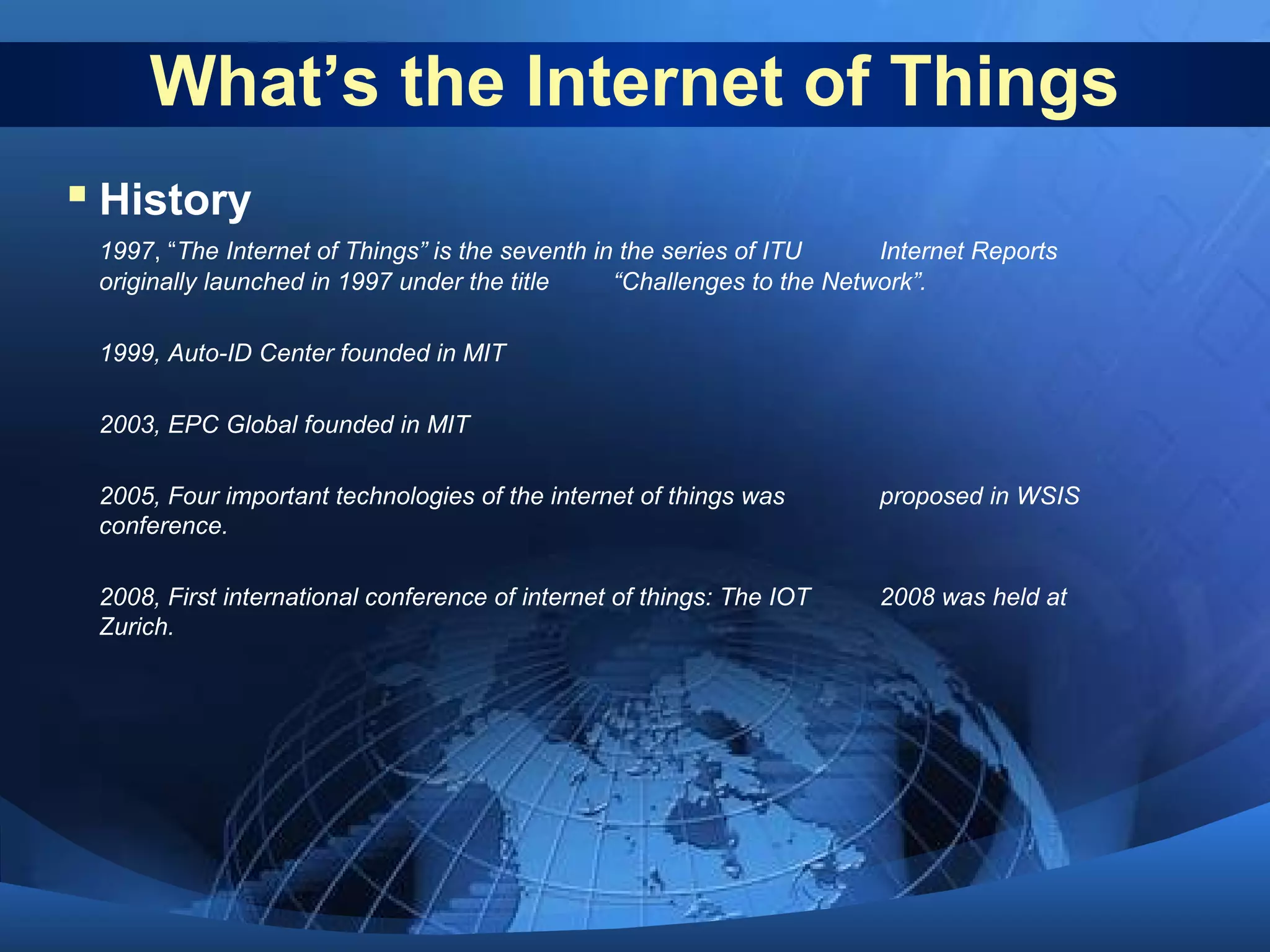
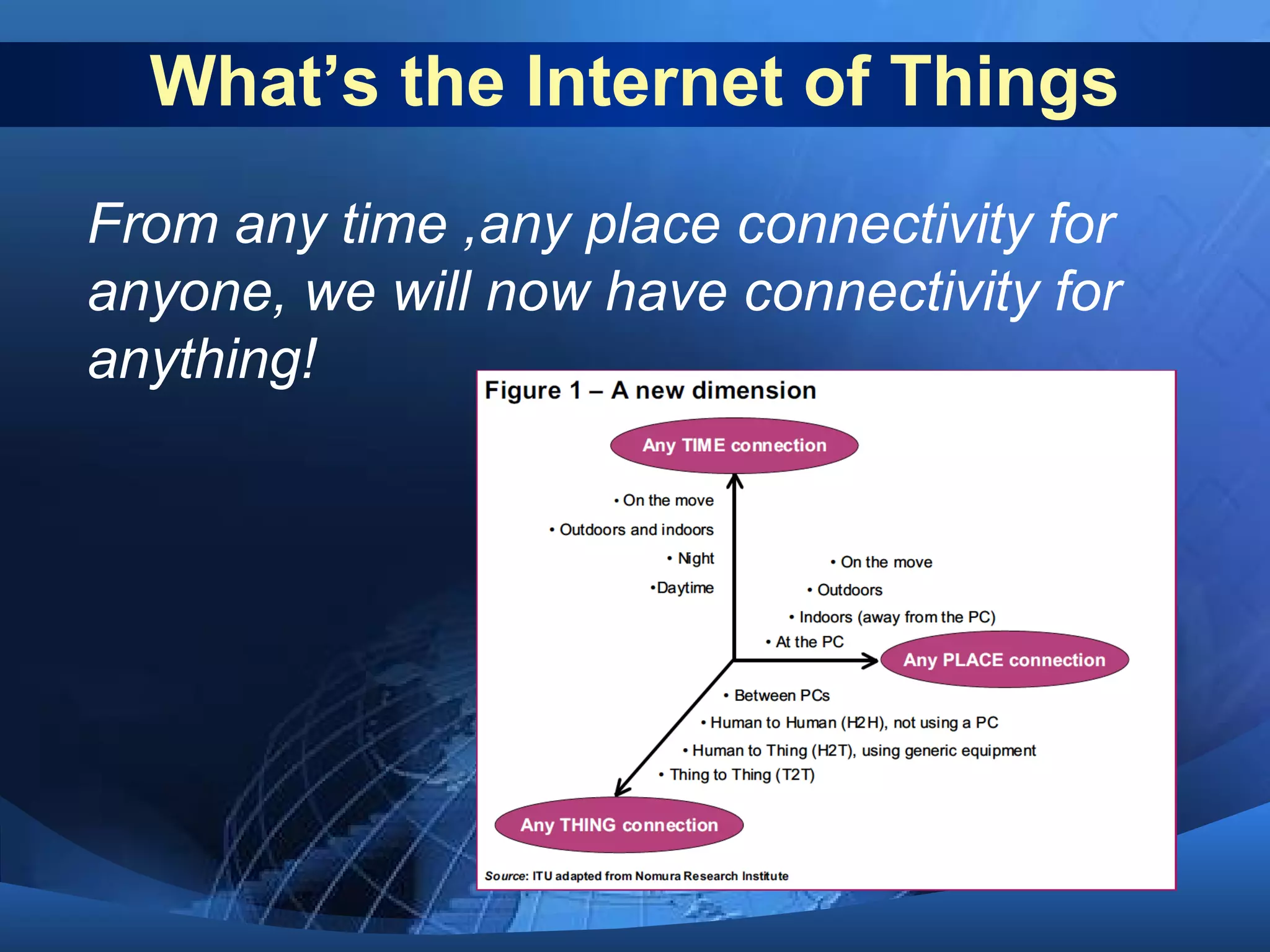
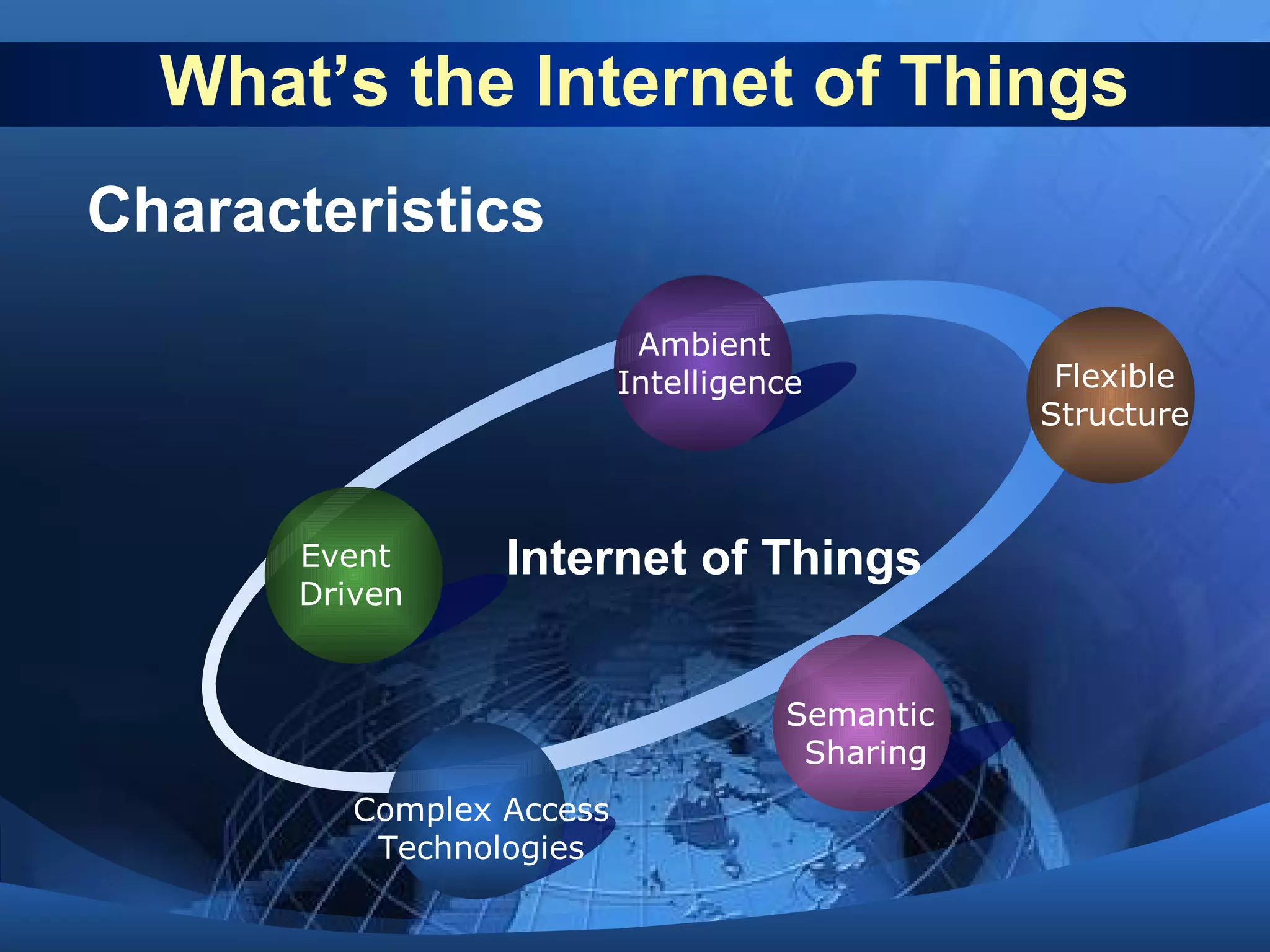
