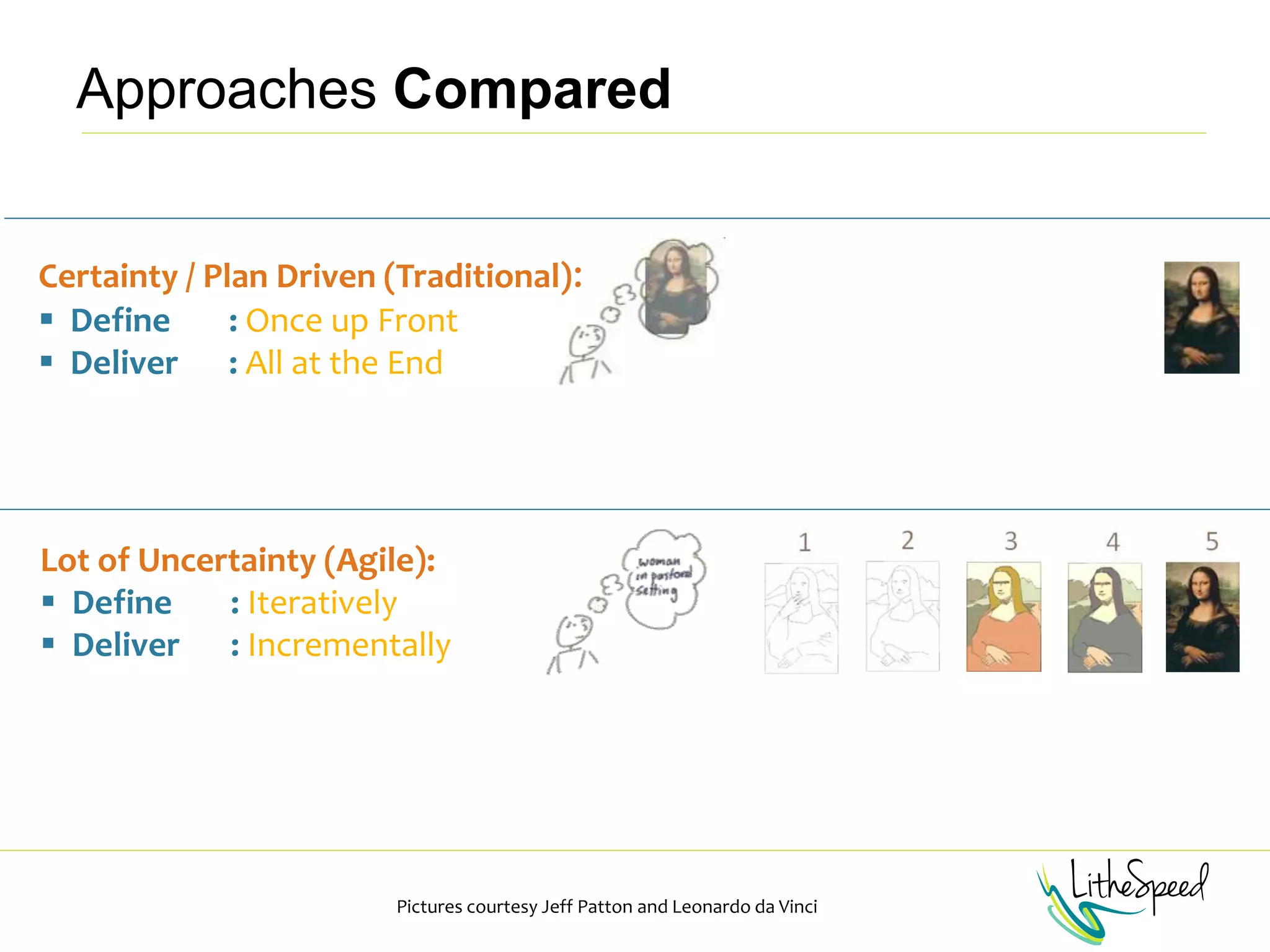
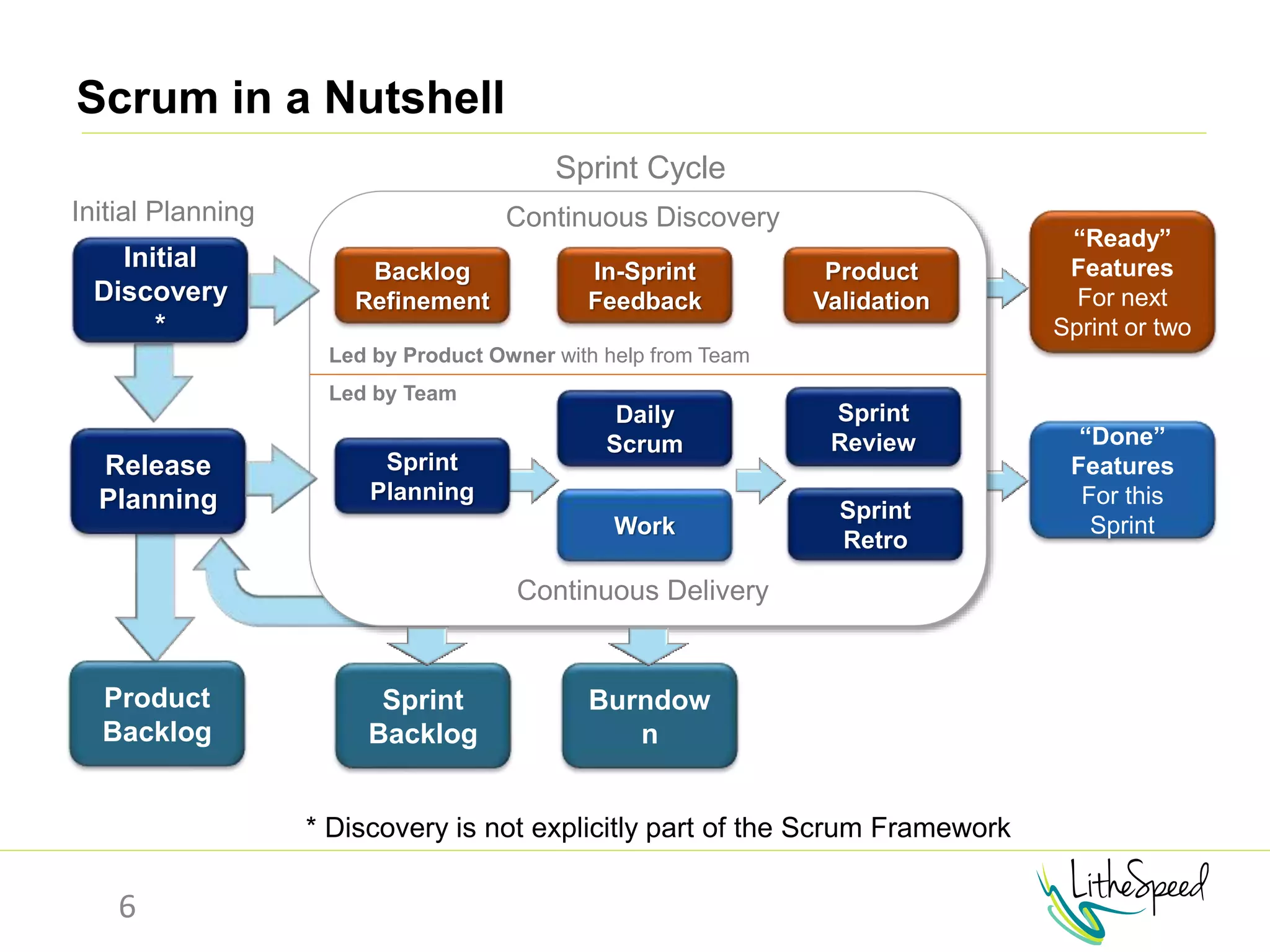
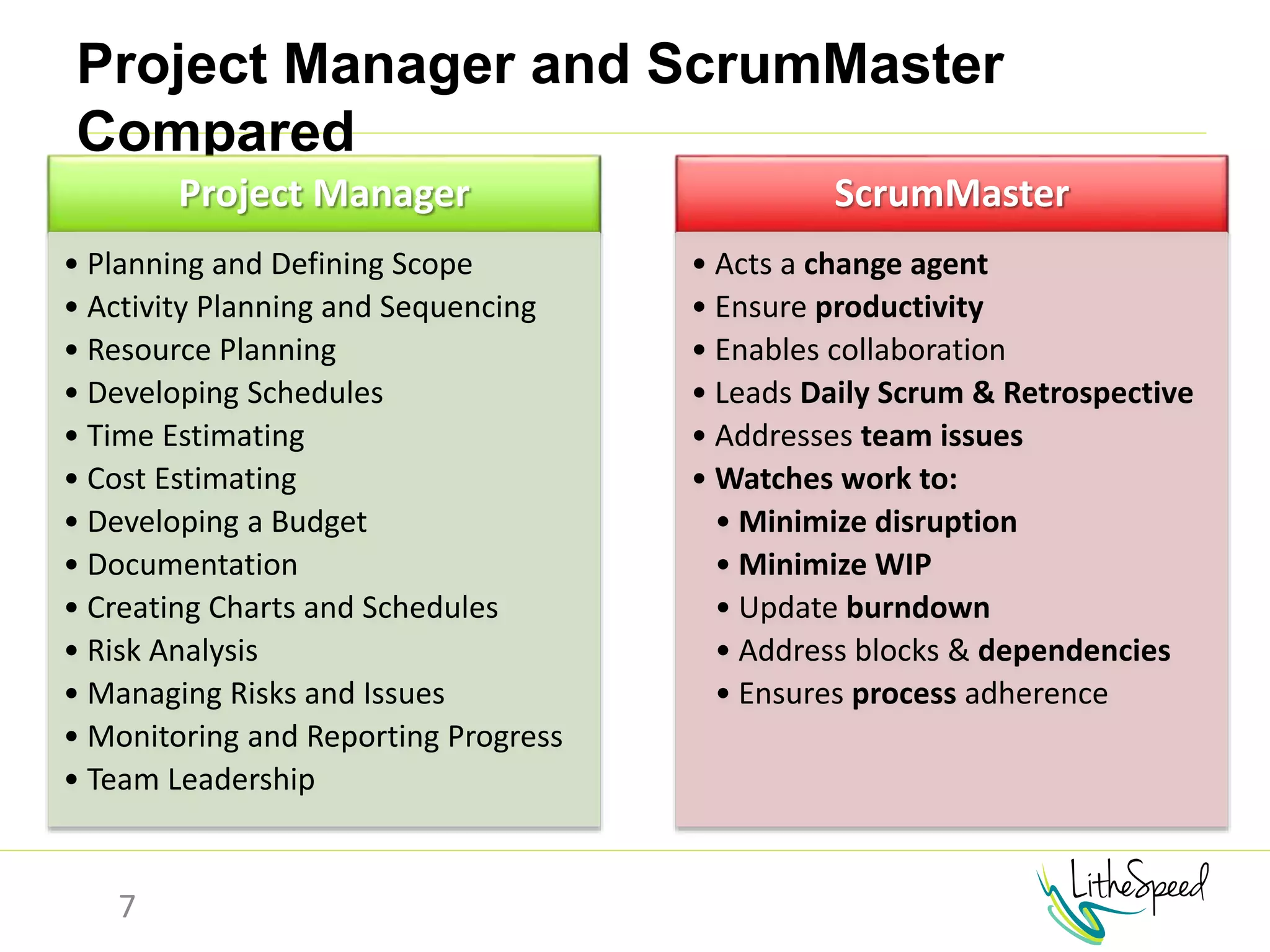
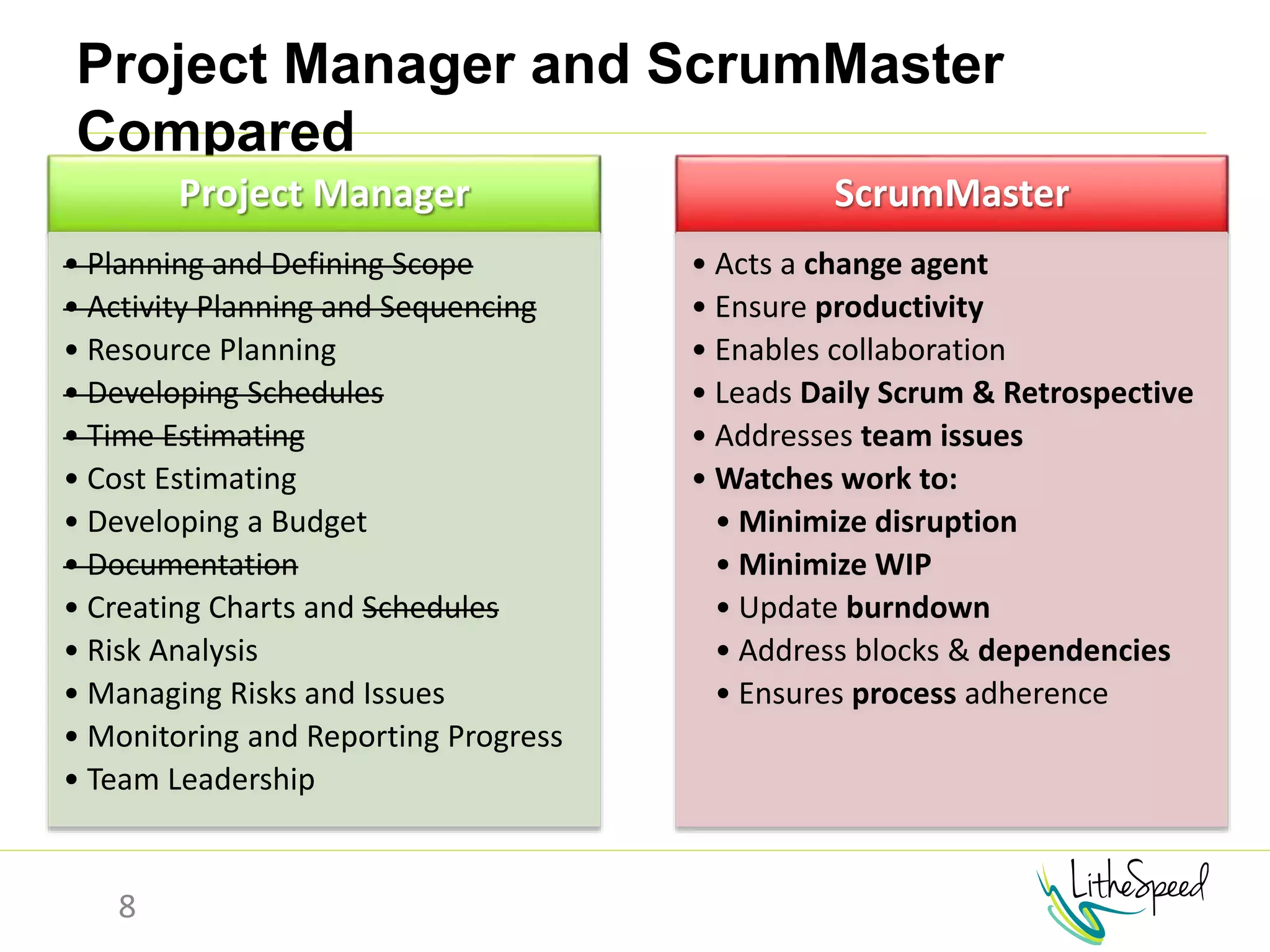
