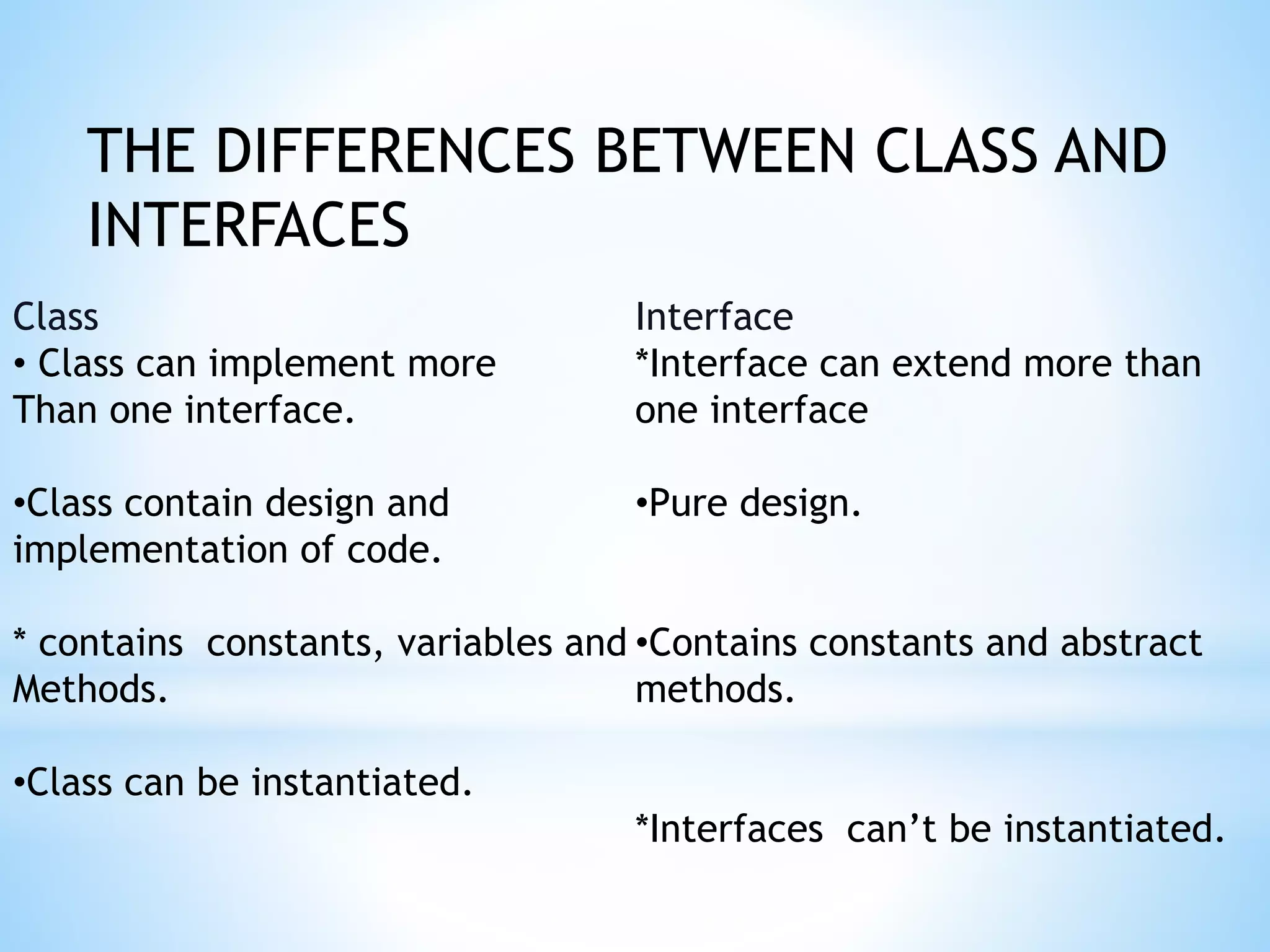
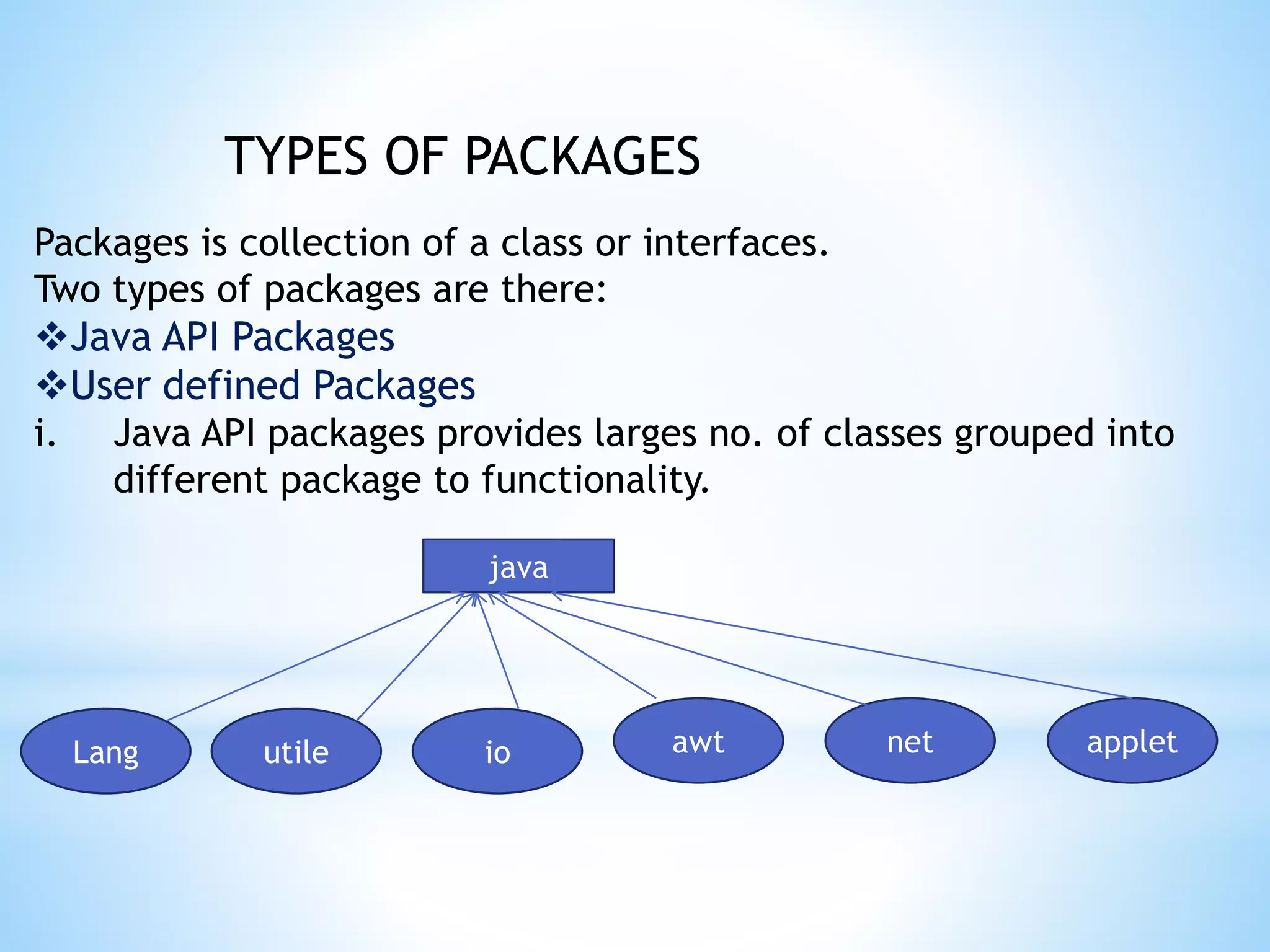
This document discusses interfaces and packages in Java. It defines an interface as a special Java class that is fully abstract and contains only static final variables and abstract methods. Interfaces can extend other interfaces but not classes. Classes can implement multiple interfaces but extend only one class. Packages in Java organize related classes and interfaces. The Java API contains predefined packages like java.lang and java.util while user-defined packages can be created using the package keyword.



![Example : for implementing interface
Interface one
{
Int i = 10;
Void show();
}
Class two implement one
{
Void show()
{
System.out.print(i);
}
}
Class Sample
{
Public static void main(String
a[])
{
Two t = new two();
t.show()
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfacepackages-170723100957/75/Interface-amp-packages-4-2048.jpg)
![Example for extending Interface:
Interface one
{
Abstract void show();
}
Class sam1 implements one
{
Int a, b;
Sam1(int i, int j)
{
a = i ;
b = j;
}
Void show()
{
System.out.print(a);
System.out.print(b);
}
{
Abstract class sam2 implements
one
{
Void print()
System.out.print(“sam2 class”)
}
}
Class sam3 extends sam2
{
Void show()
{
System.out.print(sam3 class”);
}
}
Class sample
{
Public static void main(String a[])
{
Sam1 s1 = new sam1(10 , 20);
s1.show();
Sam2 s3 = new sam3 ();
s3.print();
s3.show();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfacepackages-170723100957/75/Interface-amp-packages-5-2048.jpg)



![User defined packages:
This are the packages that are defined by user
or programmer.
o Creating packages:
Syntax: package packagesname;
‘package’ is a keyword and packagename is
identifier.
E.g : package p1;
o Accessing packages.
Packages can be access using ‘import’ statement
Import package1 [.package 2][.package
3].classname;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfacepackages-170723100957/75/Interface-amp-packages-11-2048.jpg)