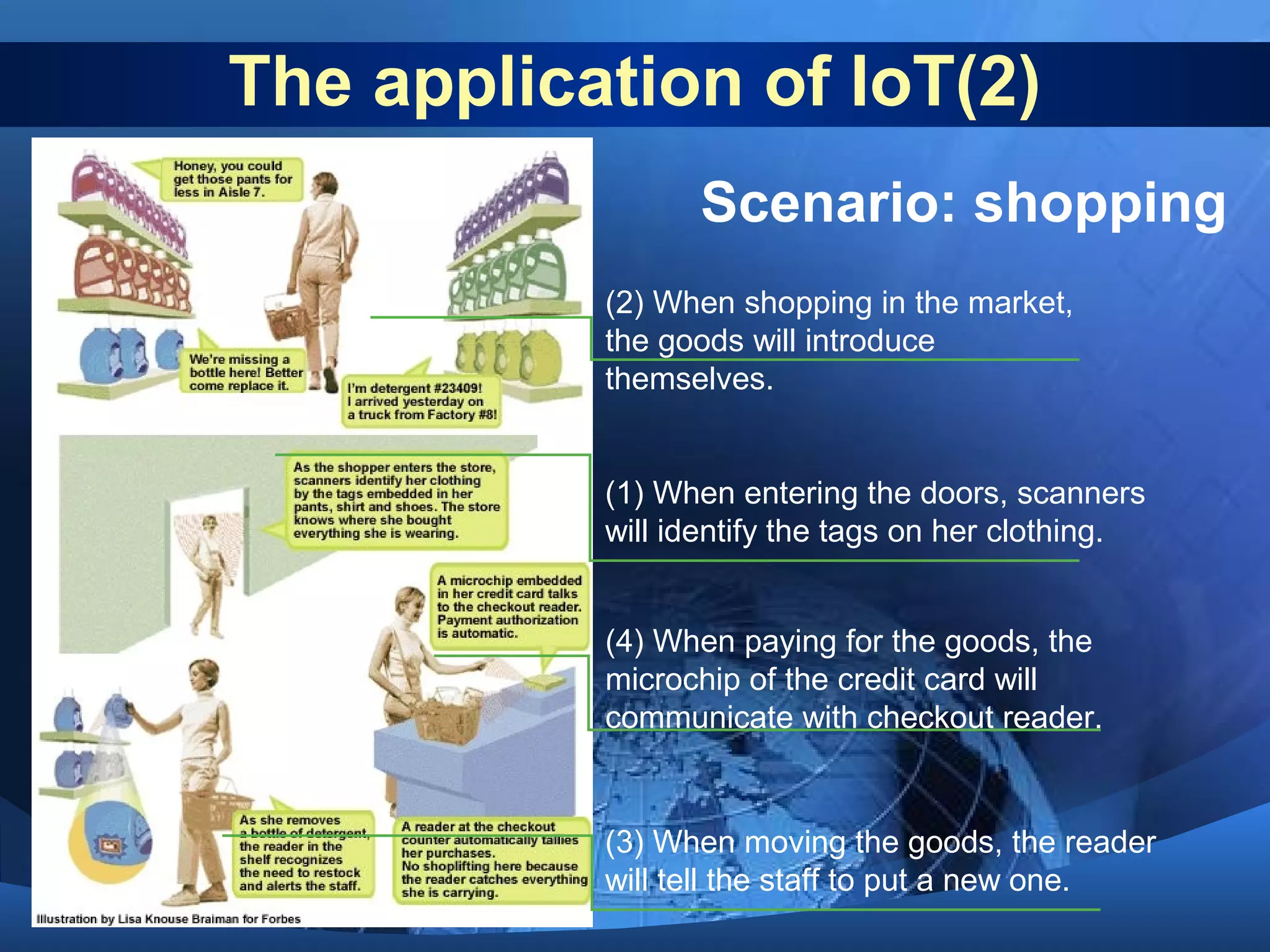
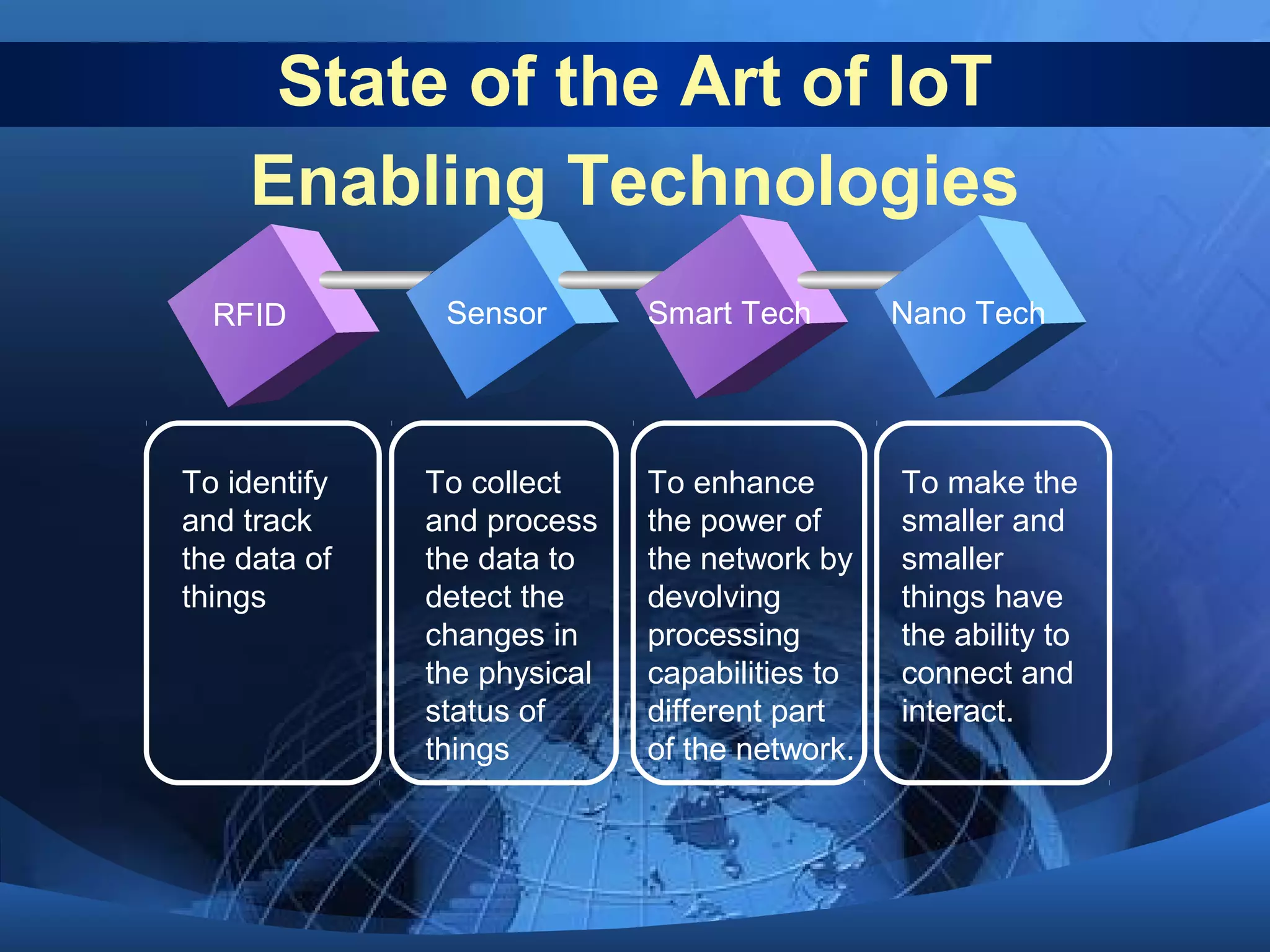
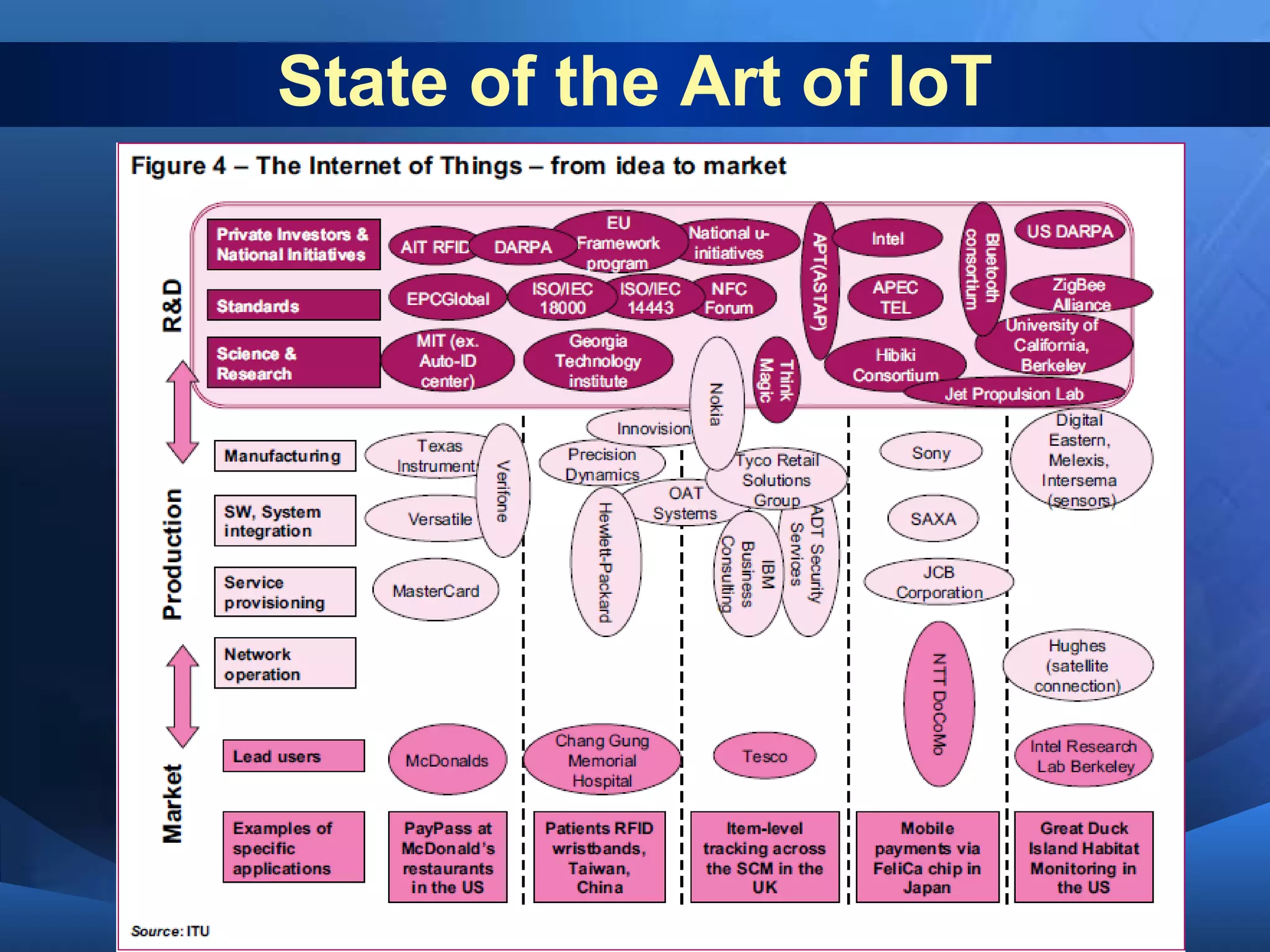
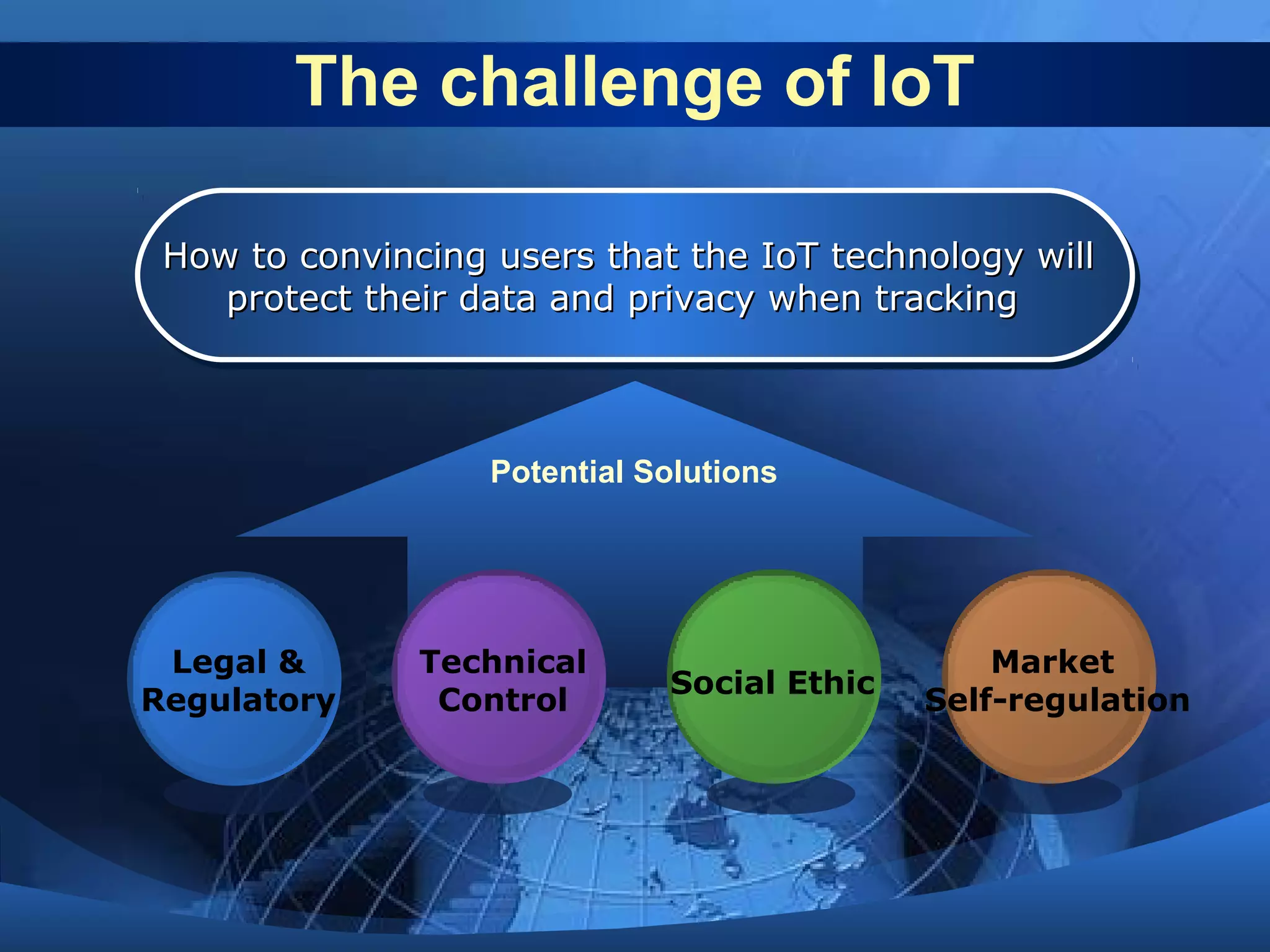