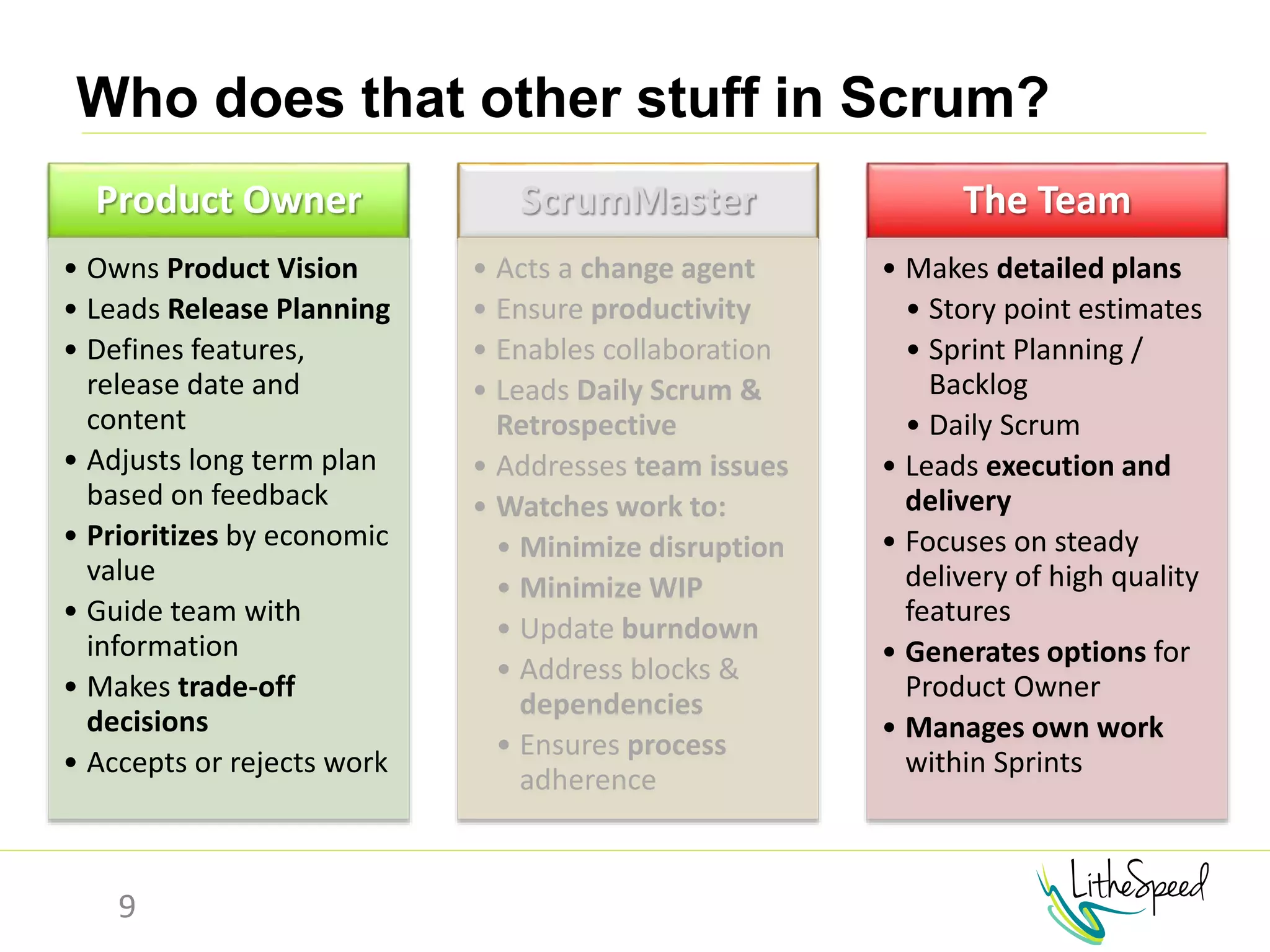
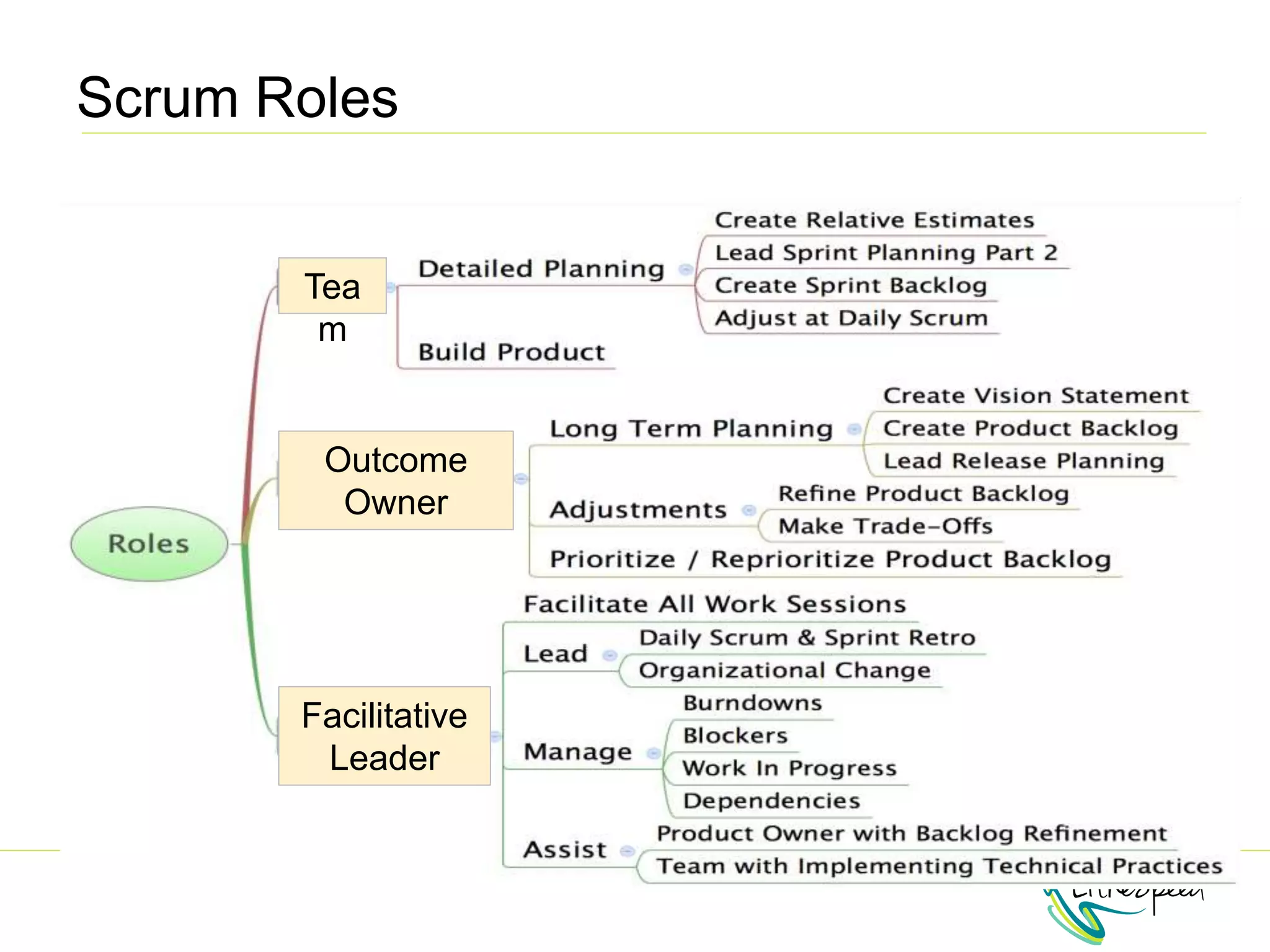
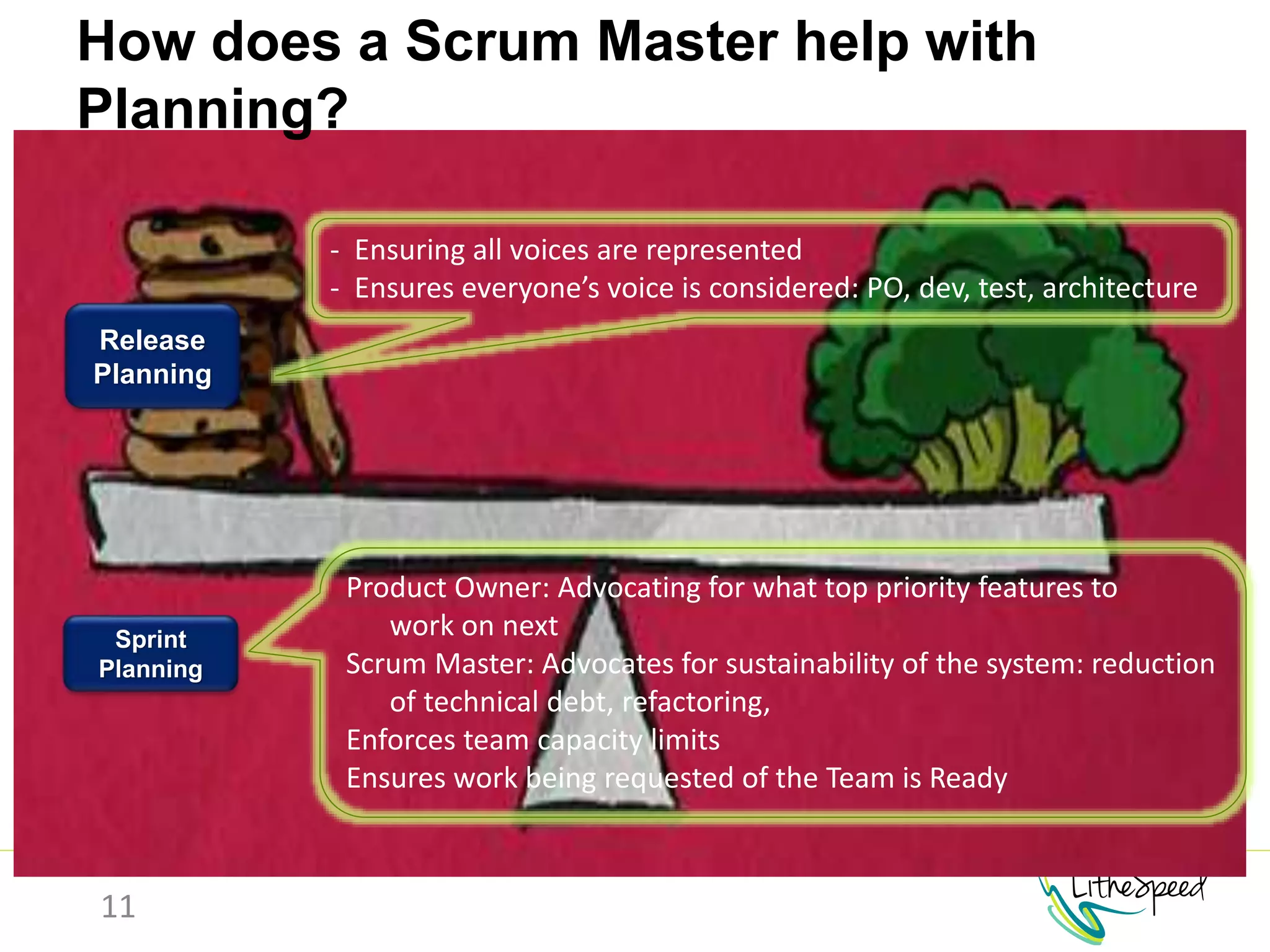
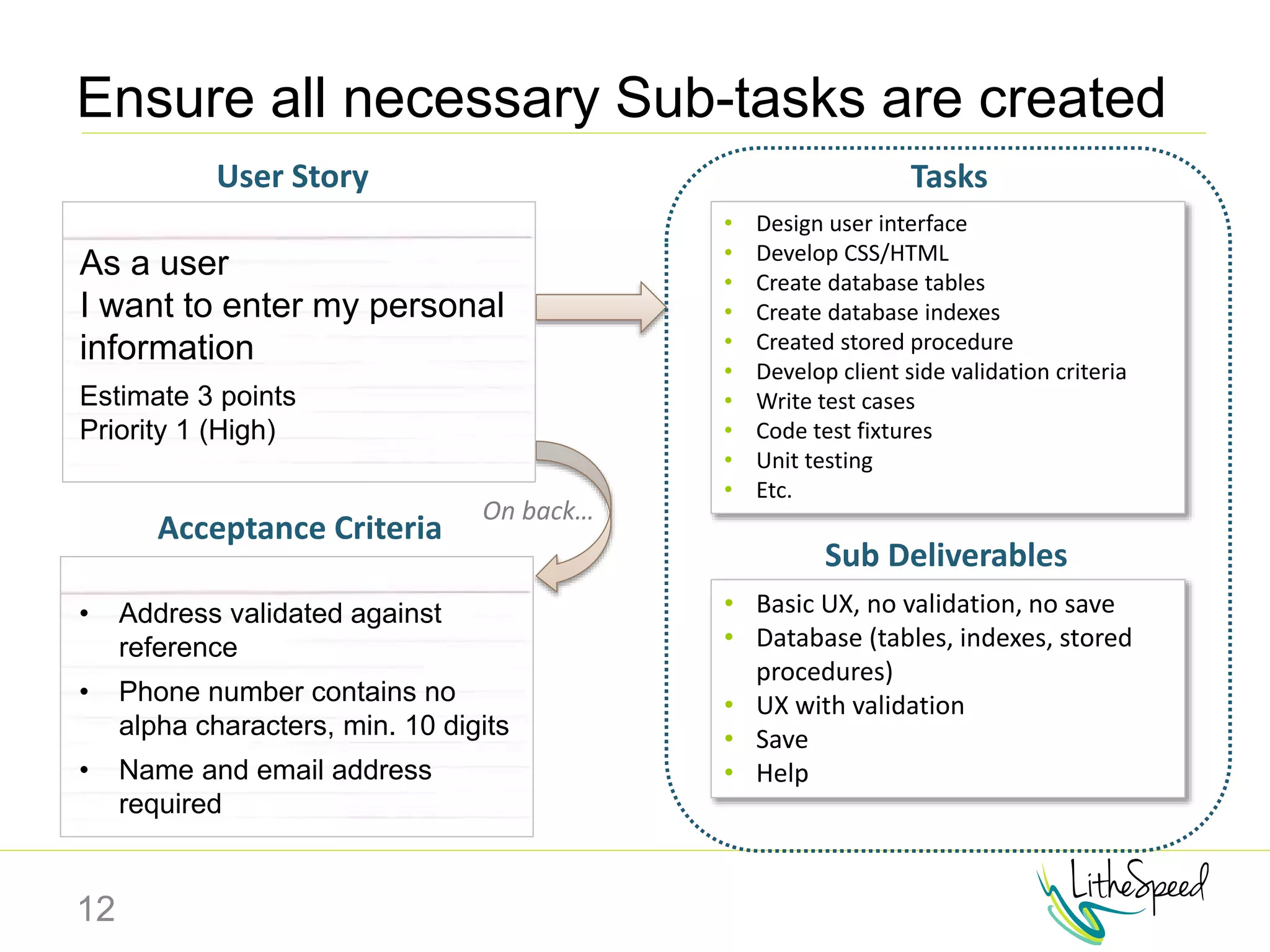
