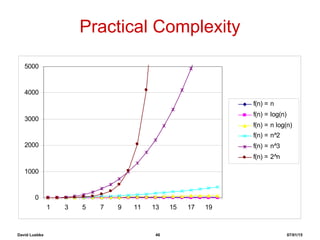
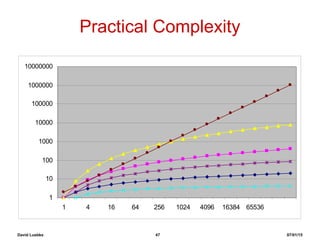
The document step-by-step demonstrates the insertion sort algorithm by running it on the sample array [30, 10, 40, 20]. It shows the state of the array and relevant variables after each iteration of the outer for loop. Each step switches the value of one element in the array to correctly sort it in ascending order. After running through all elements, the array is fully sorted as [10, 20, 30, 40].
![David Luebke 2 07/01/15
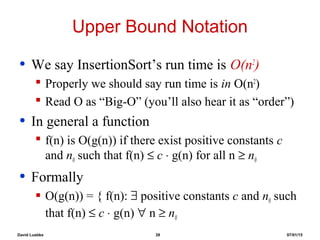
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-2-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 3 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 10 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = ∅ j = ∅ key = ∅
A[j] = ∅ A[j+1] = ∅](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-3-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 4 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 10 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 1 key = 10
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-4-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 5 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 1 key = 10
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-5-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 6 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 1 key = 10
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-6-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 7 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 0 key = 10
A[j] = ∅ A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-7-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 8 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 0 key = 10
A[j] = ∅ A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-8-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 9 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 0 key = 10
A[j] = ∅ A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-9-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 10 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 0 key = 10
A[j] = ∅ A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-10-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 11 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 0 key = 40
A[j] = ∅ A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-11-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 12 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 0 key = 40
A[j] = ∅ A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-12-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 13 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 2 key = 40
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-13-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 14 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 2 key = 40
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-14-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 15 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 2 key = 40
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-15-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 16 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 40
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-16-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 17 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-17-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 18 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-18-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 19 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-19-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 20 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-20-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 21 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-21-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 22 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-22-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 23 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-23-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 24 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-24-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 25 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-25-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 26 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-26-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 27 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-27-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 28 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 1 key = 20
A[j] = 10 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-28-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 29 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 1 key = 20
A[j] = 10 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-29-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 30 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 20 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 1 key = 20
A[j] = 10 A[j+1] = 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-30-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 31 07/01/15
An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 20 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 1 key = 20
A[j] = 10 A[j+1] = 20
Done!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-31-320.jpg)

![David Luebke 33 07/01/15
Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
What is the precondition
for this loop?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-33-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 34 07/01/15
Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
How many times will
this loop execute?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-34-320.jpg)
![David Luebke 35 07/01/15
Insertion Sort
Statement Effort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n { c1n
key = A[i] c2(n-1)
j = i - 1; c3(n-1)
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) { c4T
A[j+1] = A[j] c5(T-(n-1))
j = j - 1 c6(T-(n-1))
} 0
A[j+1] = key c7(n-1)
} 0
}
T = t2 + t3 + … + tn where ti is number of while expression evaluations for the ith
for](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-150701085904-lva1-app6891/85/Insertion-sort-35-320.jpg)