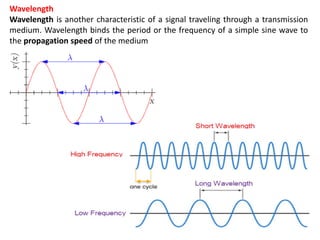
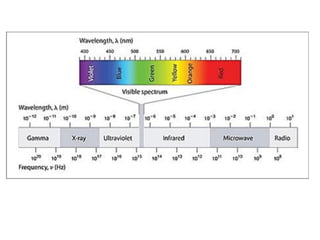
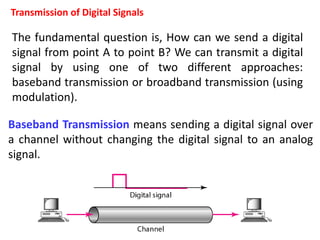
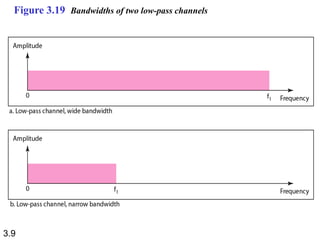
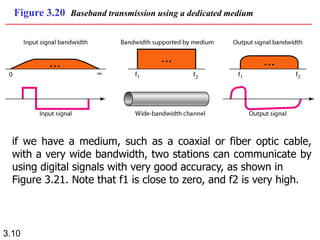
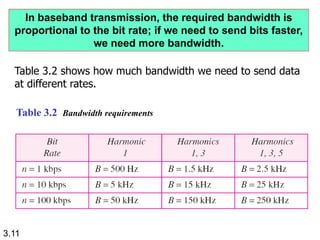
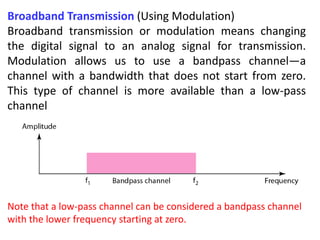
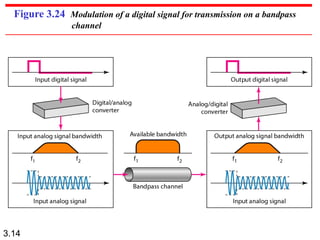
Wavelength is a characteristic of signals that depends on both the signal's frequency and the transmission medium. Wavelength is the distance a signal can travel in one period. It is normally measured in micrometers. There are two main approaches to transmitting digital signals: baseband transmission, which sends the digital signal directly over the channel without changing it to analog, and broadband transmission, which uses modulation. Baseband transmission requires a dedicated channel with bandwidth starting from zero Hertz. The bandwidth needed is proportional to the bit rate - higher bit rates require more bandwidth.