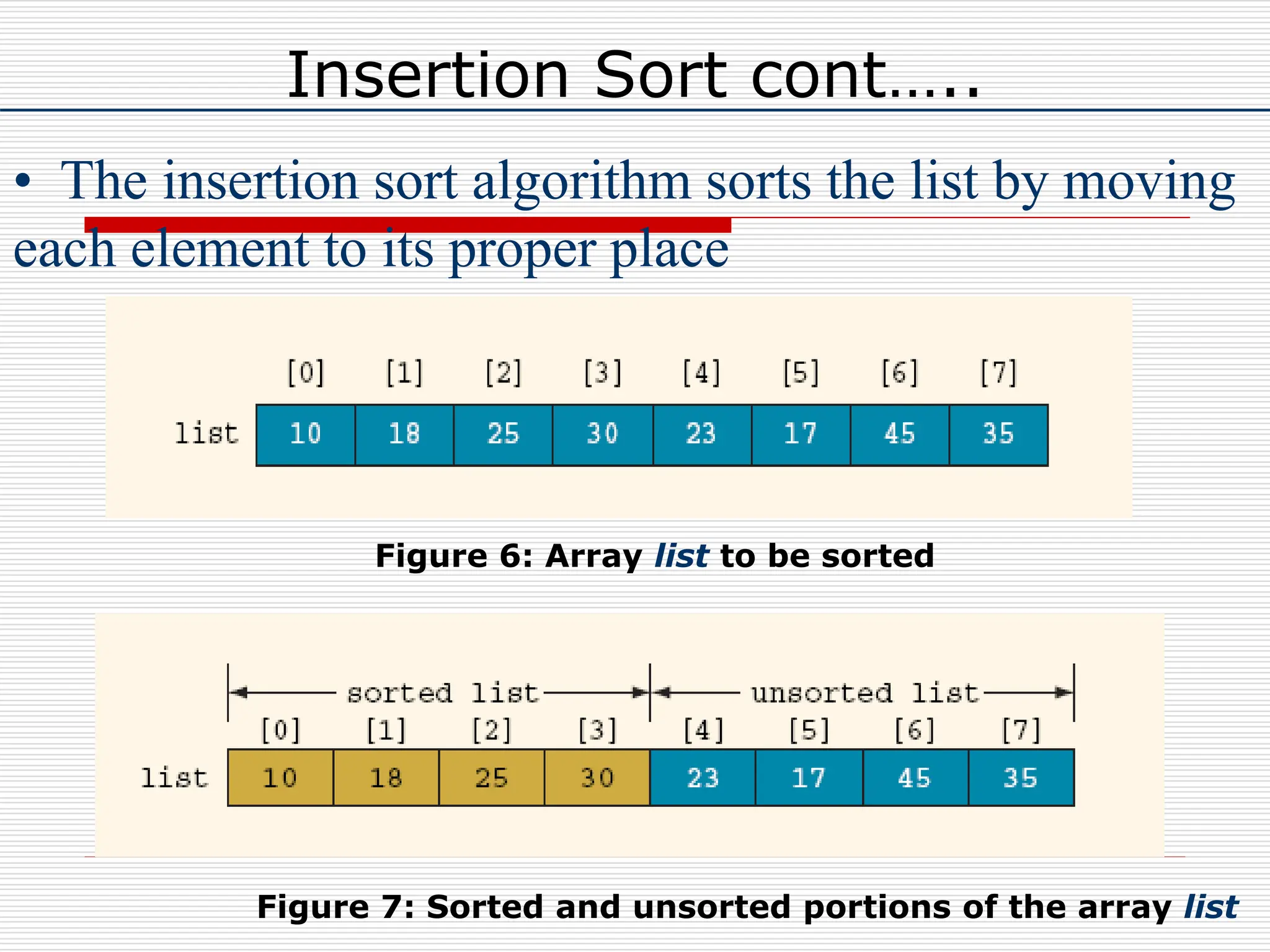
The document discusses sorting algorithms and insertion sort. It provides details on how insertion sort works by iterating through an array and inserting each element into the sorted portion of the array. It gives pseudocode for the insertion sort algorithm and provides an example to demonstrate how it works on a sample array.



