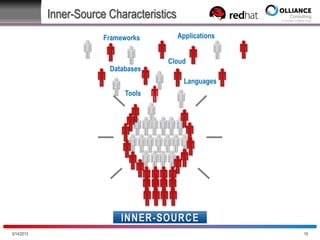
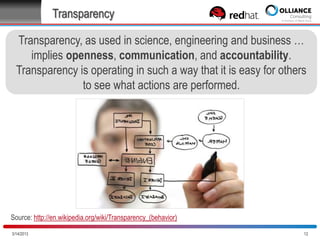
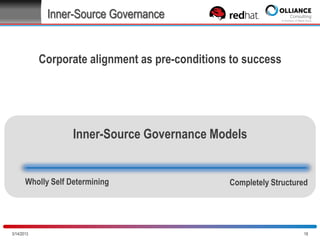
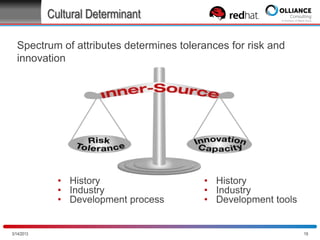
The document discusses the concept of inner source, which applies open source practices to internal software development to enhance collaboration, transparency, and innovation within organizations. It outlines key characteristics, benefits, and challenges of implementing inner source, such as fostering a meritocratic environment and measuring success through various metrics. Best practices for getting started and aligning corporate culture with inner source principles are also provided.