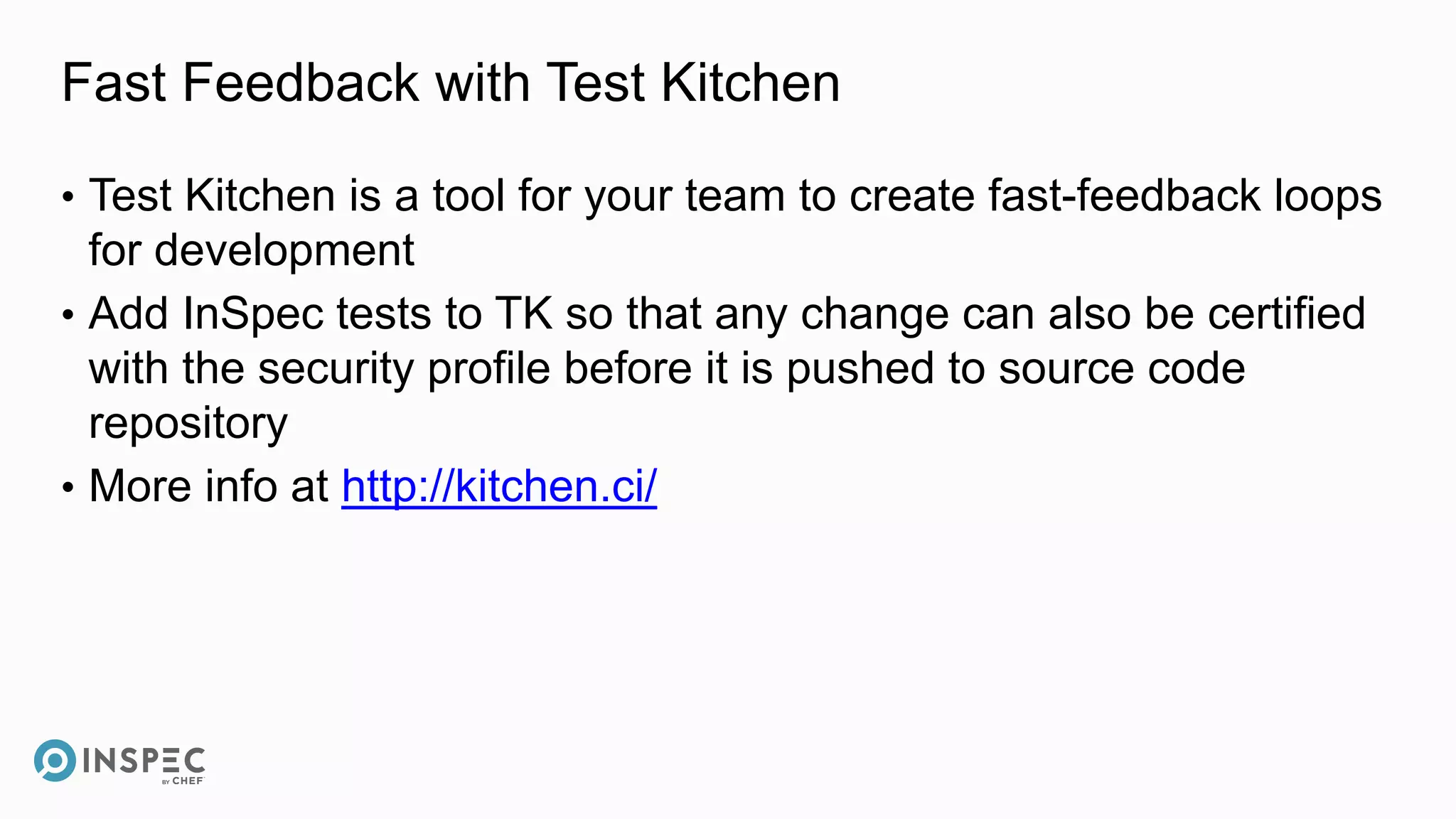
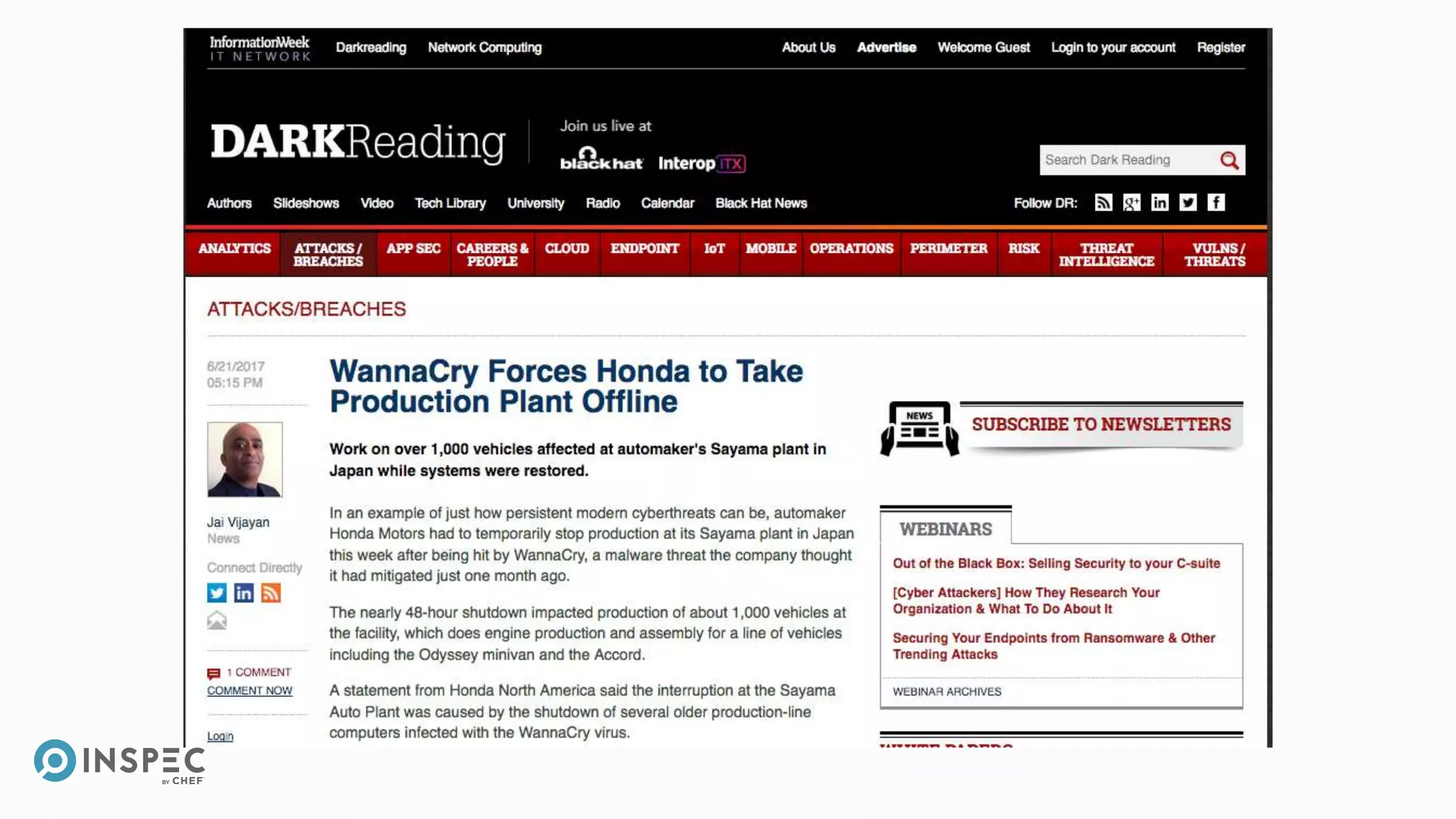
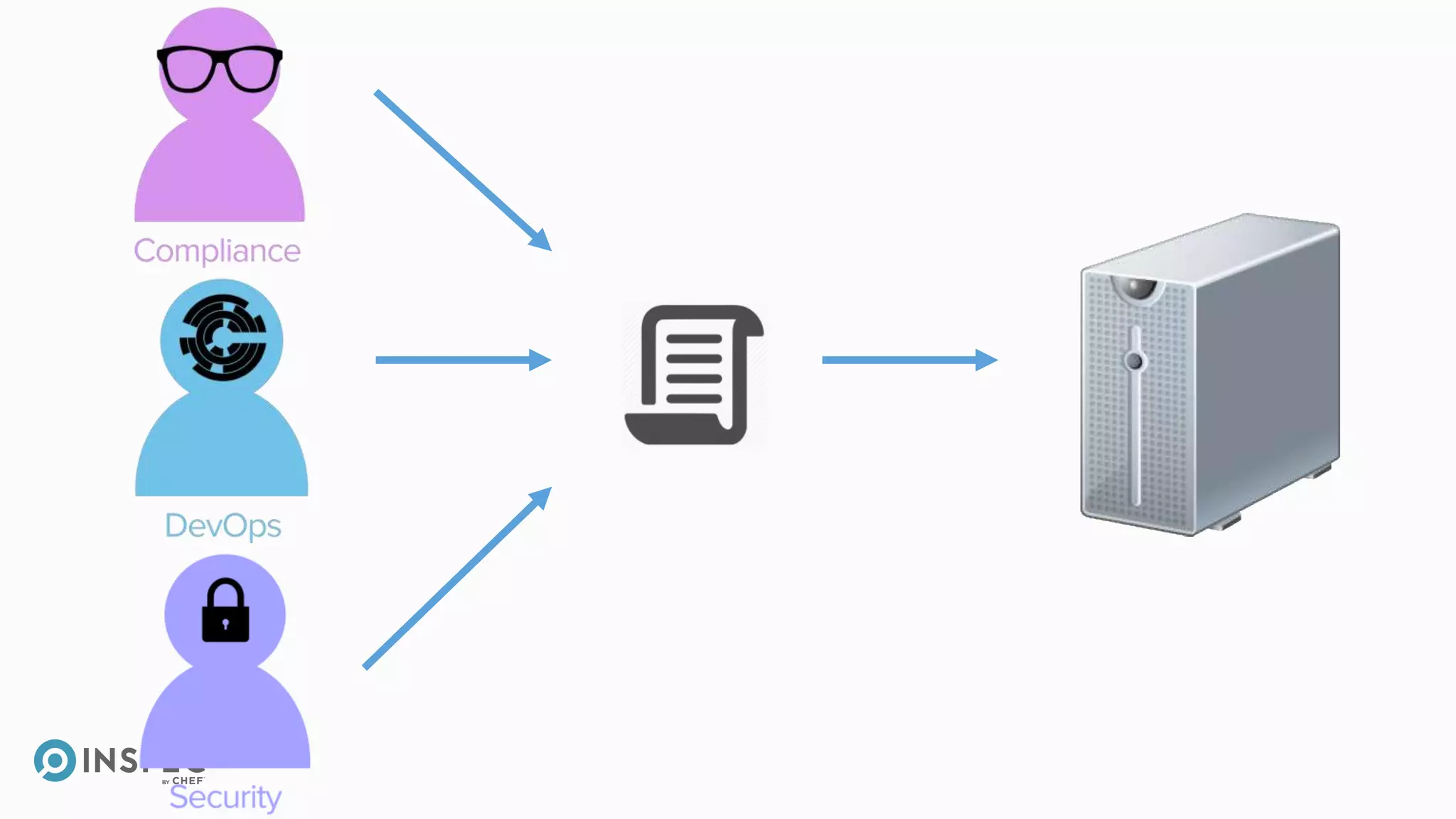
This document discusses InSpec, an open-source testing framework for infrastructure and compliance. It can be used to test security configurations and compliance across operating systems, platforms, and cloud providers. InSpec allows users to write tests in a human-readable language and execute them locally or remotely. Tests can be packaged into reusable profiles that ensure configurations meet security and compliance requirements throughout the development lifecycle.

















![Execute InSpec
[chef@ip-172-31-38-151 ~]$ inspec exec ./test.rb
Profile: tests from ./test.rb
Version: (not specified)
Target: local://
File /tmp
✔ should exist
✔ should be directory
✔ should be owned by "root"
✔ mode should cmp == "01777"
Test Summary: 4 successful, 0 failures, 0 skipped](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/walls-open28-180607122128-180608124856/75/Inspec-Turn-your-compliance-security-and-other-policy-requirements-into-automated-tests-OPEN18-20-2048.jpg)