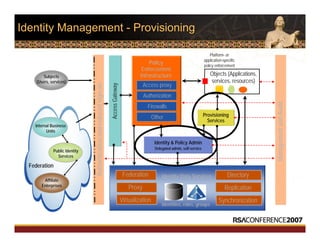
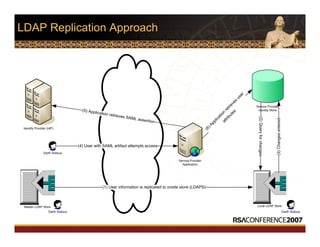
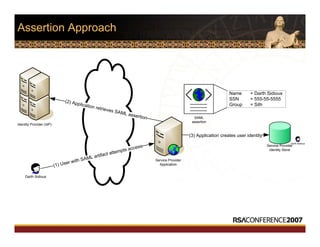
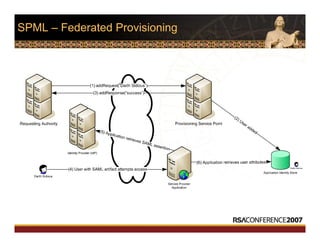
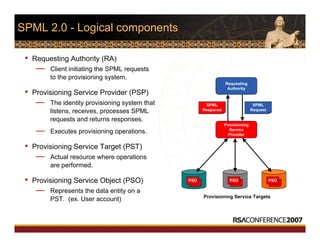
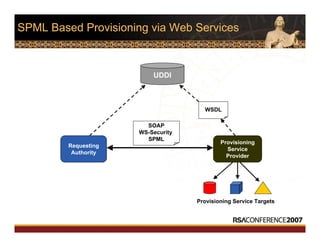
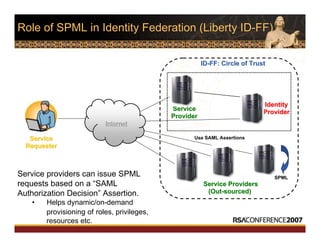
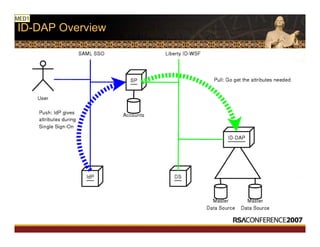
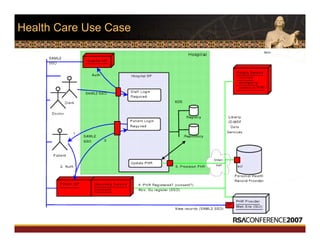
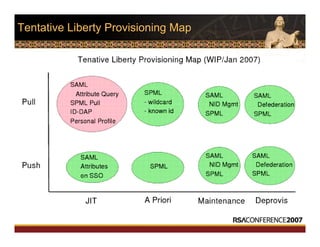
This document discusses interoperable provisioning in a distributed environment. It provides an overview of identity provisioning approaches such as batch provisioning, LDAP replication, and using assertions. The document then discusses the Services Provisioning Markup Language (SPML) standard for interoperable provisioning and describes SPML version 2.0 features and components. It also covers implementing SPML using Java web services toolkits and SPML's relationships with WS-Security and SAML standards.