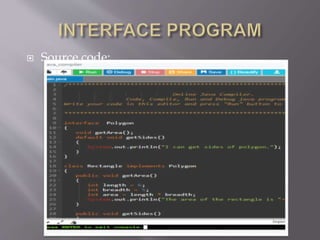
The document discusses Java packages and interfaces. It defines that packages are used to organize related classes and avoid naming conflicts. There are built-in and user-defined packages. Interfaces are used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java. They contain abstract methods that classes implement. The document provides examples of defining a package with classes, implementing an interface, and using default interface methods.









![ Import india .team;
Class pack
{
Public static void main(String args[])
{
Team c=new team(“dhoni”,”captain”,”cool”);
C.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesandinterfaces-201017075032/85/Packages-and-interfaces-10-320.jpg)








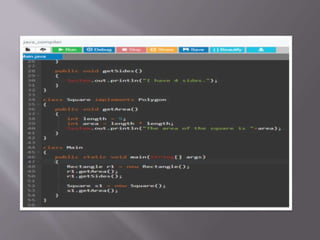
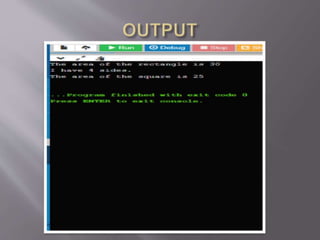

![ class Square implements Polygon {
public void getArea() {
int length = 5;
int area = length * length;
System.out.println("The area of the square is "+area);
} }
class Main { public static void main(String[] args)
{ Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle();
r1.getArea();
r1.getSides();
Square s1 = new Square();
s1.getArea();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesandinterfaces-201017075032/85/Packages-and-interfaces-25-320.jpg)


