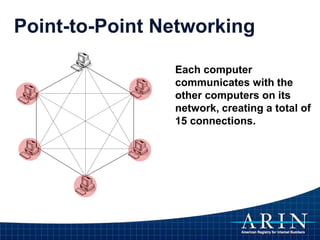
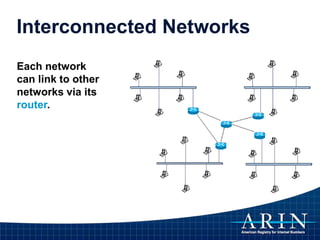
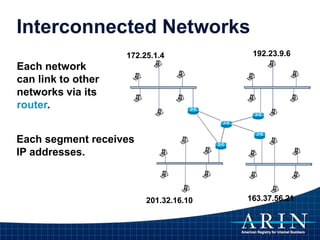
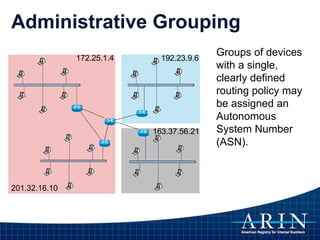
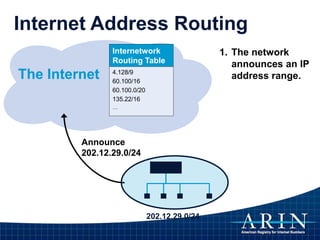
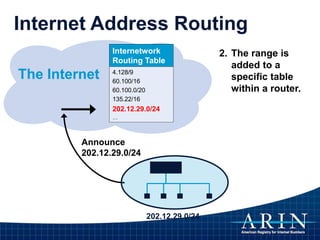
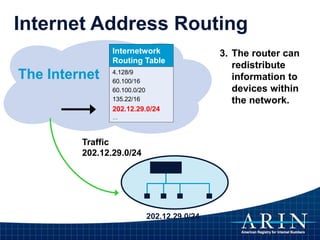
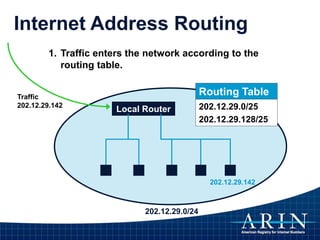
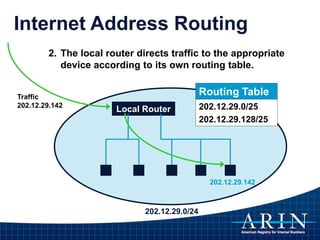
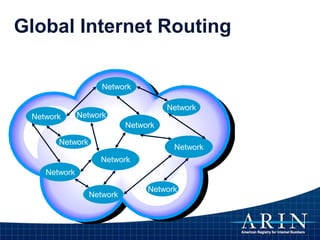
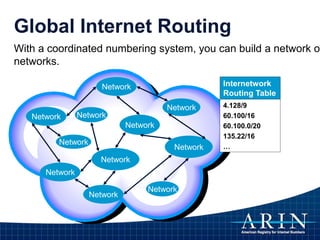
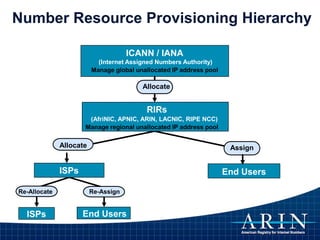
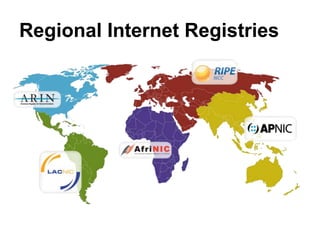
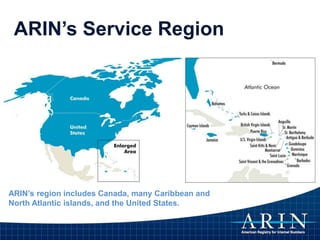
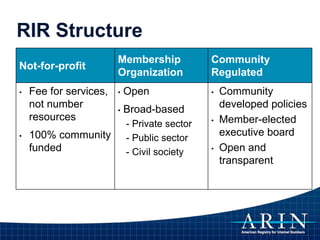
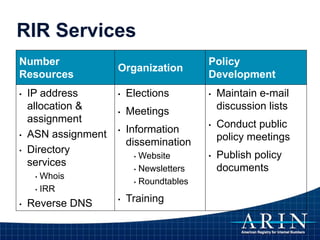
The document provides an overview of Internet Protocol (IP) addressing and the role of the American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) and other Regional Internet Registries (RIRs). It discusses IP addresses and autonomous system numbers, the domain name system, IP address allocation and management, and the purpose of WHOIS directories. ARIN is responsible for managing IP address space and ASNs in its service region, which includes Canada, the US, and many Caribbean islands.











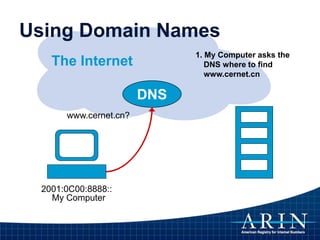
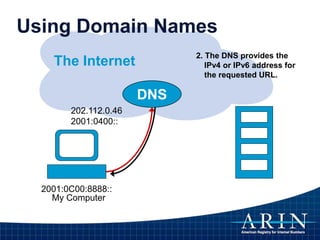
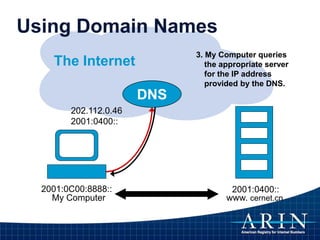
![IP Addresses are Not Domain Names
• IP Address [Identifier]
– “Computer-friendly”
– Unique number identifies computer on Internet
– Used for routing (moving information across an inter-network
from a source to a destination)
• DNS Name [Reference]
– “People-Friendly”
– Maps host name to unique IP address
– A means of storing and retrieving information about
hostnames and IP addresses in a distributed data
base](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internetoperationsandtherirs-151211162122/85/Internet-Operations-and-the-RIRs-17-320.jpg)