![Insertion sort
Suppose an array A with n elements
A[1], A[2],……..A[N] in memory.
The insertion sort algorithm scan A form
A[1] to A[N], inserting each elements
A[K] into its proper position in the
previously sorted sub array A[1],
A[2]……….A[K-1] that is,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-6-2048.jpg)
![Insertion sort
Pass1: A[1] by itself is trivially sorted.
Pass 2: A[2] in inserted either before or after A[1] so
that A[1], A[2] is sorted.
Pass 3: A[3] is inserted into its proper position in A[1],
A[2], so that all the three elements will be sorted.
Pass 4. A[4] is inserted into its proper place so that…..
Pass N. A[N] is inserted into its proper place so that
A[1], A[2], …………A[N] is sorted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-7-2048.jpg)
![Insertion Sort Algorithm (Cont’d)
Figure 8: Move list[4] into list[2]
Figure 9: Copy list[4] into temp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-9-2048.jpg)
![Insertion Sort Algorithm (Cont’d)
Figure 10: Array list before copying list[3] into list[4], then
list[2] into list[3]
Figure 11: Array list after copying list[3] into list[4], and then
list[2] into list[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-10-2048.jpg)
![Insertion Sort Algorithm (Cont’d)
Figure 12: Array list after copying temp into list[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-11-2048.jpg)

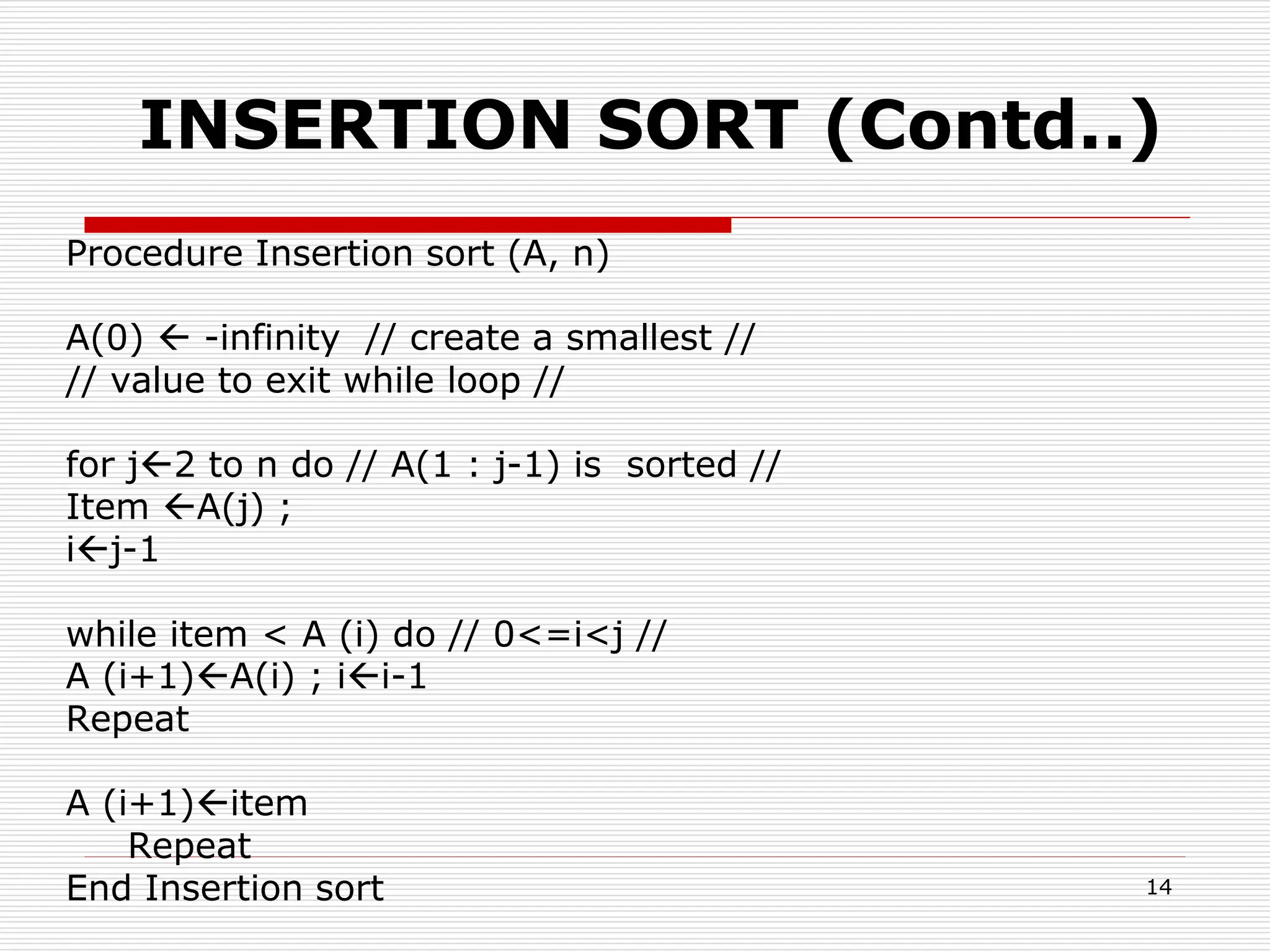
![Insertion sort algorithm
INSERTION ( A, N).
this algorithm sorts the array A with N elements.
1. Set A[0]:= -infinity.
2. Repeat step 3 to 5 for K=: 2 to N
3. Set temp:= A[K] and PTR:= K-1
4. Repeat while TEMP < A[PTR]
a. Set A[PTR+1]:= A[PTR] [moves elements forward]
b. Set PTR:= PTR-1
[end of loop]
5. Set A[PTR + 1]:=TEMP. [insert elements in proper
position]
[end of step 2 loop]
6. exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-13-2048.jpg)


![Algorithm: INSERTIONSORT
Input: An array A[1..n] of n elements.
Output: A[1..n] sorted in nondecreasing
order.
1. for i 2 to n
2. x A[i]
3. j i - 1
4. while (j >0) and (A[j] > x)
5. A[j + 1] A[j]
6. j j - 1
7. end while
8. A[j + 1] x
9. end for
Example sort : 34 8 64 51 32 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-17-2048.jpg)
![An Example: Insertion Sort
InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 10 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = j = key =
A[j] = A[j+1] = ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-18-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 10 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 1 key = 10
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-19-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 1 key = 10
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-20-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 1 key = 10
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-21-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 0 key = 10
