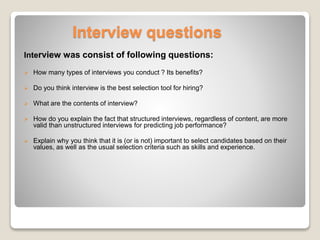
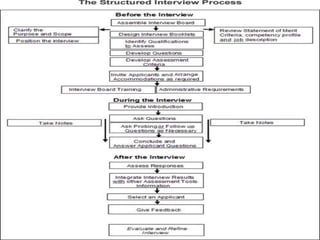
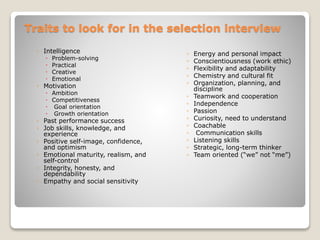
Dow University of Health Sciences conducts different types of interviews for selection, appraisal, and promotion purposes. Selection interviews involve behavioral and situational questions asked by an interview panel, while appraisal interviews discuss employee performance with supervisors. Structured interviews are more valid than unstructured at predicting job performance because they keep interviewers focused on relevant behaviors and answers. The study assessed Dow University's interview practices to understand how interviews are used and what factors influence outcomes.