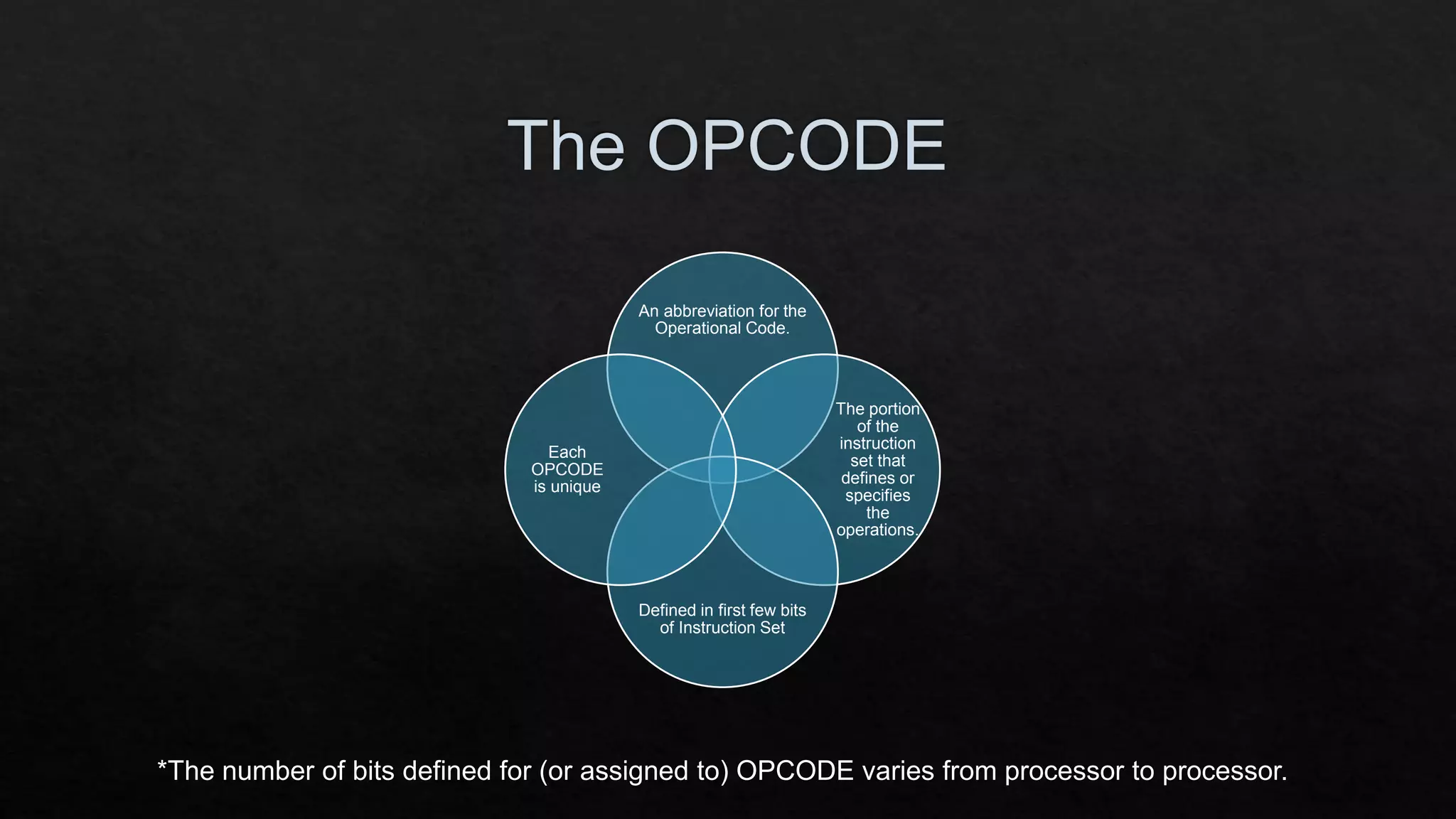
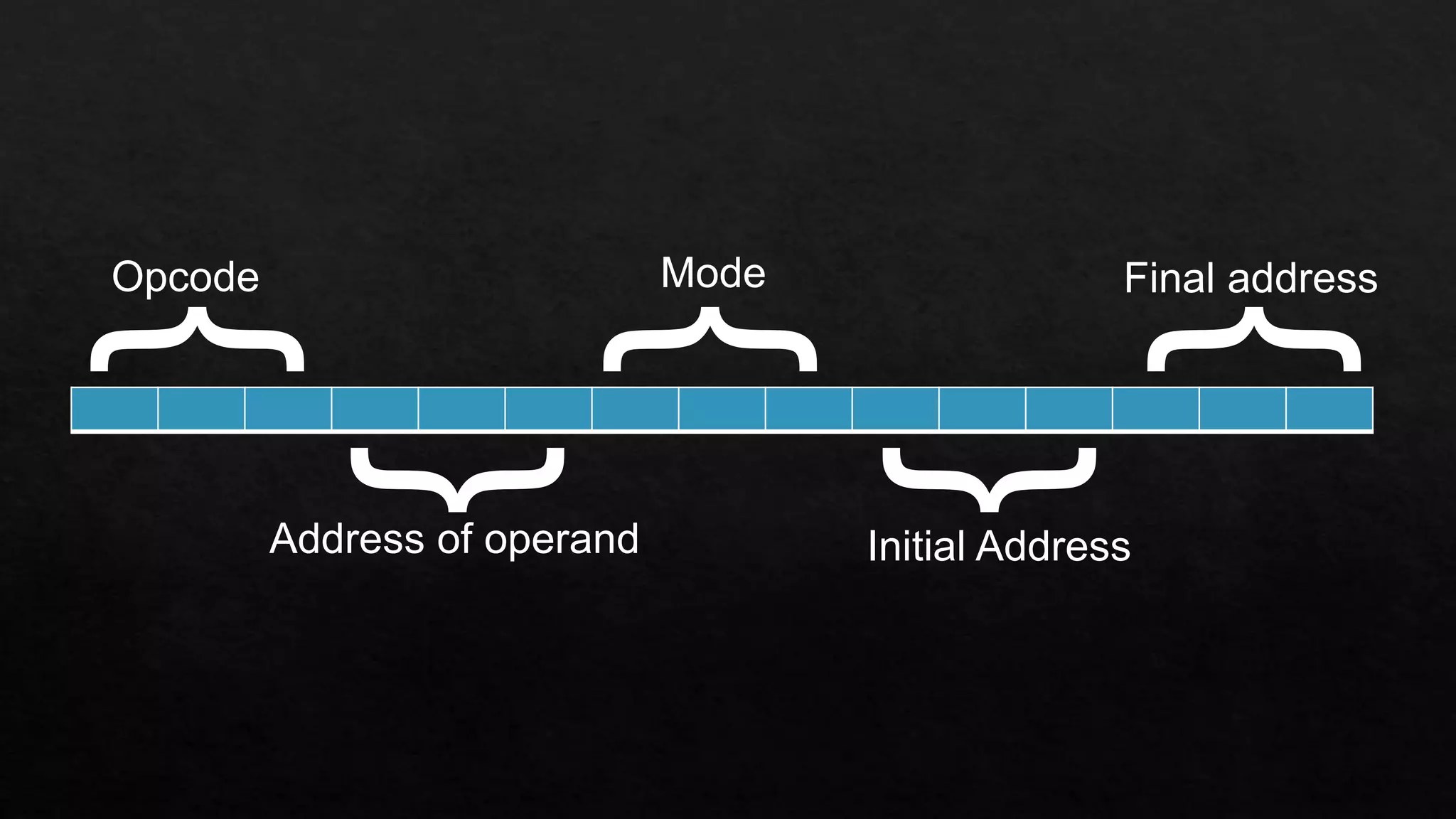
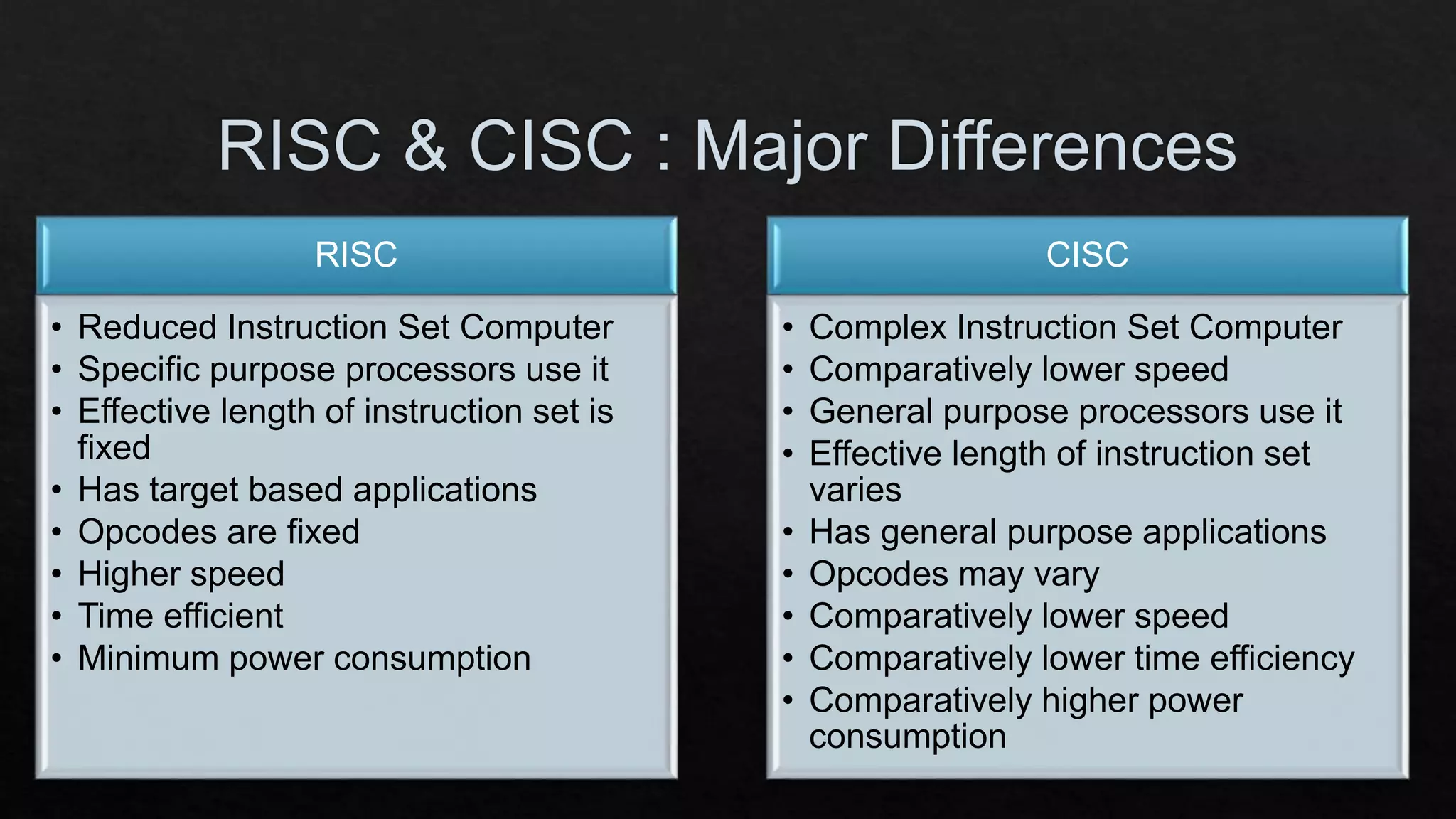
The document discusses the differences between RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) and CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) architectures, highlighting their respective instruction set characteristics and performance implications. RISC features fixed-length instructions, higher speed, and energy efficiency, while CISC allows for a more variable instruction length at the cost of speed and power consumption. The document emphasizes the trade-offs in using larger instruction sets and associated resource requirements.