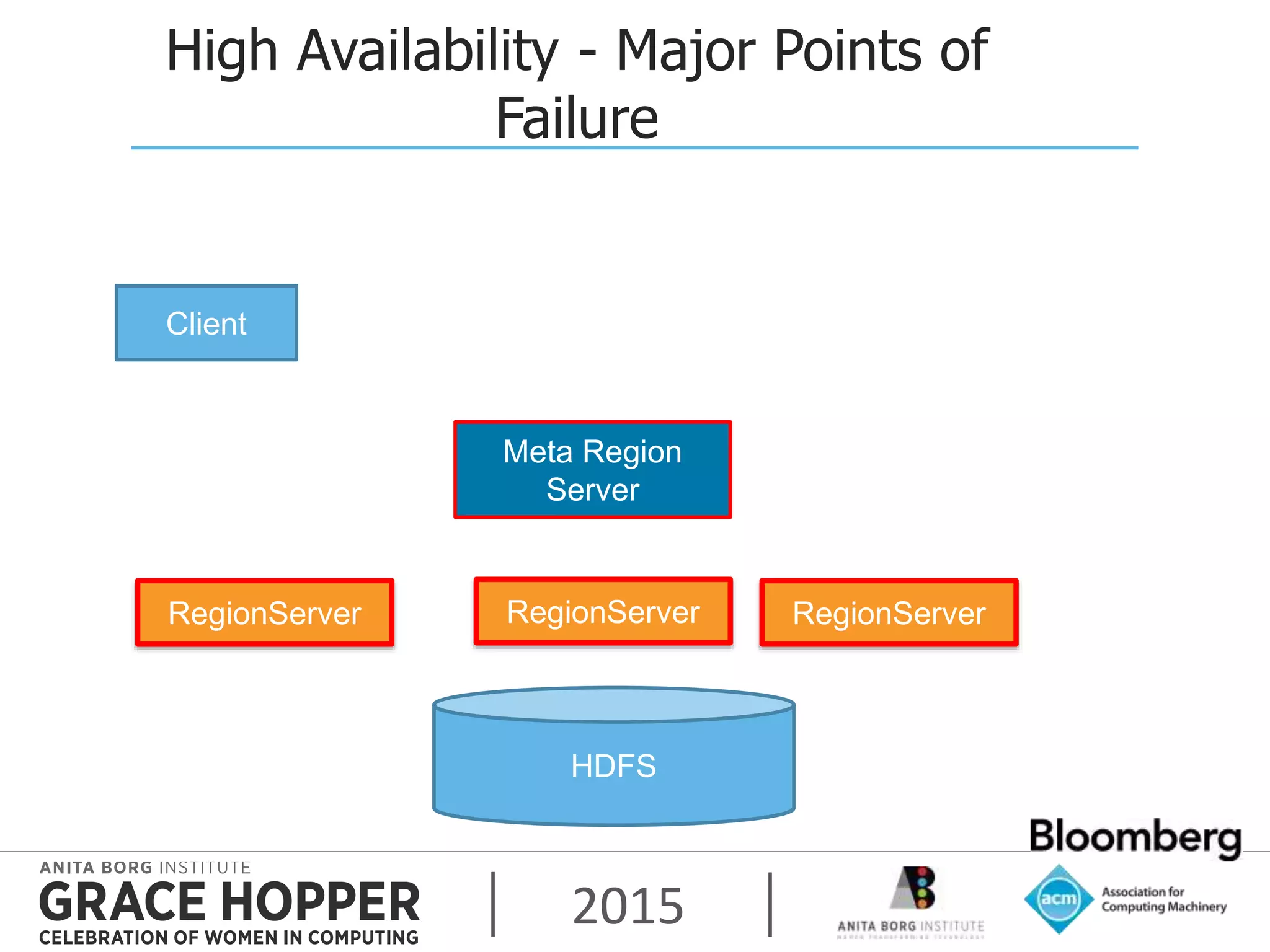
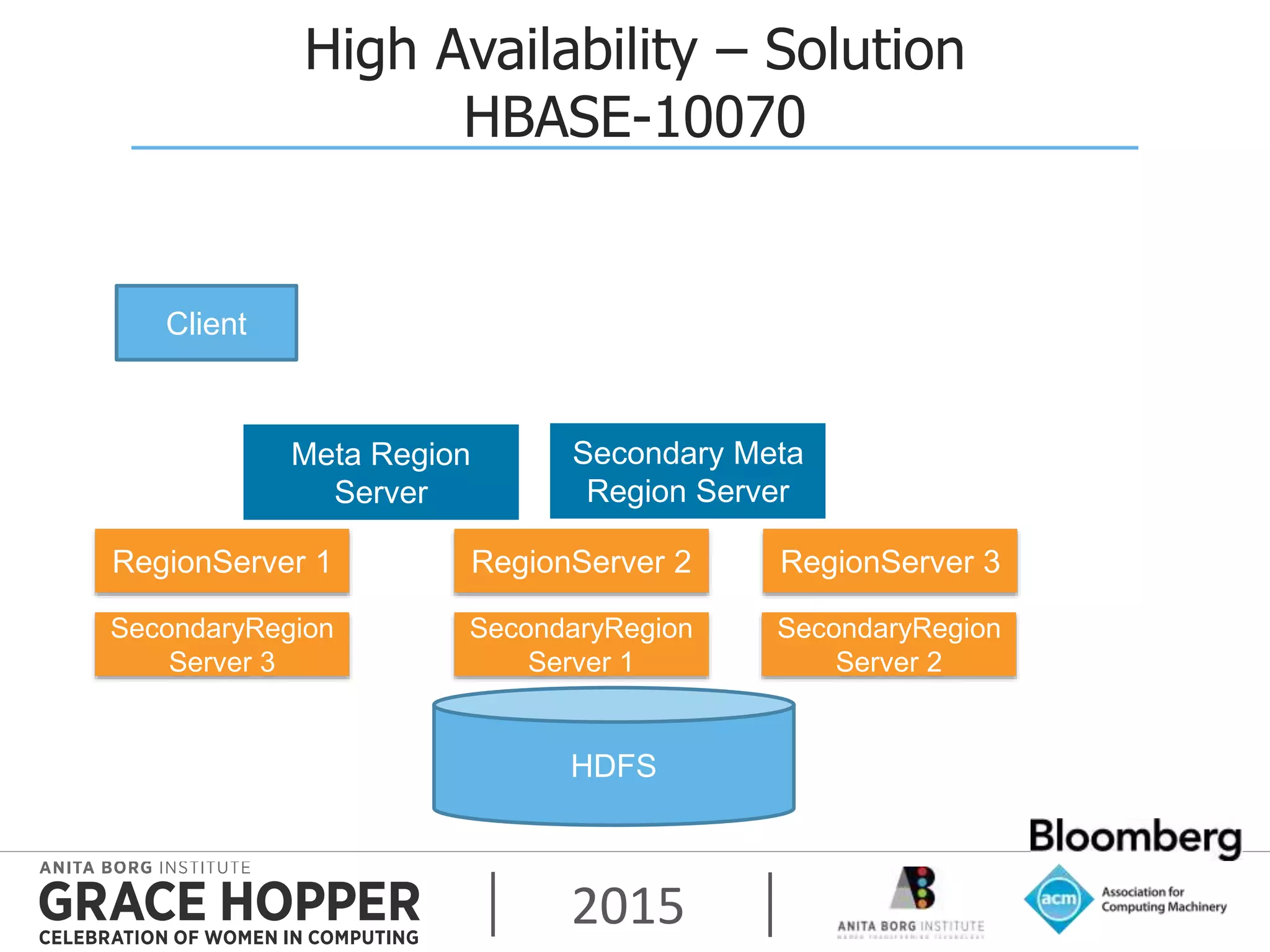
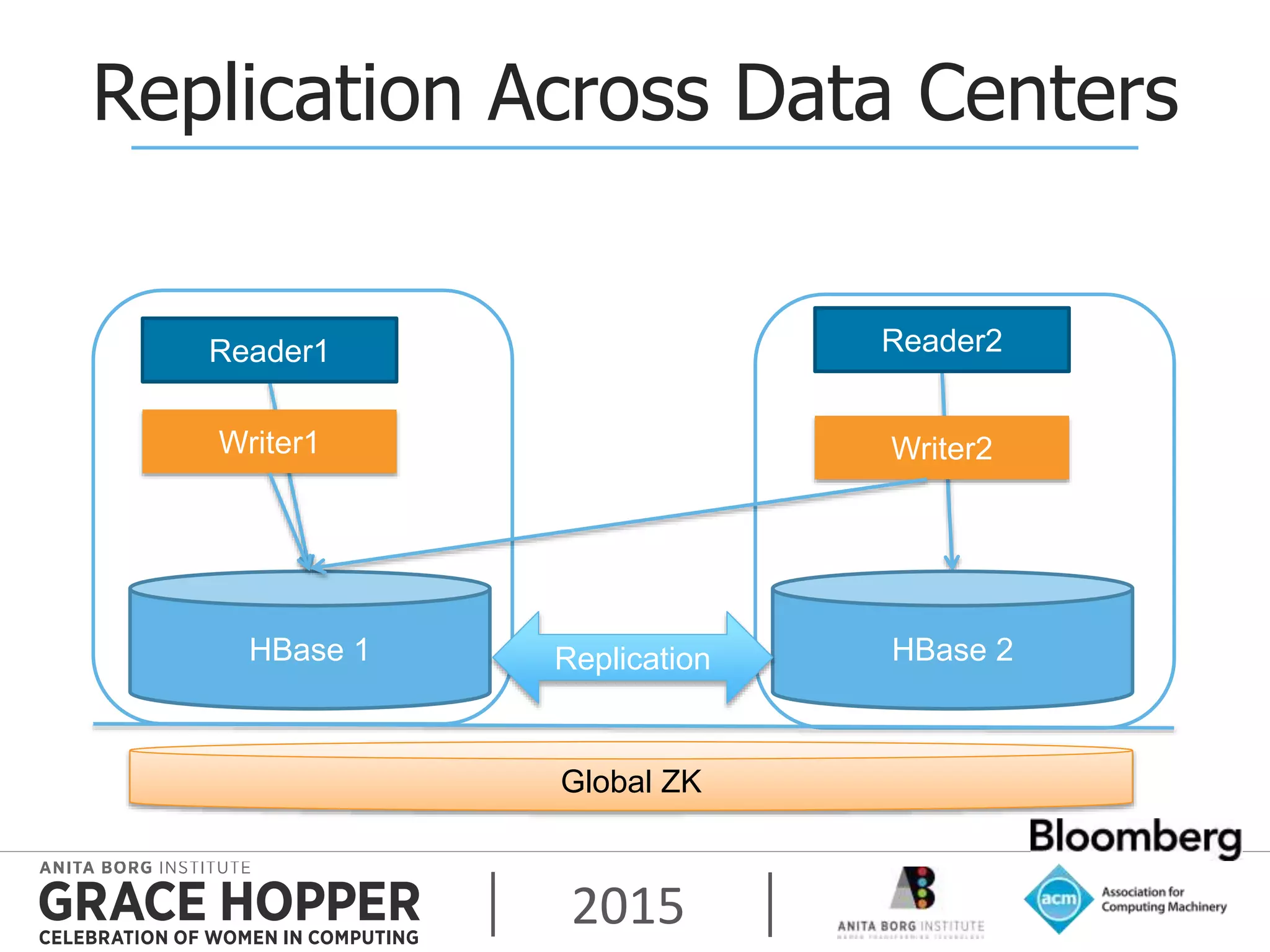
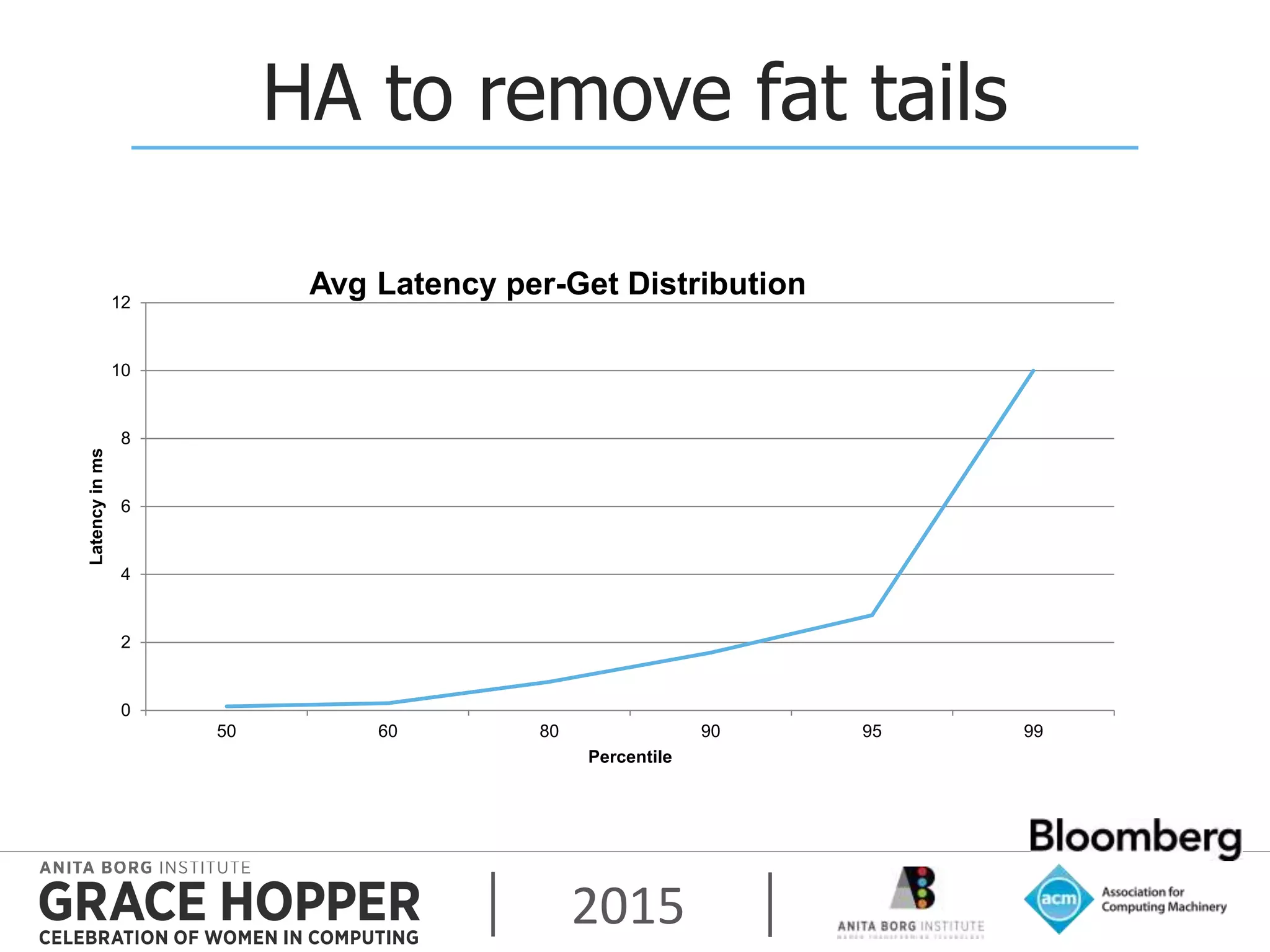
This document discusses techniques for achieving high availability and high frequency analytics on big data. It describes handling 2 terabytes of data with 4 billion writes and 140 trillion reads daily within 50ms latency. High availability is achieved through replication across multiple servers and data centers. High frequency is addressed through techniques like garbage collection tuning to reduce latency spikes. The key takeaways are that high availability solves most uptime and performance issues, supporting multiple data centers is needed, and tuning settings is important to maximize performance.