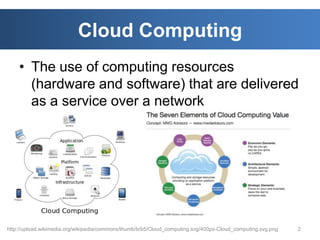
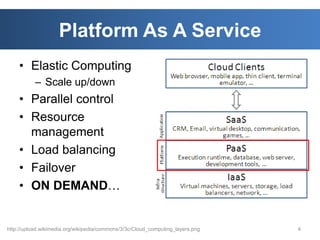
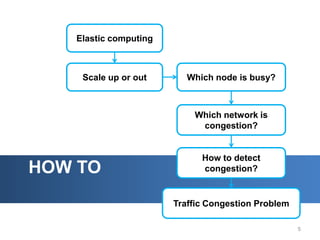
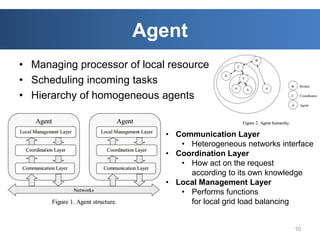
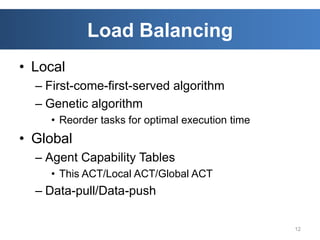
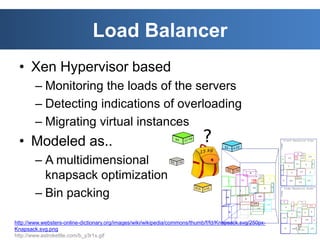
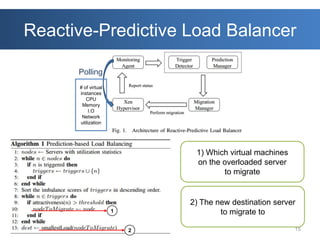
The document discusses intelligent cloud computing. It describes cloud computing concepts like SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. It then discusses using intelligent agents and predictive techniques for load balancing in cloud platforms and datacenters. This includes predicting resource usage and migrating virtual machines between servers to balance workloads and avoid congestion. The goal is to develop intelligent techniques to control data flows and scheduling in cloud systems.