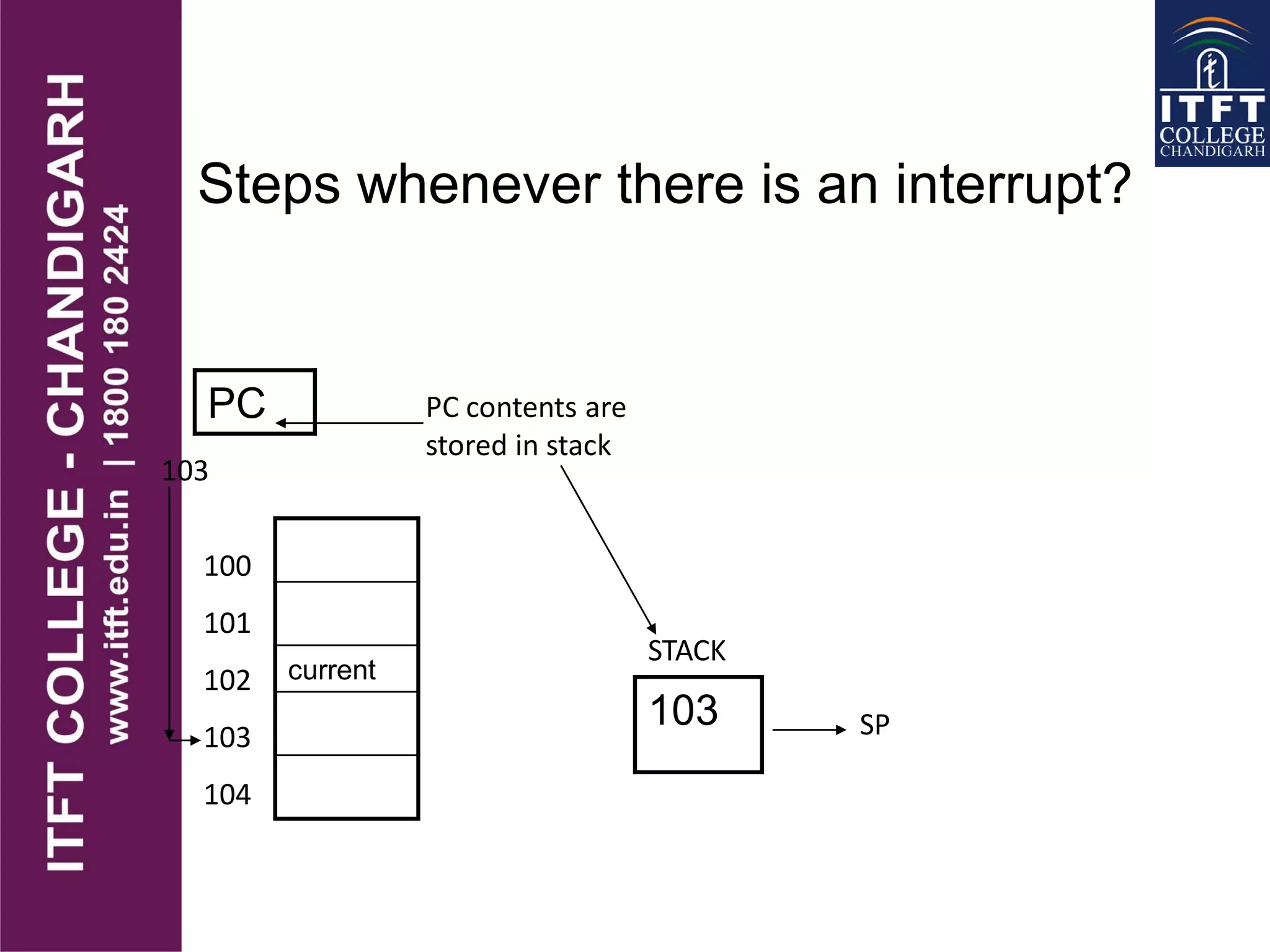
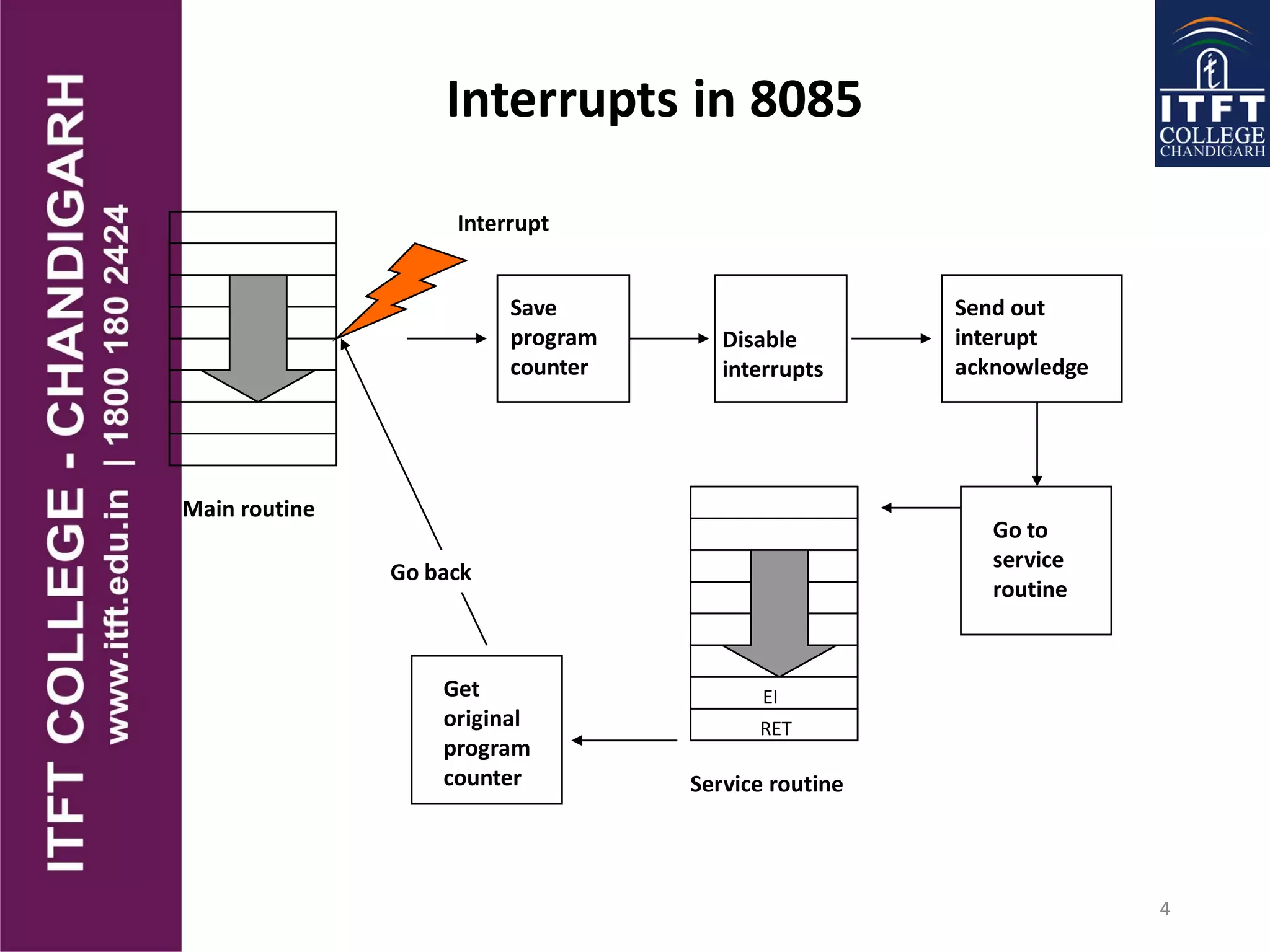
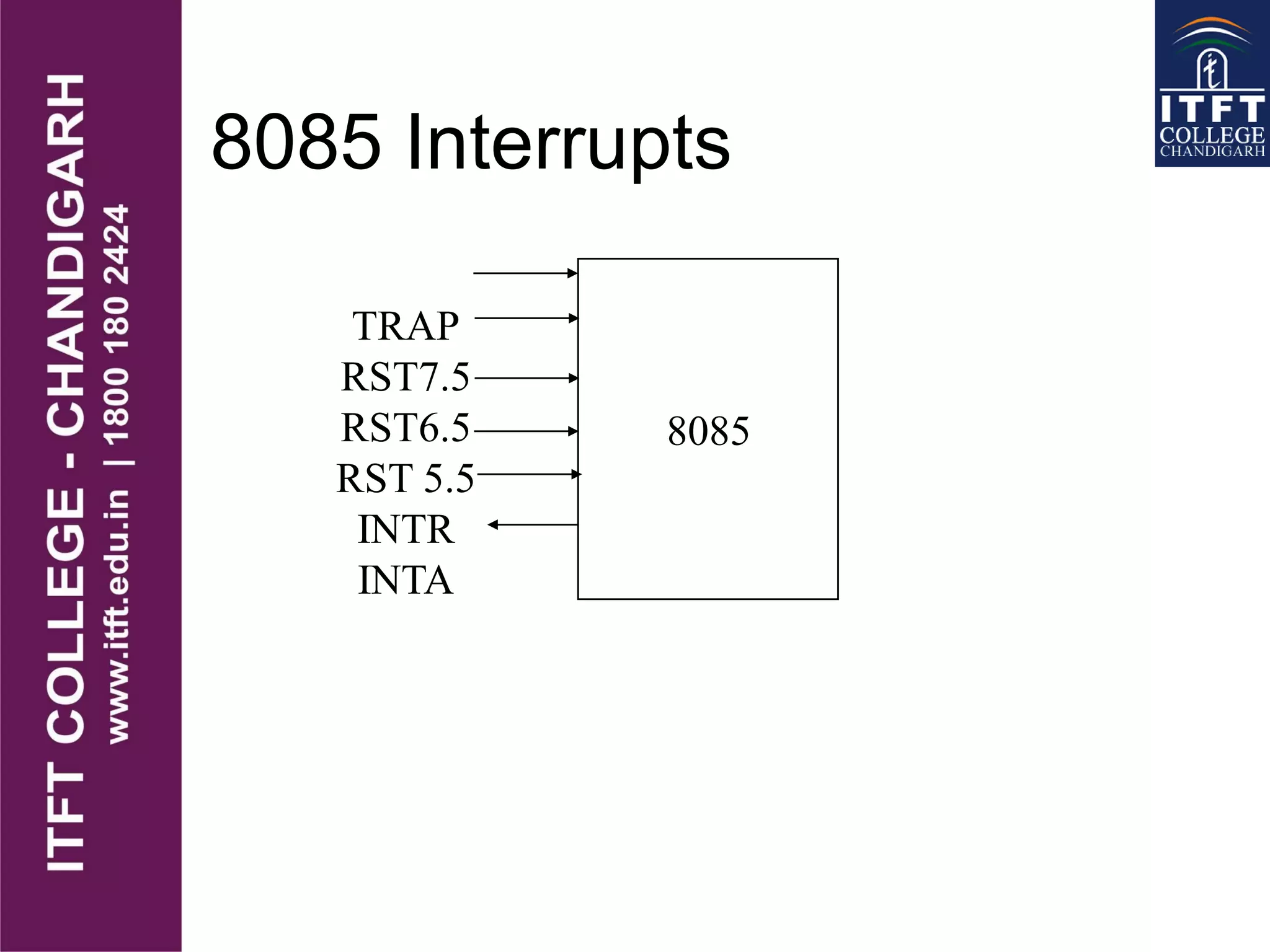
