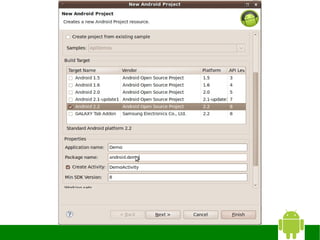
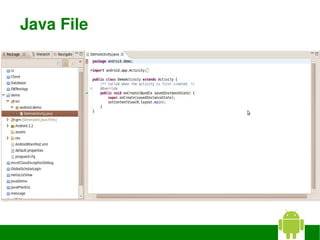
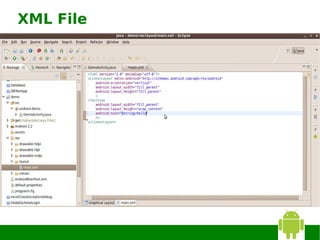
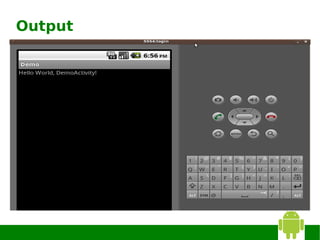
The document provides instructions for installing Eclipse, the Android SDK, and configuring them for Android development. It discusses:
1) The requirements which include Java JDK/JRE, Android SDK, Eclipse IDE, and the ADT plugin.
2) Downloading and installing the Android SDK from the Android developer website to get tools like the emulator, debugger, and Eclipse plugin.
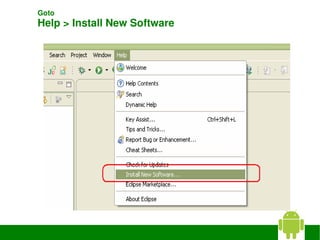
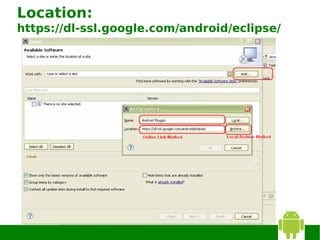
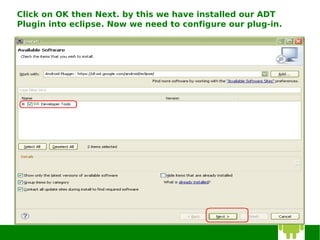
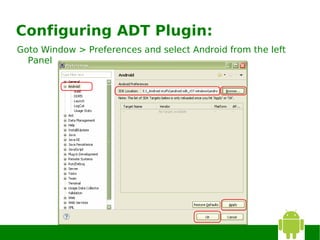
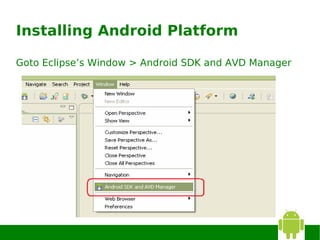
3) Configuring the ADT plugin in Eclipse and installing Android platforms.
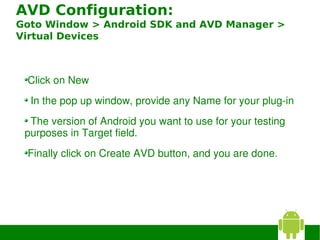
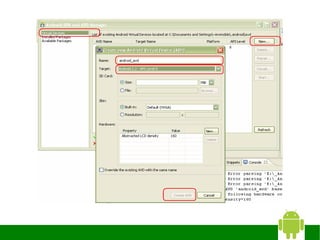
4) Creating an Android Virtual Device (AVD) for testing applications.