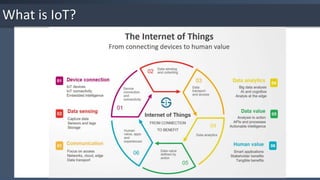
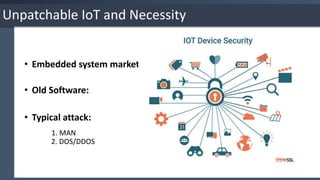
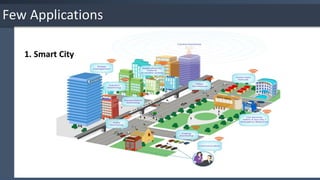
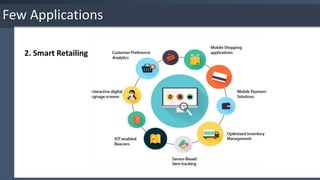
The document provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT), detailing its key characteristics such as intelligence, connectivity, and security. It discusses various technologies used in IoT, including wireless protocols and their specifications, as well as the importance of IoT security and associated threats and countermeasures. Additionally, it highlights applications of IoT in areas like smart cities, retail, homes, and wearable technology.