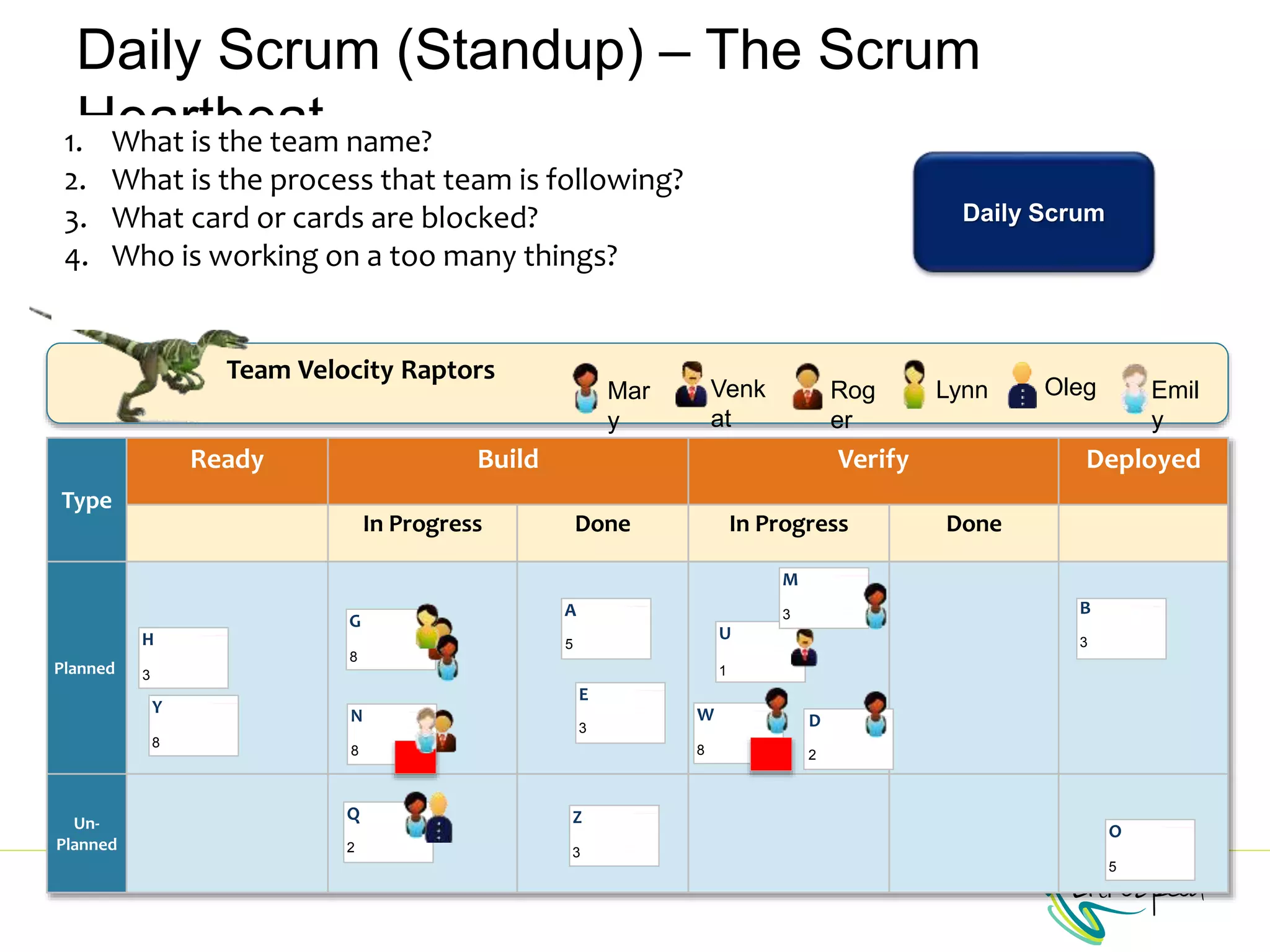
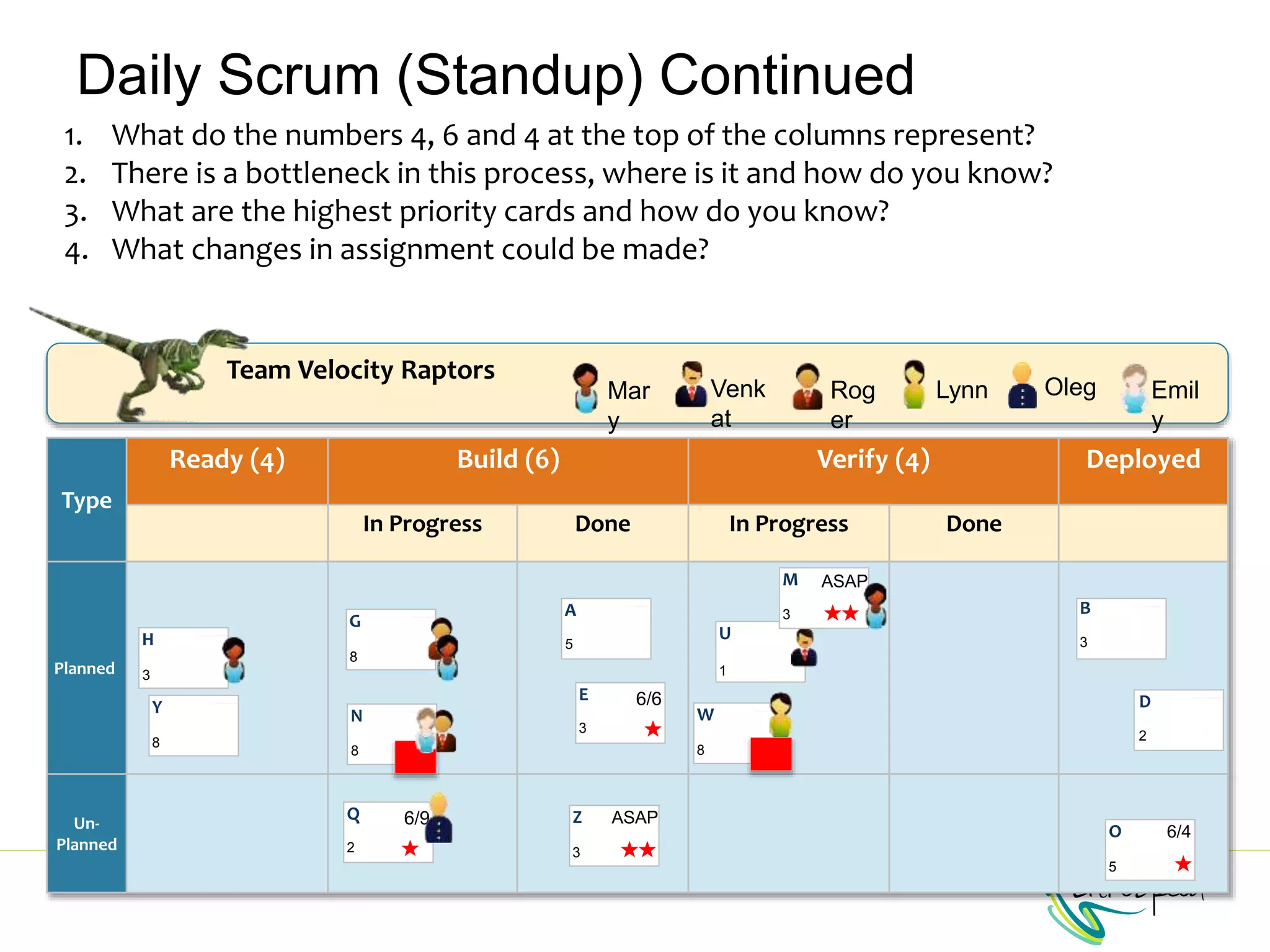
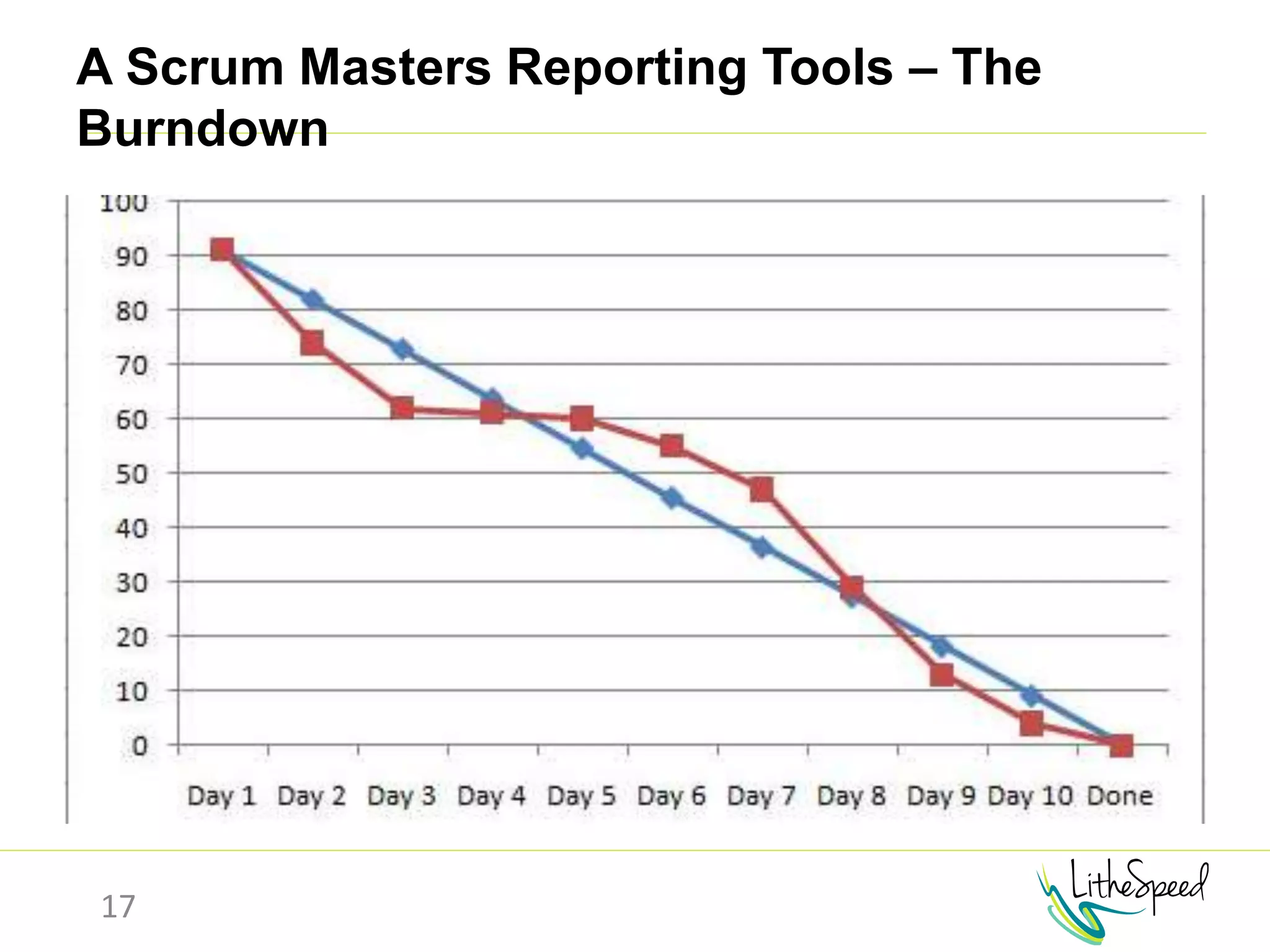
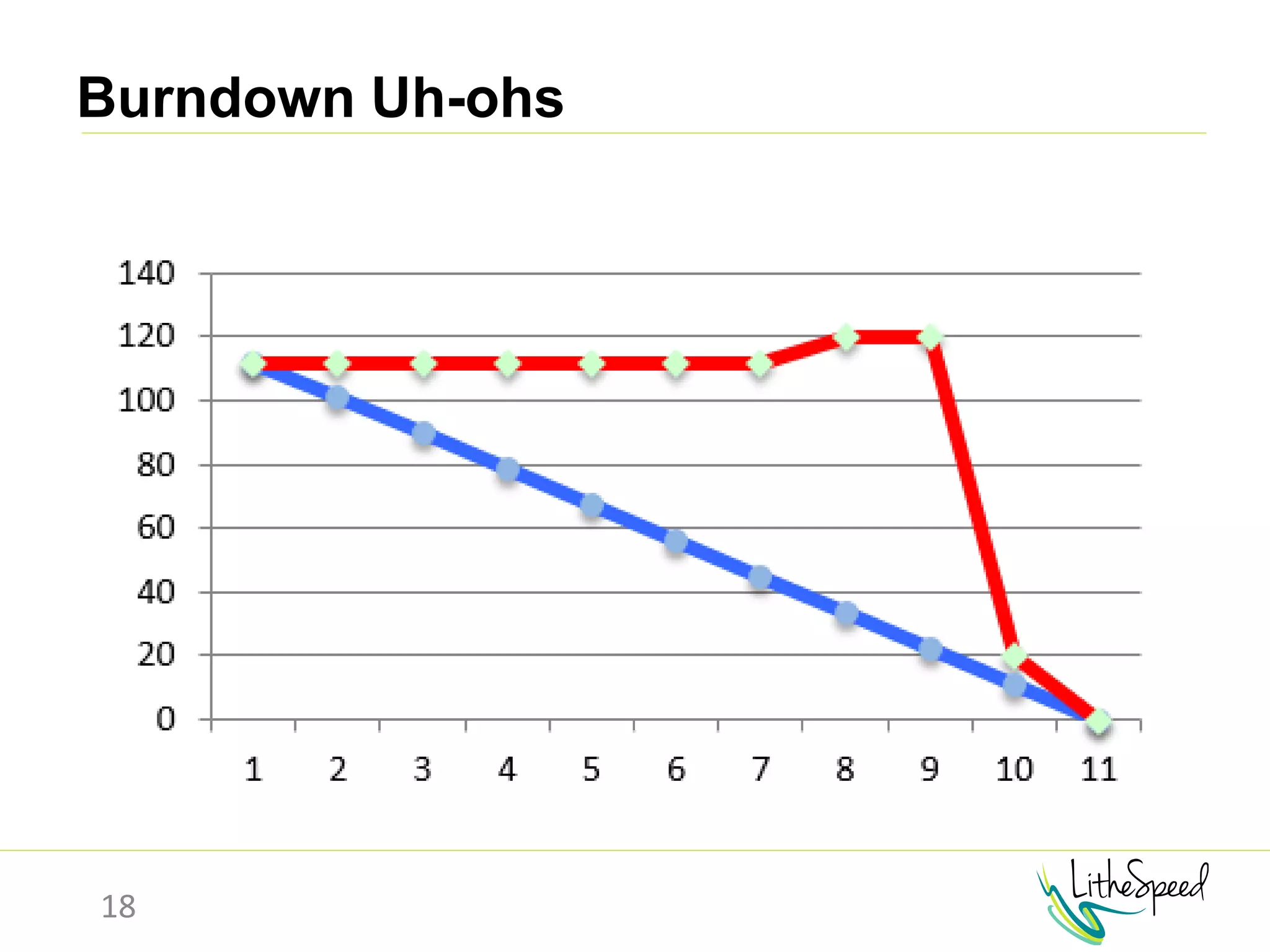
