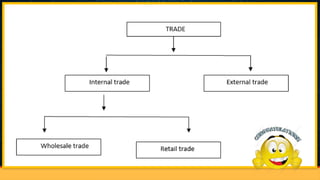
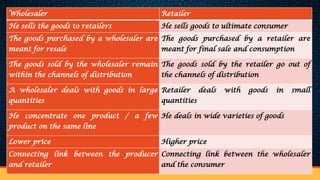
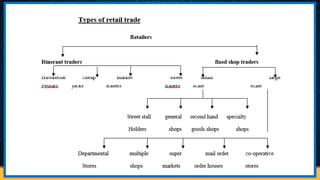
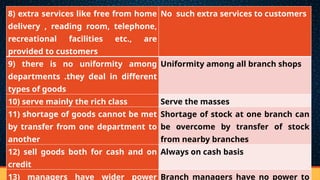
The document discusses the structure and functions of internal trade, focusing on wholesalers and retailers. Wholesalers act as intermediaries between producers and retailers, handling large quantities of goods, while retailers sell smaller quantities to consumers, providing services such as credit and market information. The text also describes various types of retail establishments, including department stores, multiple shops, supermarkets, and mail-order businesses, each with distinct features and operational methods.