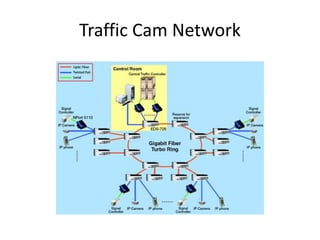
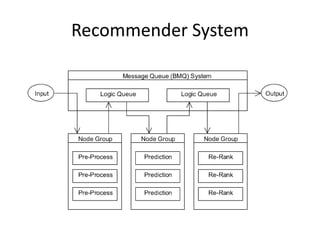
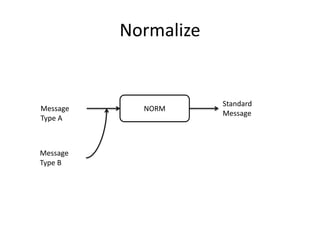
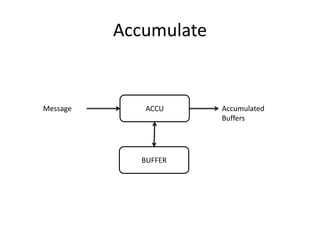
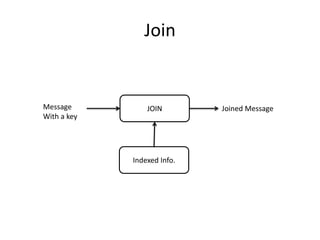
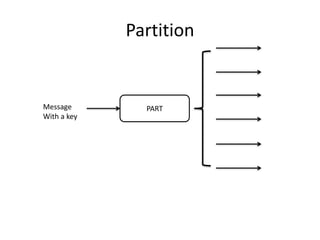
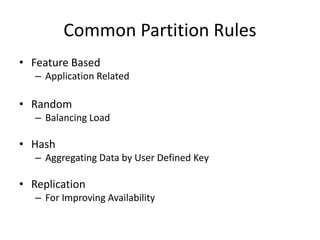
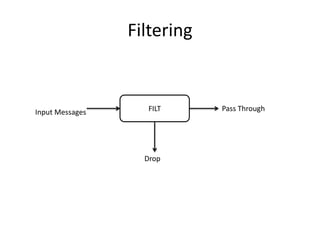
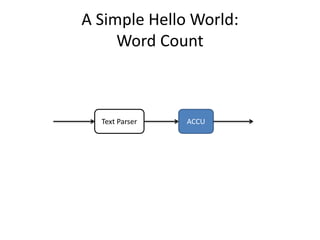
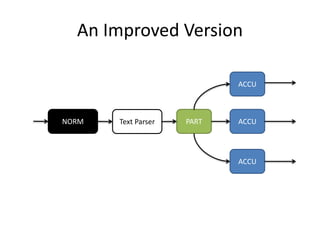
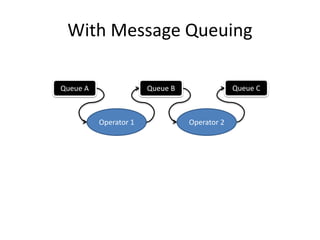
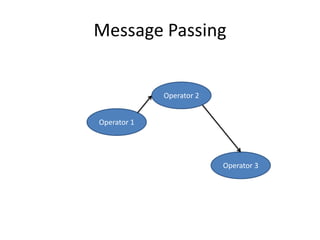
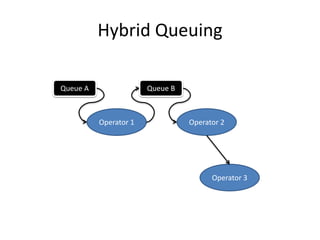
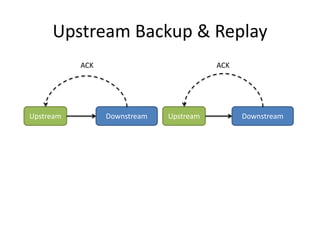
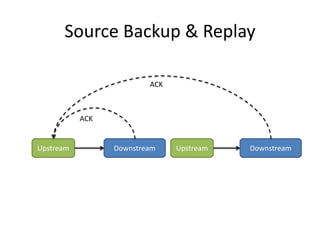
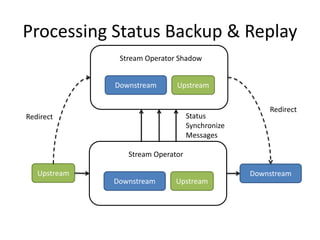
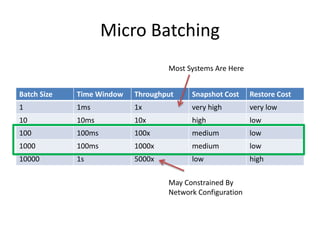
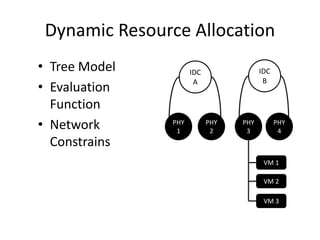
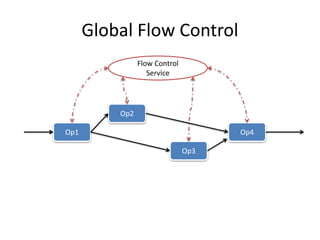
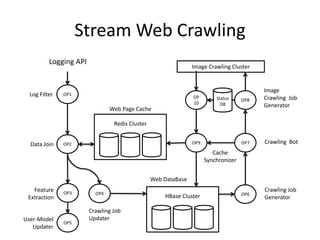
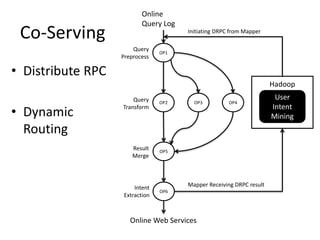
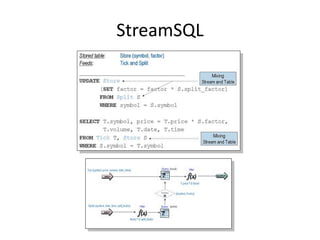
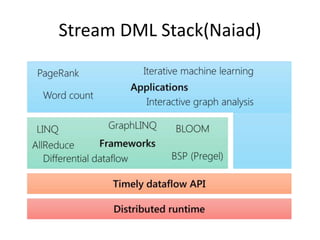
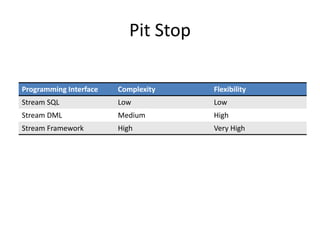
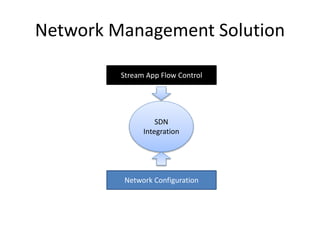
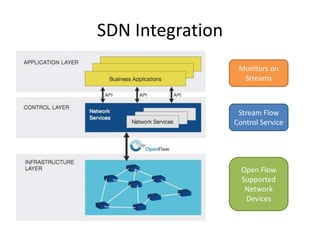
The document discusses stream processing architecture, including the definition of streams and their characteristics, reliability solutions, and handling workload fluctuations. It emphasizes the importance of message relay, uptime, and offers a high-level overview of programming complexities and network management challenges. The conclusion highlights future trends in stream processing, including the trade-off between reliability and performance, with a focus on high-level programming and scale-up strategies.