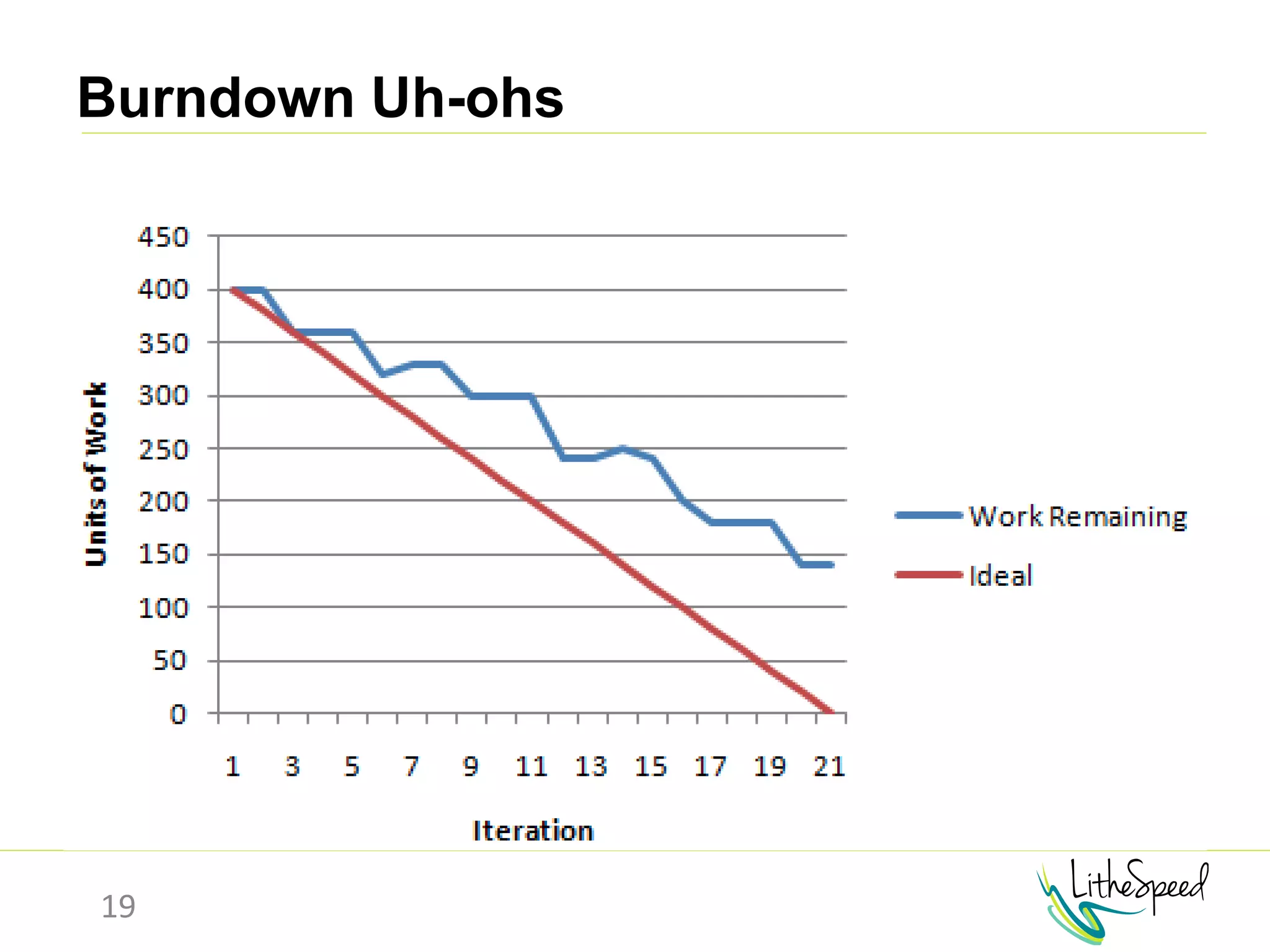
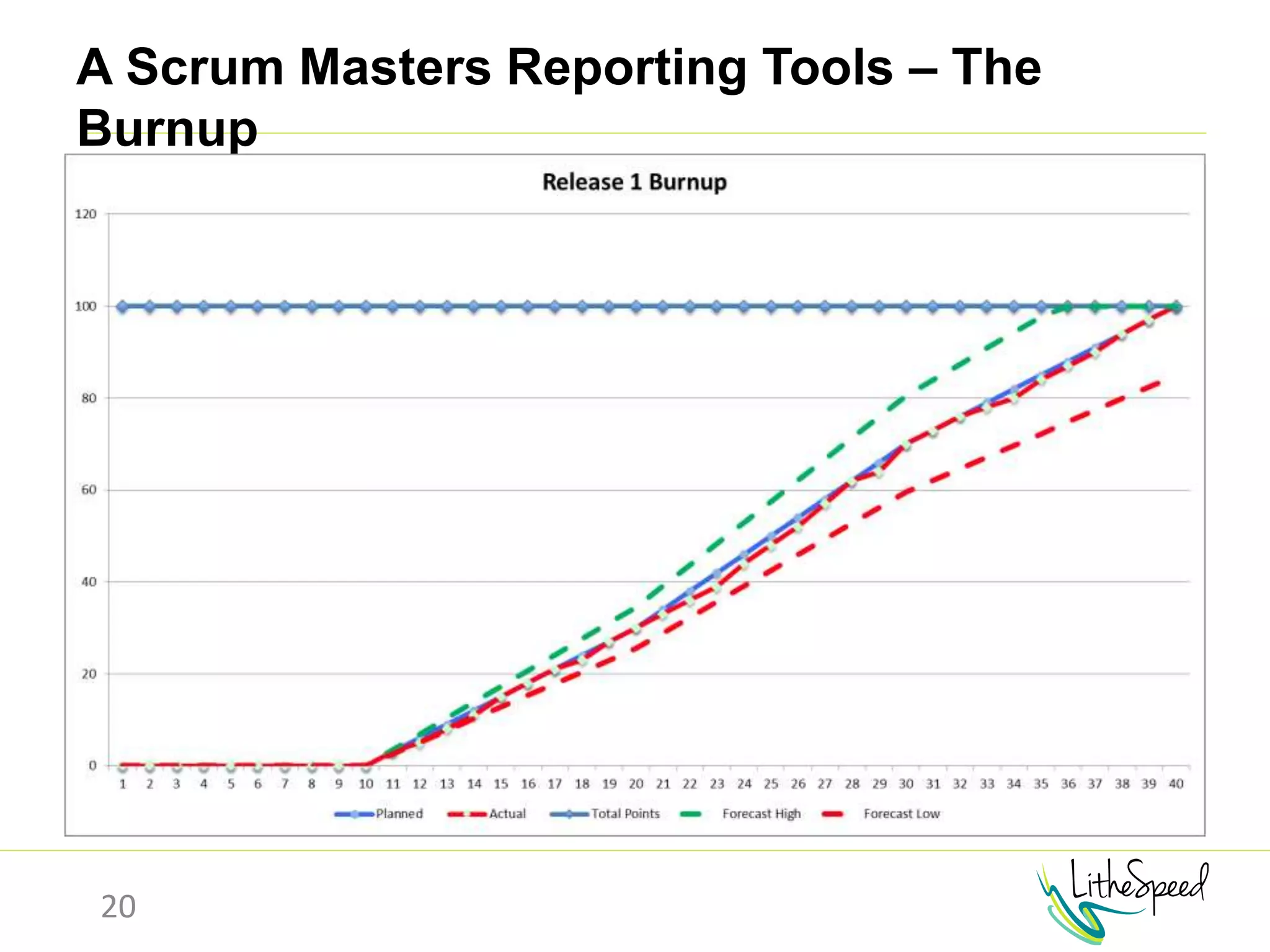
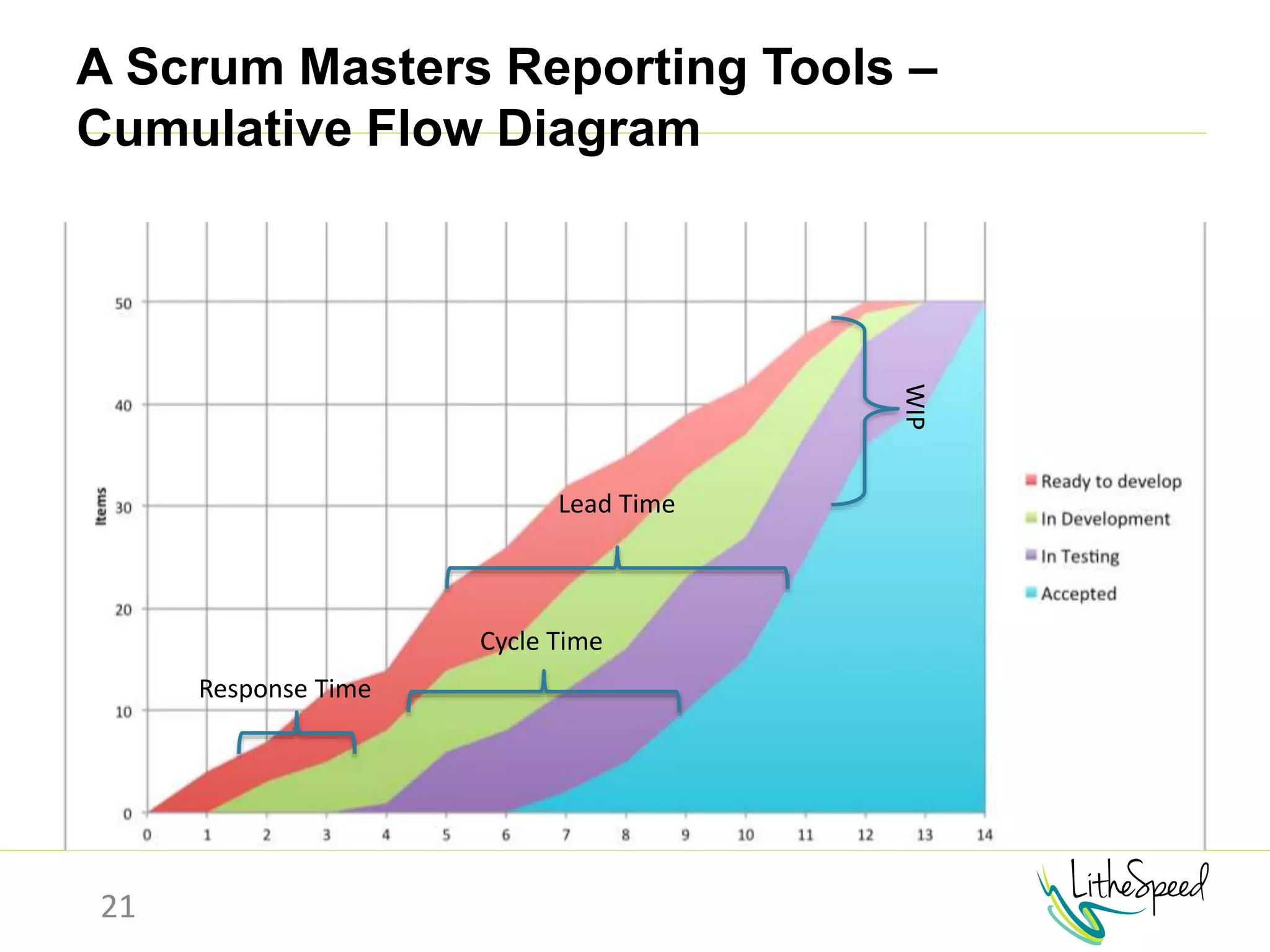
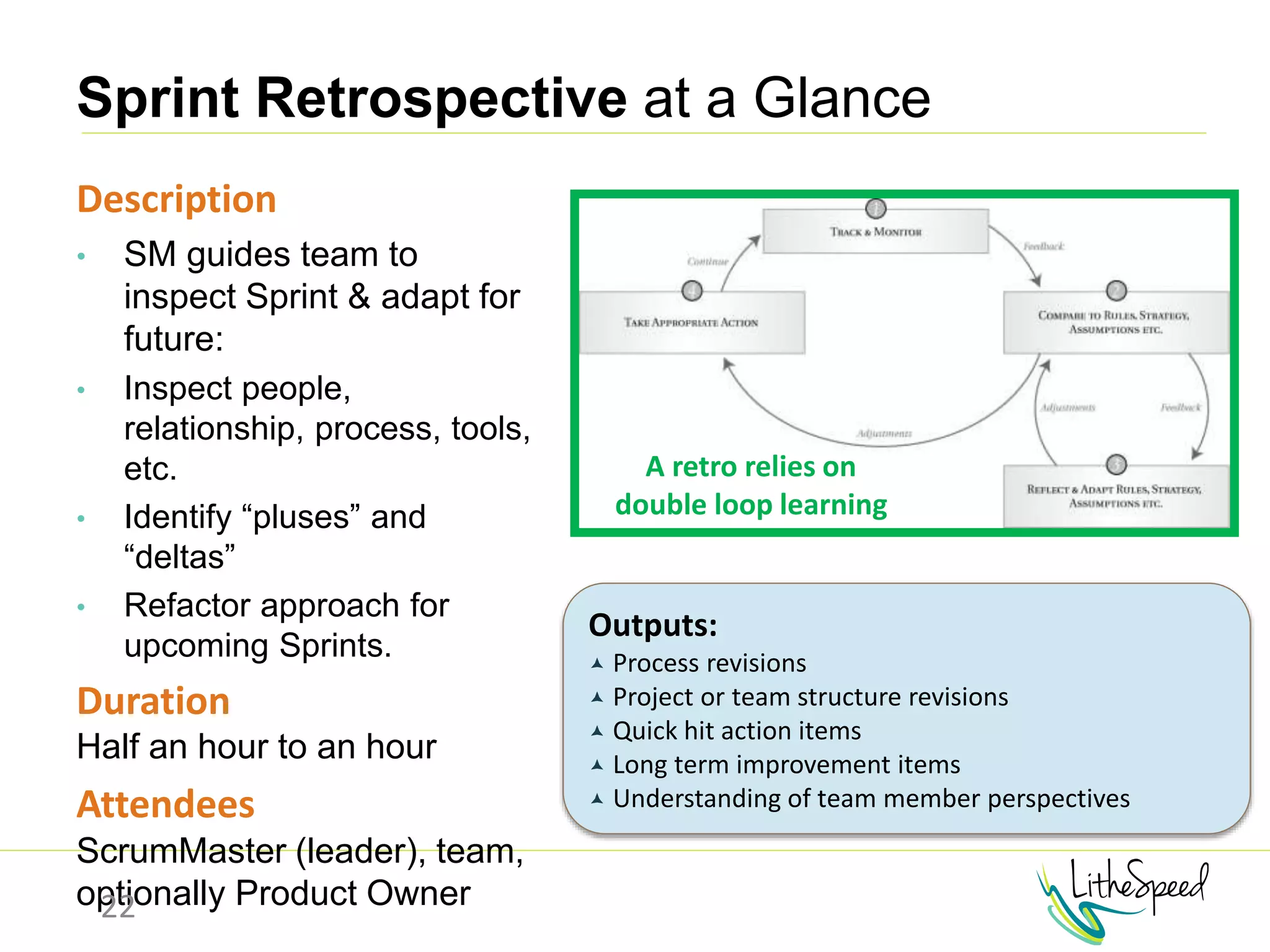
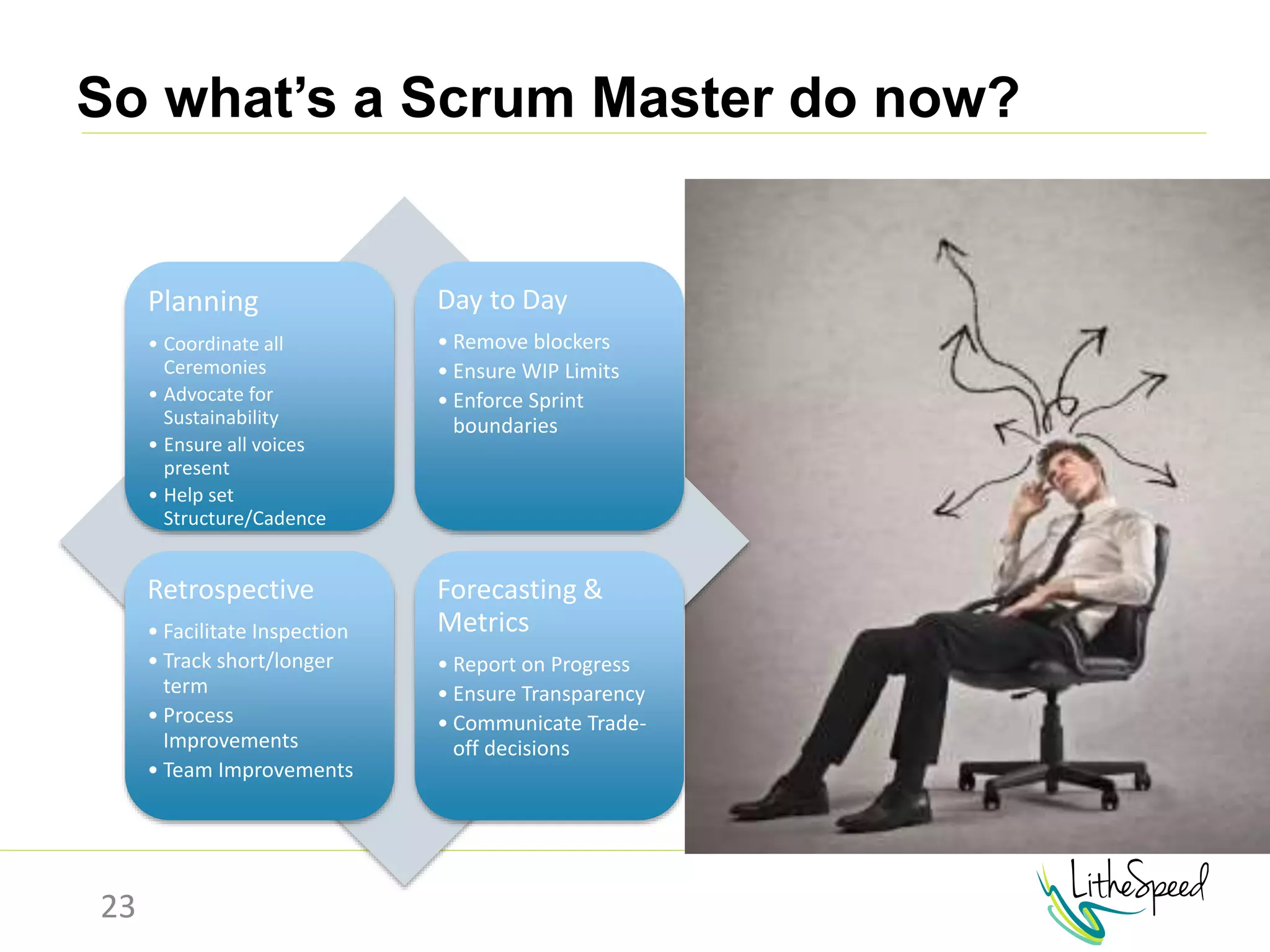
The document provides information to help a project manager transitioning to a ScrumMaster role. It begins with an exercise to define the roles of project manager and ScrumMaster. It then compares their responsibilities, with the project manager focusing on planning and tracking tasks while the ScrumMaster facilitates processes like the daily scrum and removes impediments. The document outlines the Scrum framework and roles of product owner, ScrumMaster and team. It provides examples of how the ScrumMaster helps with planning, daily standups, reporting tools and retrospectives. It concludes with an overview of the ScrumMaster's new responsibilities.