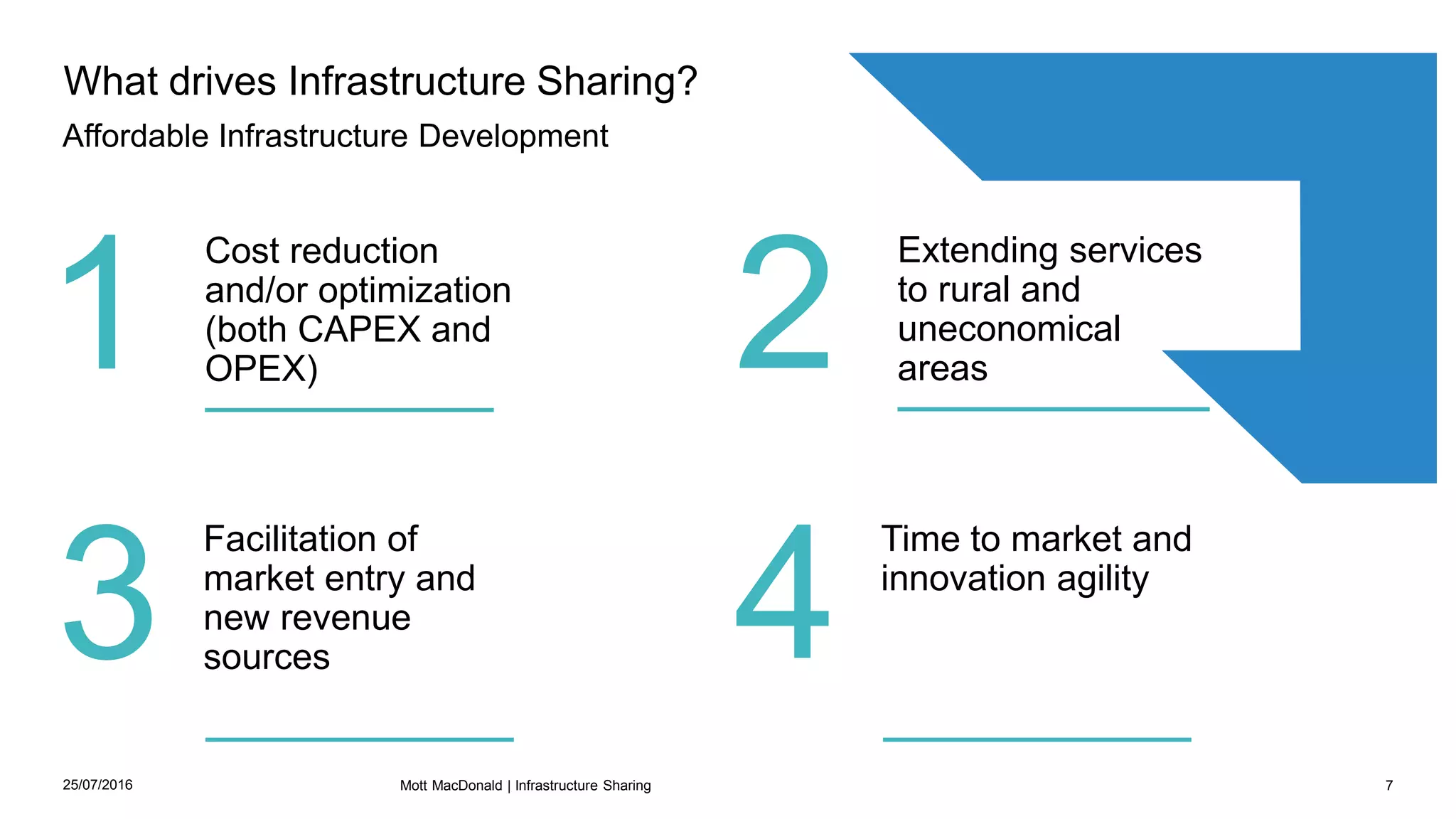
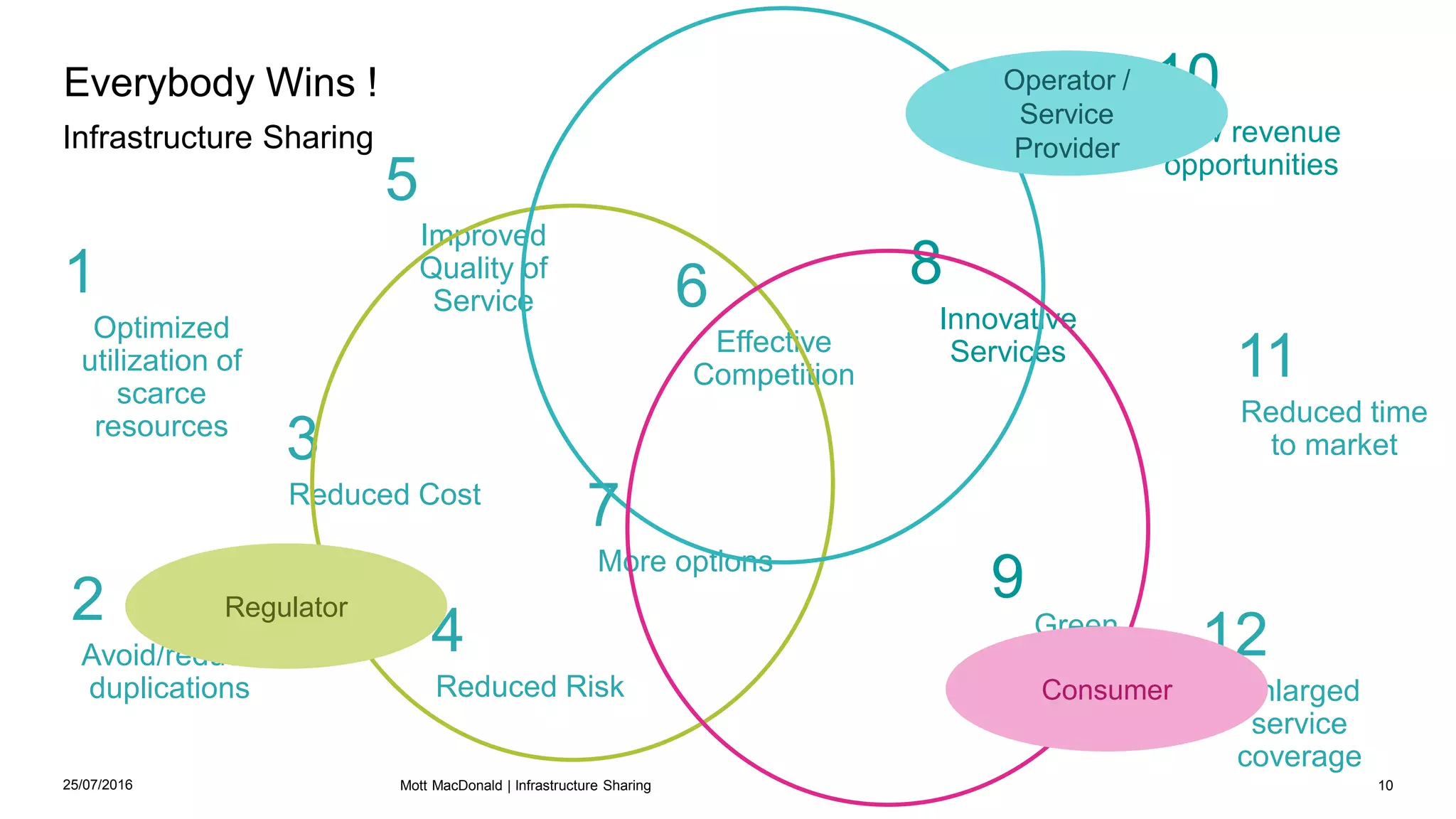
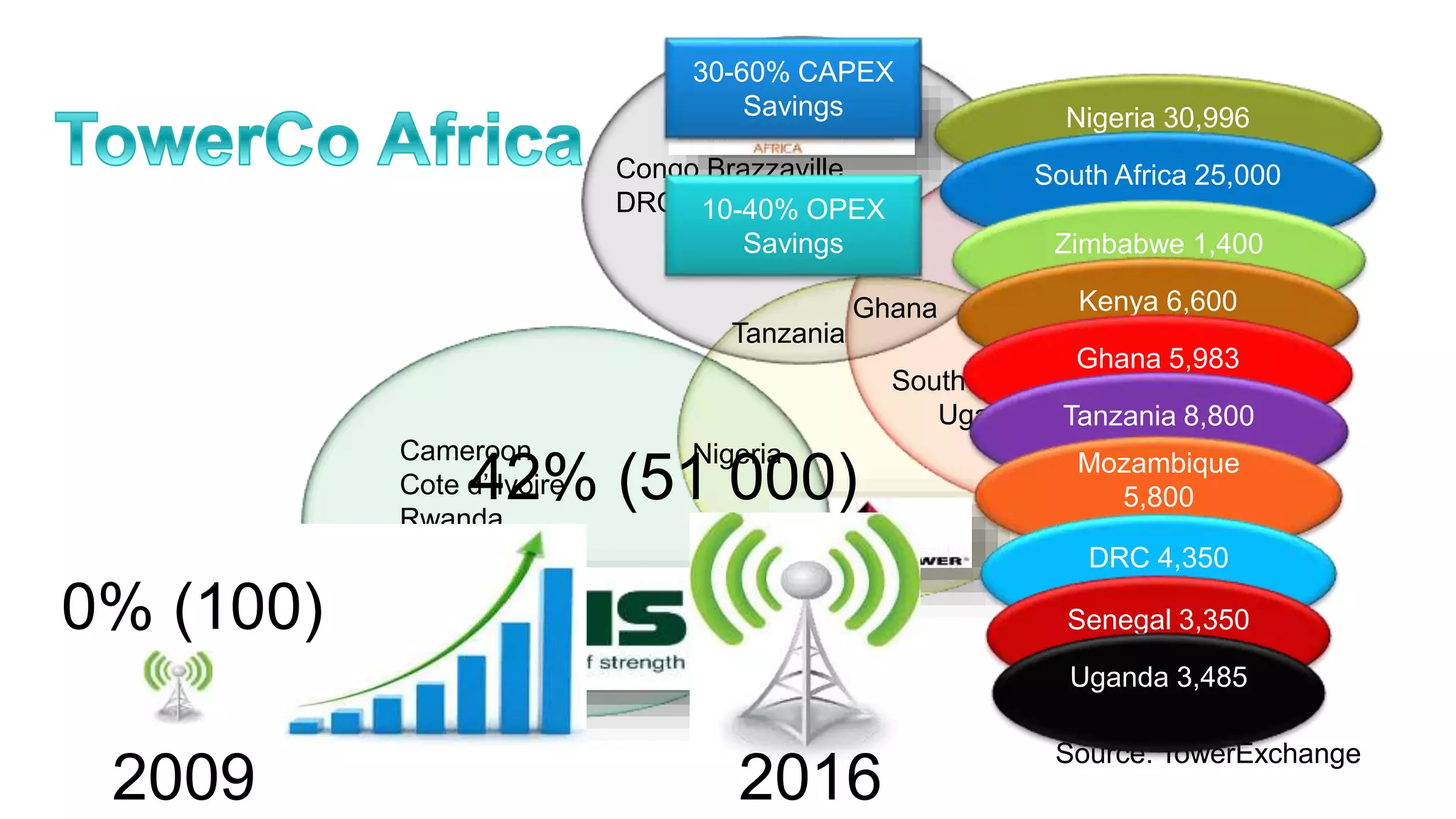
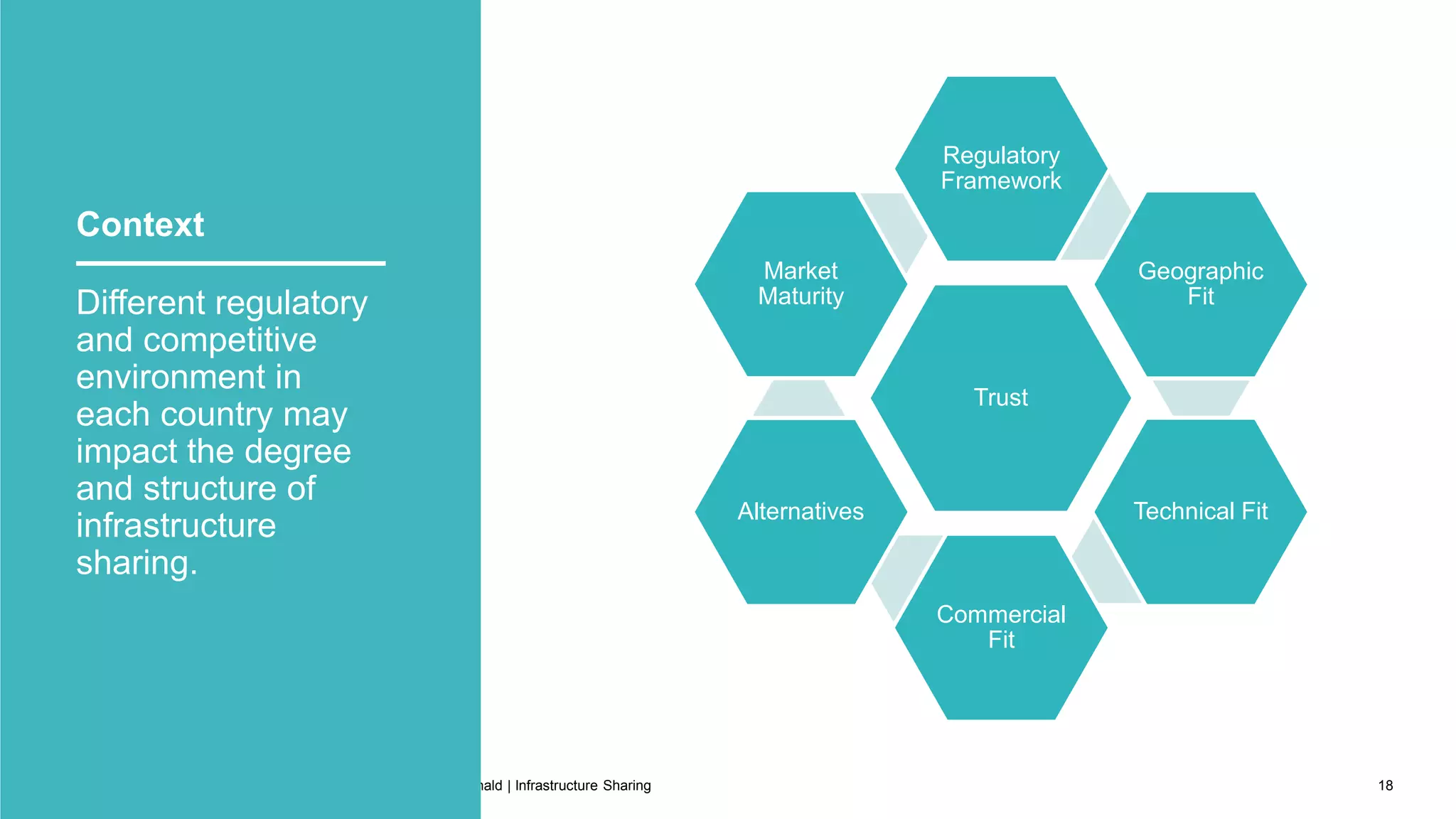