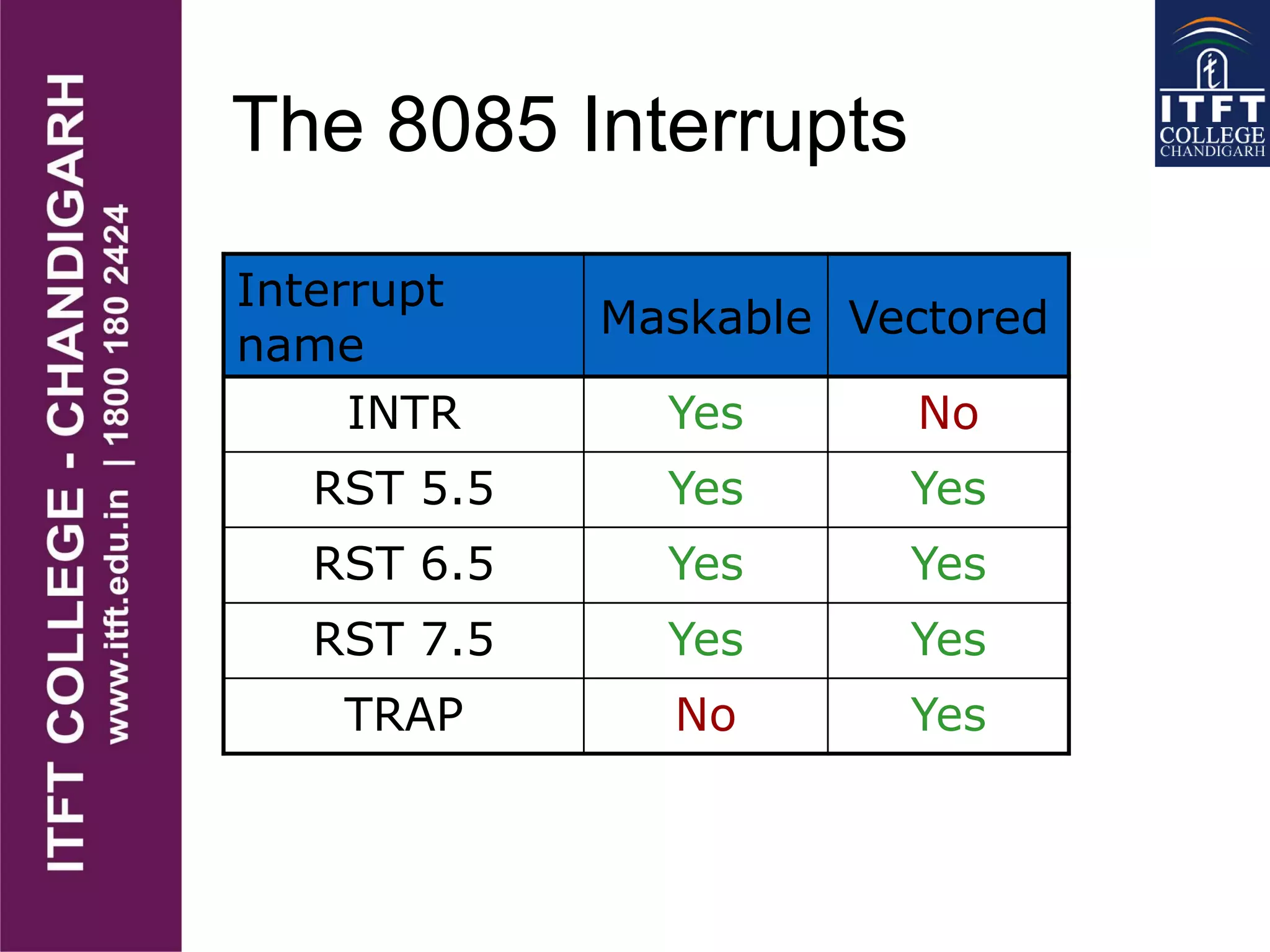
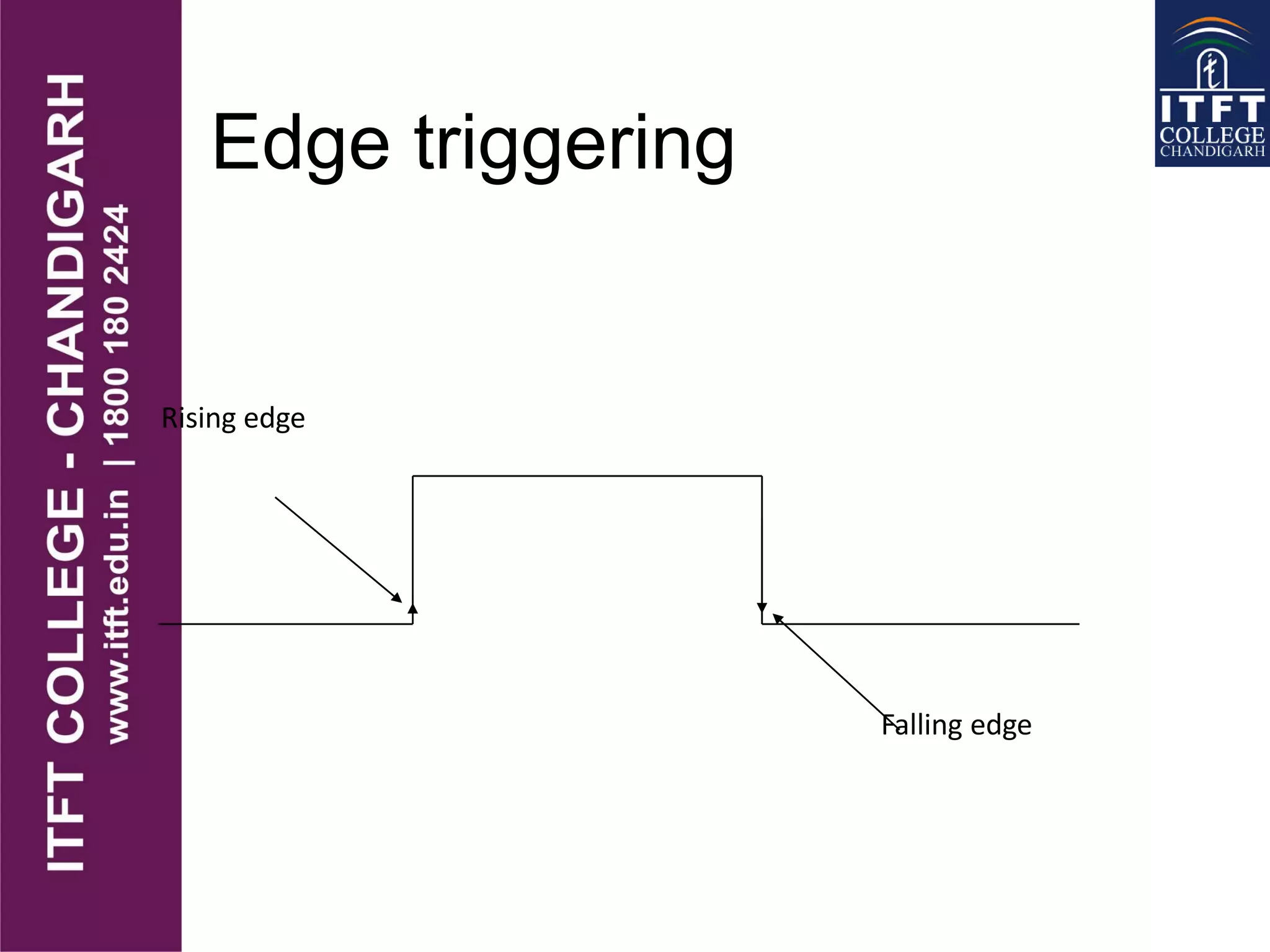
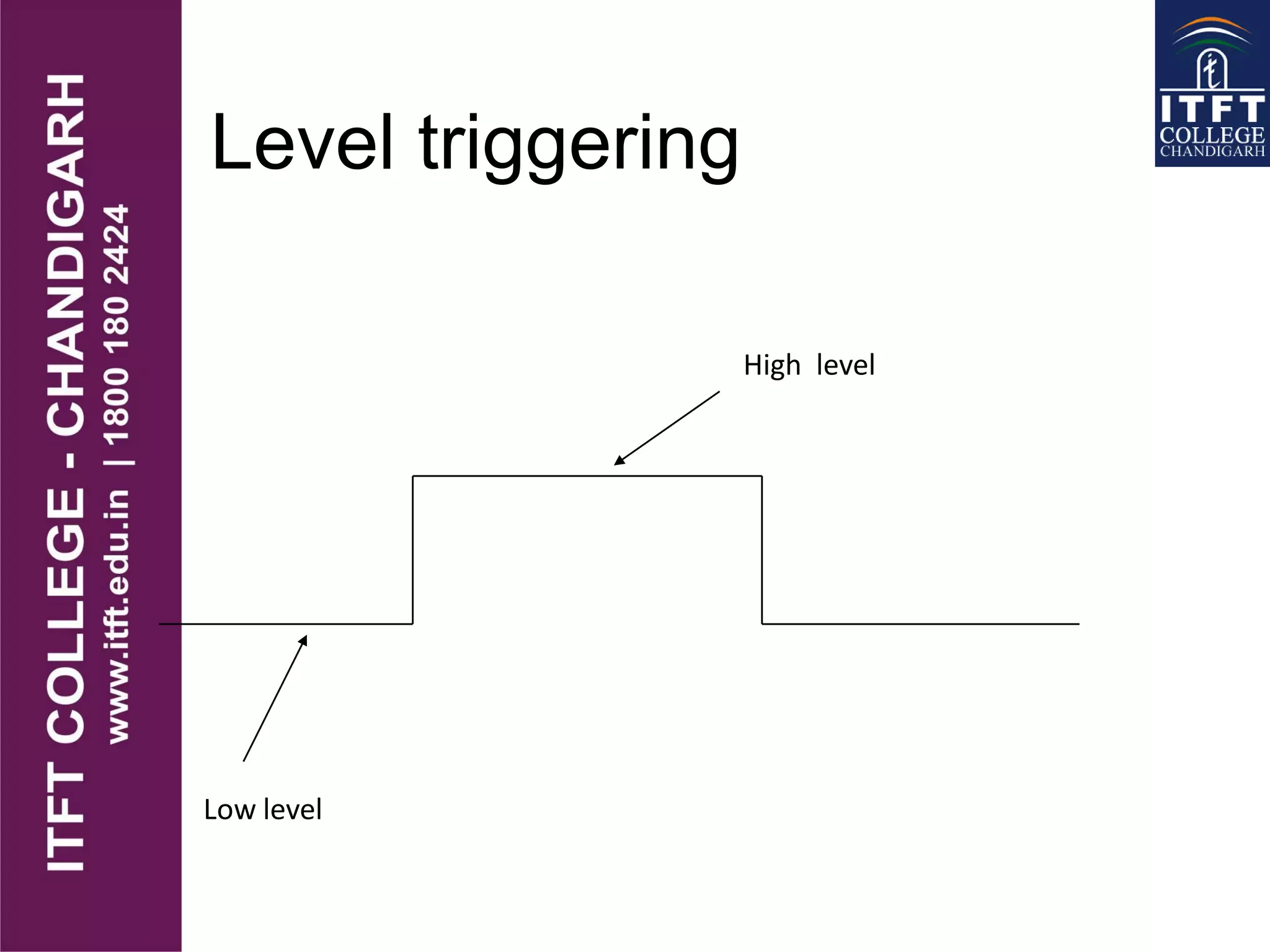
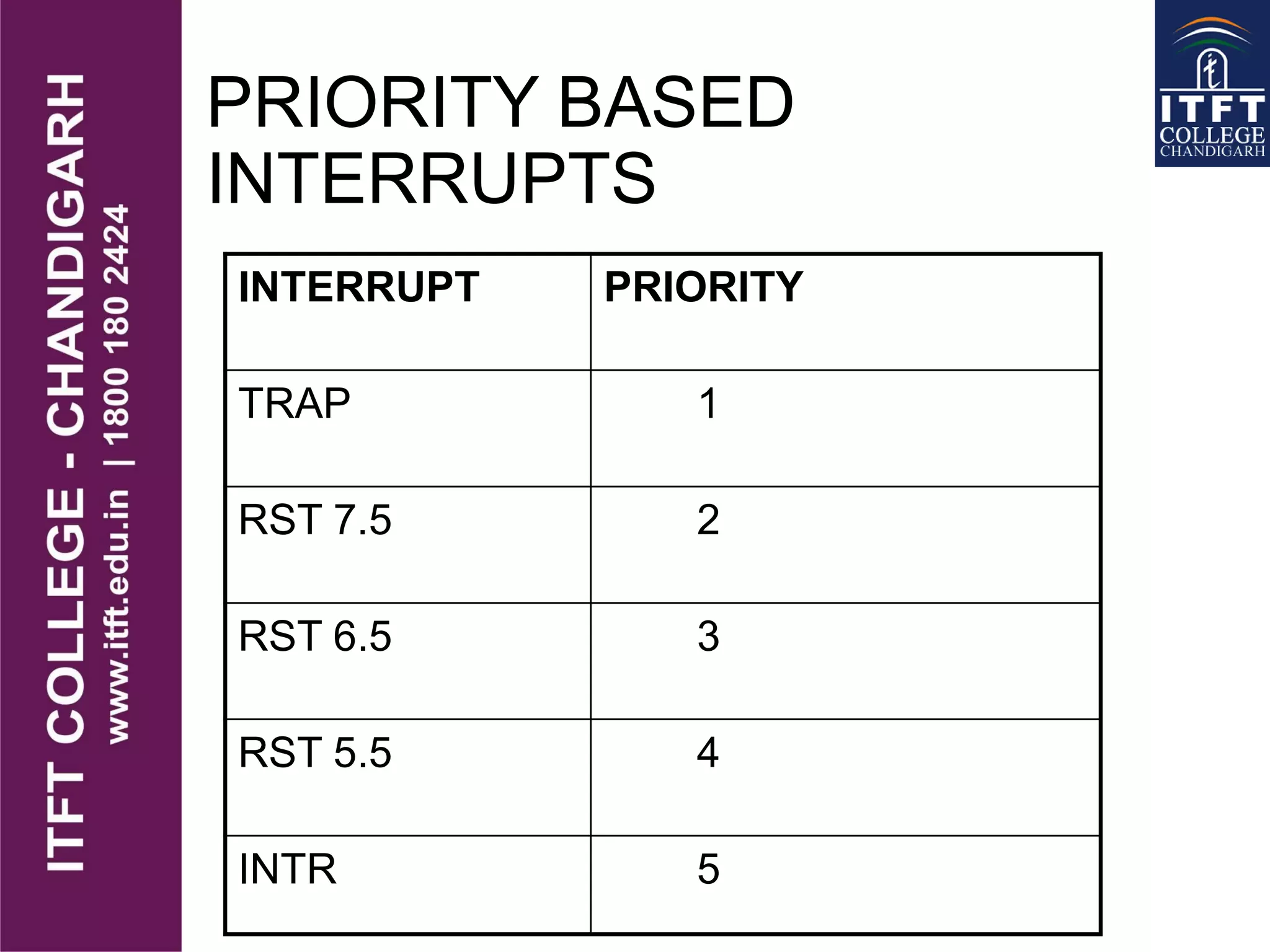
An interrupt pauses the normal execution of a microprocessor. When an interrupt occurs, the program counter is saved to the stack and interrupts are disabled. An interrupt acknowledge signal is sent and the service routine address is executed. After servicing, the original program counter is retrieved from the stack and execution resumes. There are hardware and software interrupts. Hardware interrupts come from I/O devices and software from CPU instructions. Interrupts can be maskable/non-maskable, vectored/non-vectored, edge/level-triggered, and have different priorities like the 8085's TRAP, RST 7.5, RST 6.5, RST 5.5, and INTR interrupts.