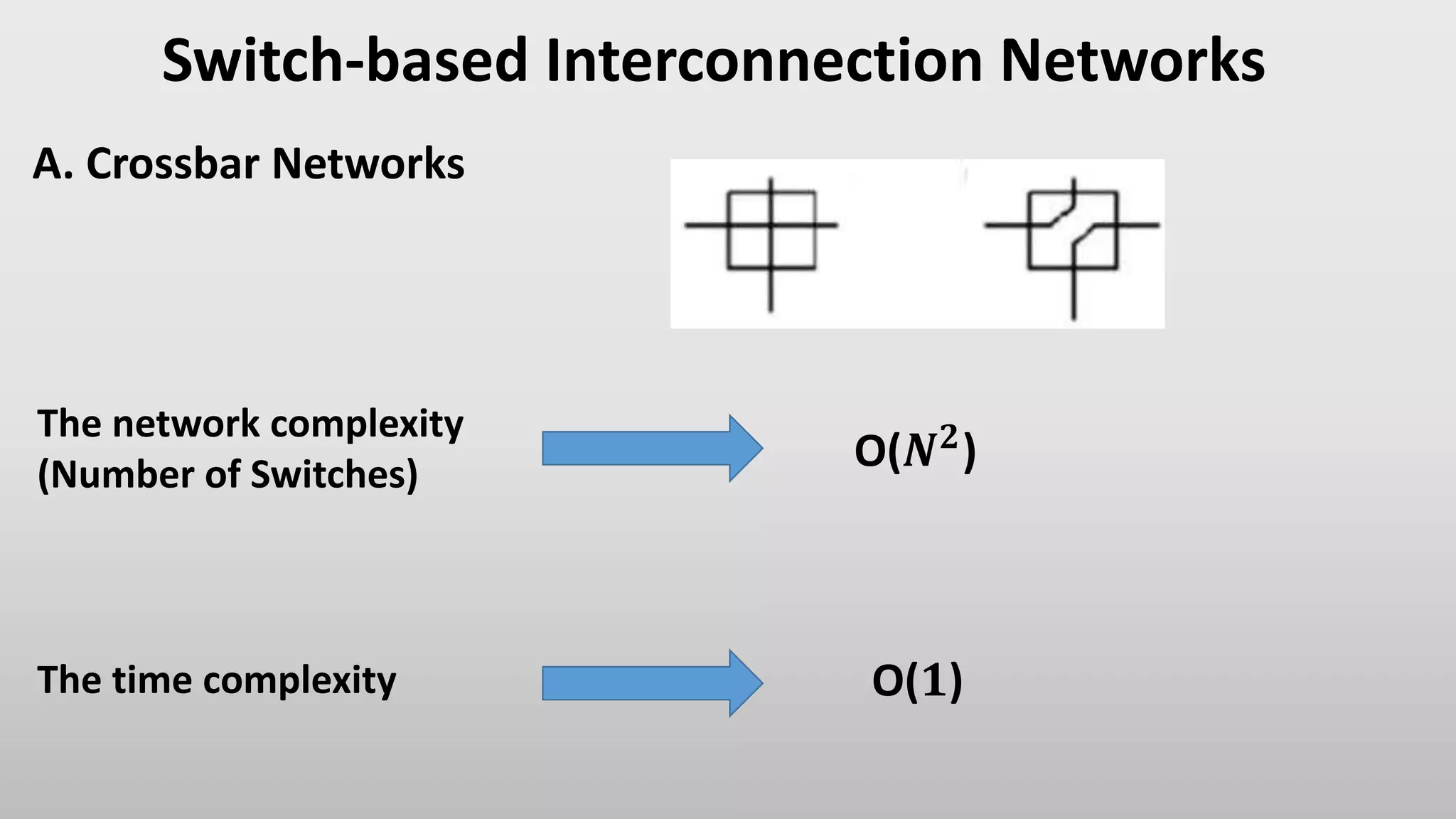
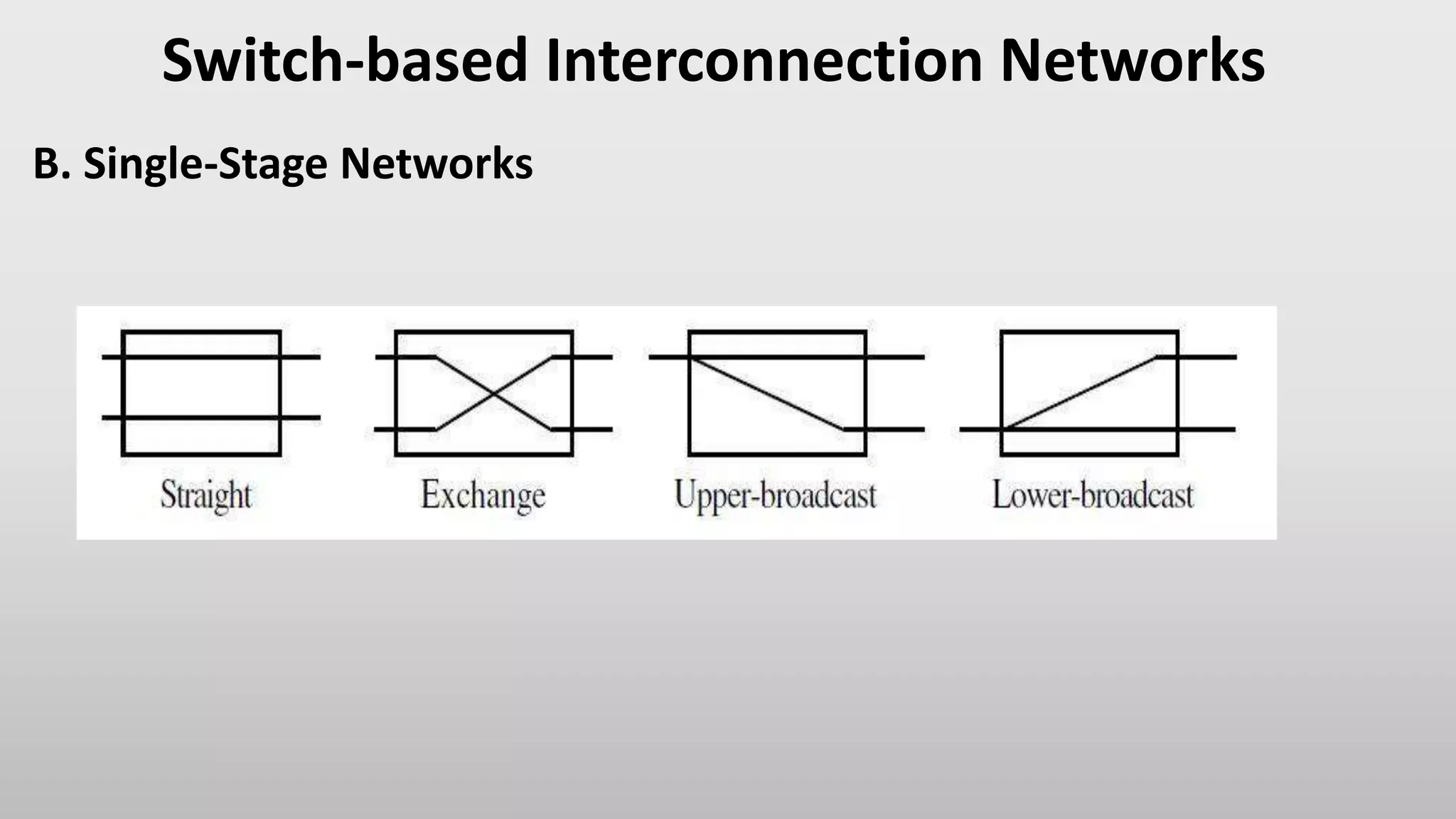
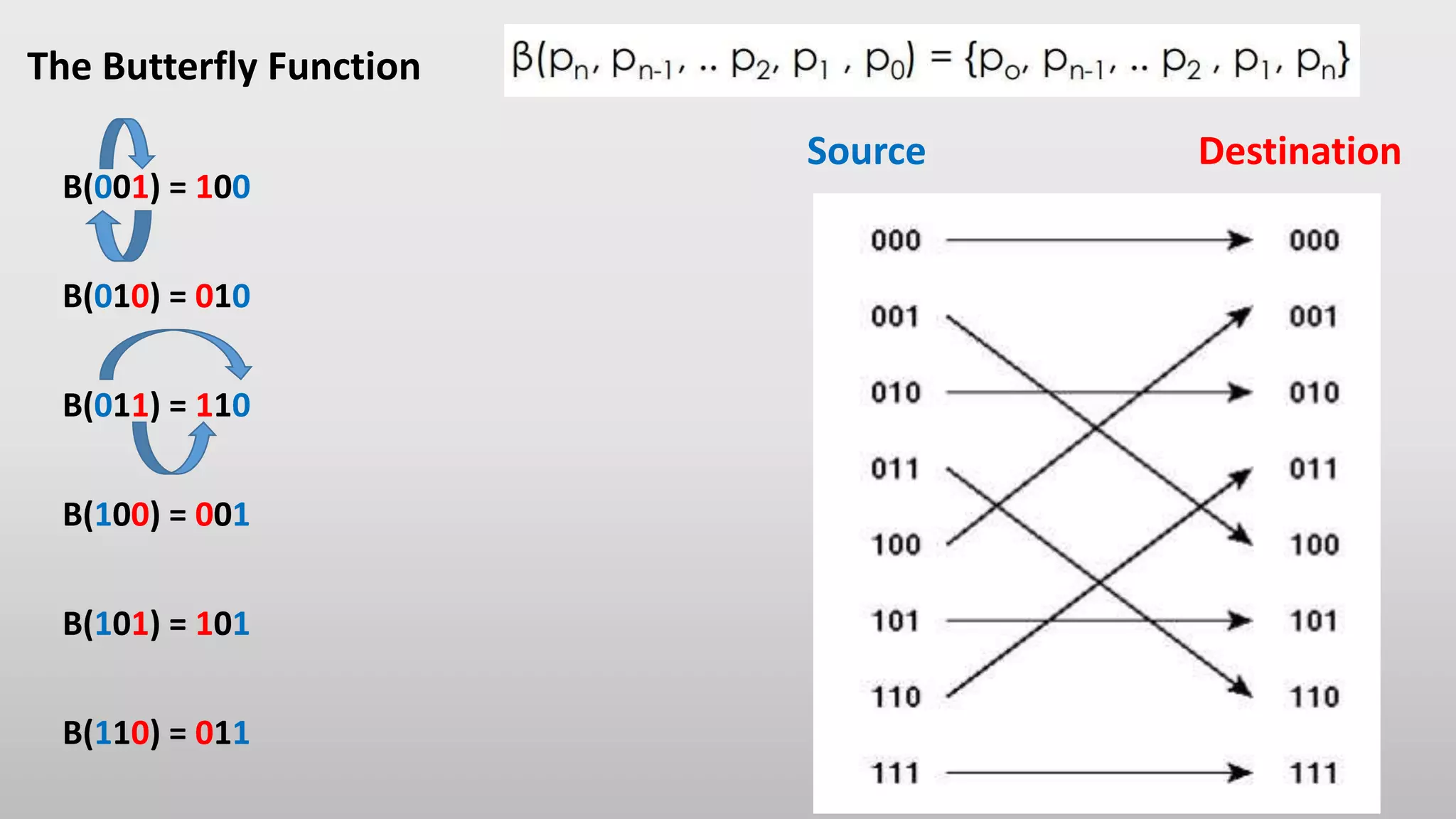
The document discusses and provides examples of different types of single-stage interconnection networks, including shuffle-exchange networks, cube networks, plus-minus networks, and butterfly networks. Specifically, it shows how sources and destinations are mapped in each type of network by applying routing functions like shuffling bits, adding/subtracting modulo the number of nodes, and bit-reversal. These single-stage networks provide constant-time routing but require more switches than crossbar networks.