Embed presentation
Download to read offline







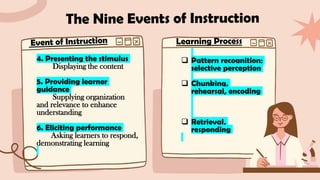



Robert Gagné is known for his theories on learning outcomes and conditions as well as his nine events of instruction. His theories have been applied to instructional design in various fields including the military, instructional systems development, and flying. Gagné focused on learning outcomes, conditions, and a nine step instructional process involving gaining attention, informing objectives, stimulating recall of prior knowledge, presenting new material, providing guidance, eliciting performance, giving feedback, assessing performance, and enhancing retention and transfer.










