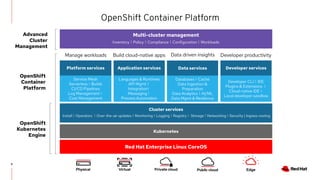
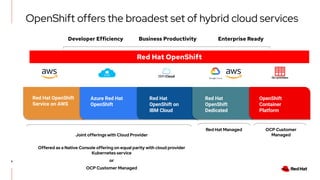
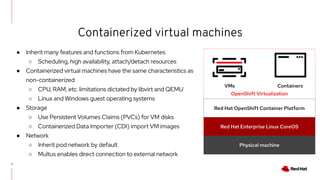
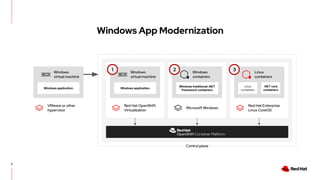
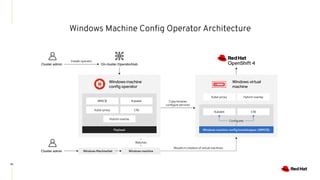
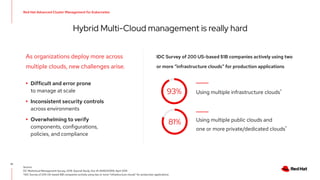
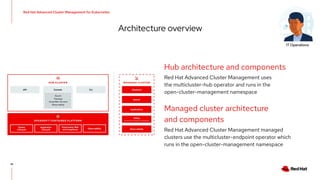
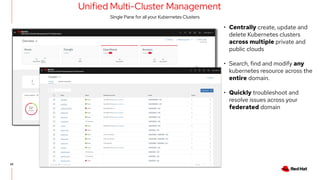
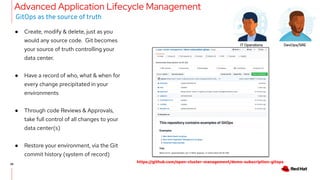
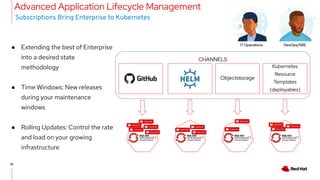
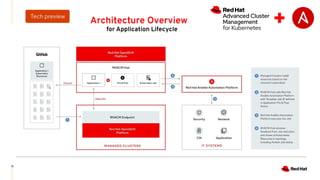
The document discusses the features and benefits of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes, including improved developer productivity, enhanced application lifecycle management, and centralized control across hybrid cloud environments. It highlights the challenges of managing multiple cloud infrastructures and presents Red Hat's solutions for security and compliance. Additionally, it covers architectural components, deployment processes, and the integration of tools like Quarkus for efficient application development.