2. DIY/Component-Based Solutions (e.g., ADS1299 + Arduino/ESP32)
This is the "bare bones" approach and the most budget-friendly if you are willing to invest a lot of time and effort.
When to choose a DIY solution: This is the best option if your mini-project is the circuit itself. If you want to learn about analog front-end design, PCB layout, and low-level programming (e.g., configuring an ADS1299 chip), then this is the way to go. It offers the lowest hardware cost but the highest time and knowledge investment. This is not recommended for a beginner who wants to focus on the application (e.g., controlling a game with brain signals) rather than the hardware.


![Dept. of ECE, Vemana IT 3
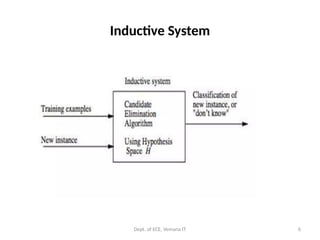
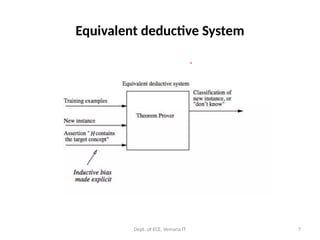
Inductive bias: definition
Given:
-a concept learning algorithm L for a set of instances X
-a concept e defined over X
-a set of training examples for c: Dc = {(x, c(x))}
-L(xi, Dc) outcome of classification of xi, after learning.
Inductive inference (>):
Dc ^ xi >L(xi, Dc)
The inductive bias is defined as a minimal set of assumptions
B, such that (|- for deduction)
∀(xi X) [(B^Dc ^x
∈ i ) |- L(xi, Dc)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ismlppt-260130162028-1d9c3399/85/Intelligence-system-seminar-presentation-3-320.jpg)