A[j] = A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-22-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
30 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 0 key = 10
A[j] = A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-23-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 2 j = 0 key = 10
A[j] = A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-24-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 0 key = 10
A[j] = A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-25-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 0 key = 40
A[j] = A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-26-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 0 key = 40
A[j] = A[j+1] = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-27-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 2 key = 40
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-28-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 2 key = 40
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-29-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 3 j = 2 key = 40
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-30-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 40
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-31-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-32-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-33-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-34-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 20
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-35-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-36-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-37-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 3 key = 20
A[j] = 40 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-38-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-39-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 40 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-40-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-41-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 2 key = 20
A[j] = 30 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-42-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 1 key = 20
A[j] = 10 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-43-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 30 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 1 key = 20
A[j] = 10 A[j+1] = 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-44-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 20 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 1 key = 20
A[j] = 10 A[j+1] = 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-45-2048.jpg)
![InsertionSort(A, n) {
for i = 2 to n {
key = A[i]
j = i - 1;
while (j > 0) and (A[j] > key) {
A[j+1] = A[j]
j = j - 1
}
A[j+1] = key
}
}
10 20 30 40
1 2 3 4
i = 4 j = 1 key = 20
A[j] = 10 A[j+1] = 20
Done!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort-240112183312-37cfecd4/75/insertion-sort-ppt-46-2048.jpg)