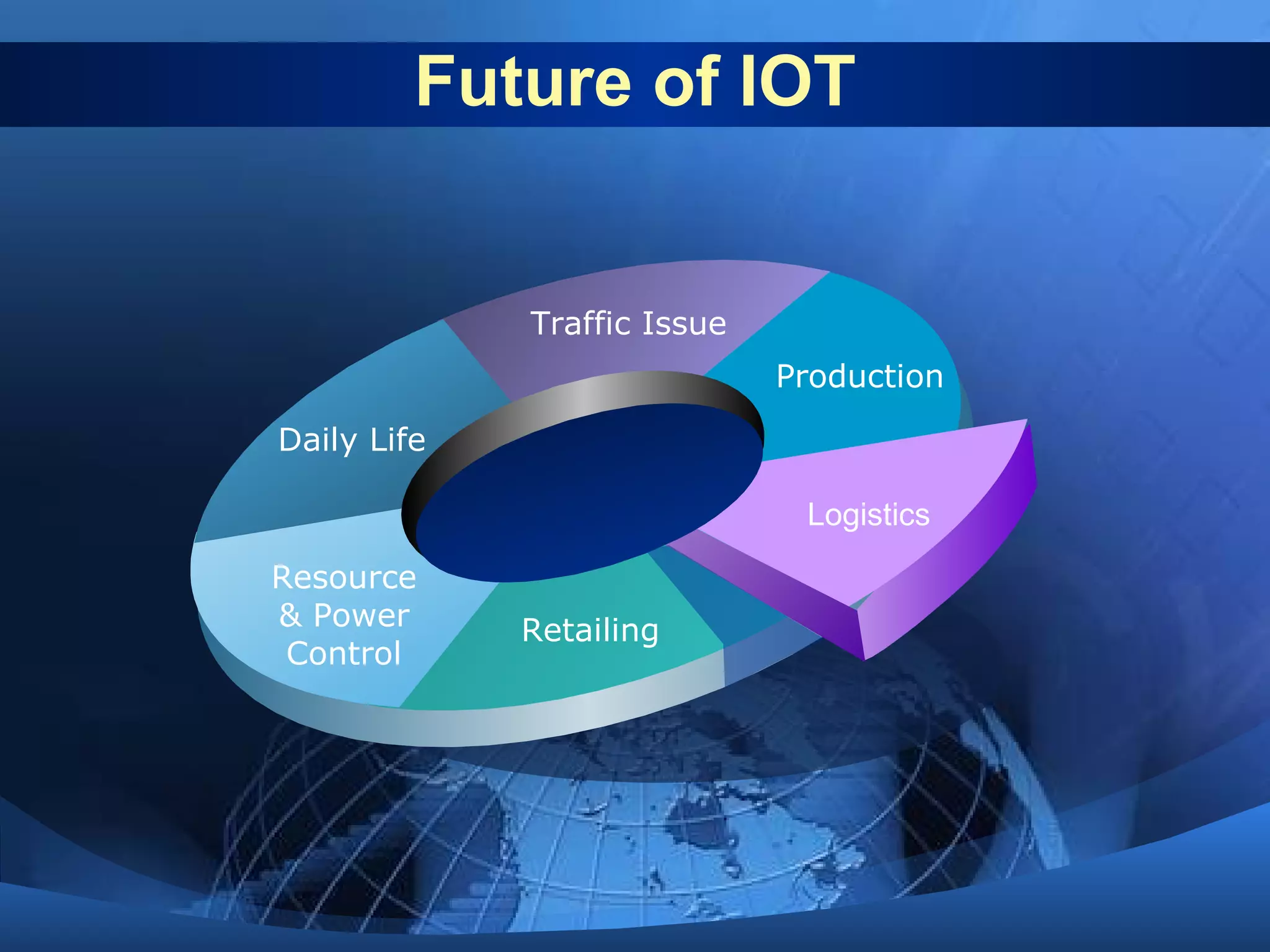
This document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT). It defines IoT as the network between wireless connected objects and devices. The history of IoT is explored, beginning in 1997 with the first mention of the term and important developments in 1999, 2003, 2005 and 2008. Key characteristics of IoT are described including being event driven, ambient, flexible and using semantic sharing. Examples of IoT applications discussed include smart homes, health care, transportation and more. Current technologies enabling IoT are also summarized such as RFID, sensors, smart technologies and nanotechnologies. Challenges and limitations of IoT are outlined including standardization, privacy, security and governance. Potential solutions and the future of IoT in various industries are