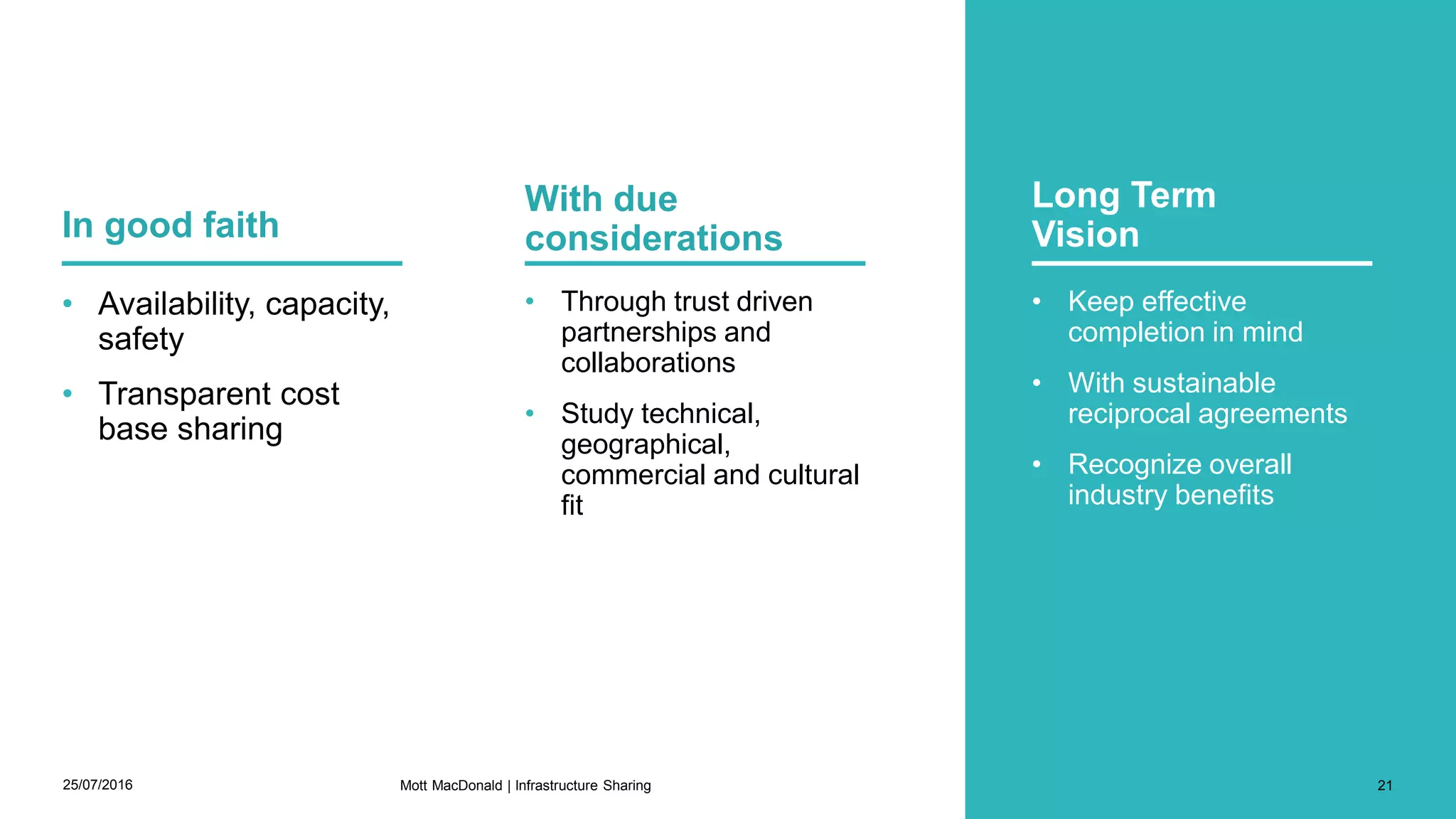
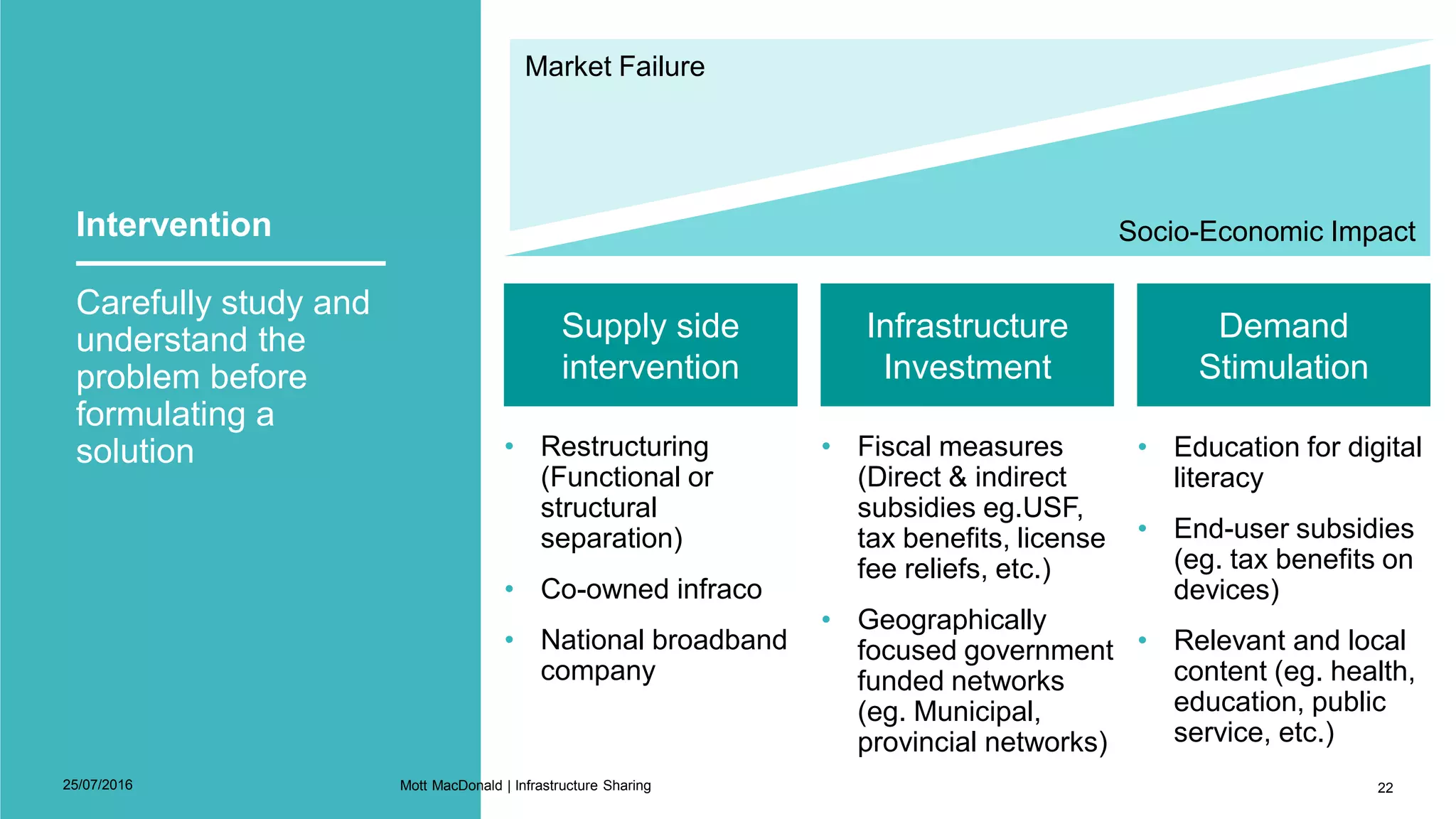
This document discusses infrastructure sharing, which refers to the joint use or development of telecommunications infrastructure between operators to efficiently deliver services. It defines infrastructure sharing, outlines the strategic drivers like cost reduction, discusses benefits such as optimized resource use and reduced costs, and provides examples of successful infrastructure sharing initiatives. The document also covers considerations for infrastructure sharing and provides recommendations, emphasizing the need to carefully study technical, geographical and commercial fit based on a long term vision and partnerships built on trust.