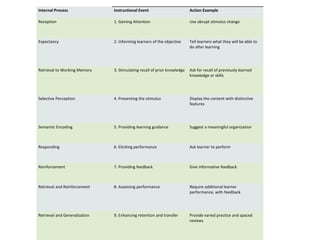
Robert Gagne developed an instructional theory based on the idea that different learning conditions lead to different types of learning. His theory includes four main elements: 1) Internal and external conditions of learning, 2) Three associations of learning - classical, operant, and verbal conditioning, 3) Five categories of learning - intellectual skills, verbal information, cognitive strategies, motor skills, and attitudes, and 4) Nine instructional events to facilitate learning - from gaining attention to enhancing retention and transfer.