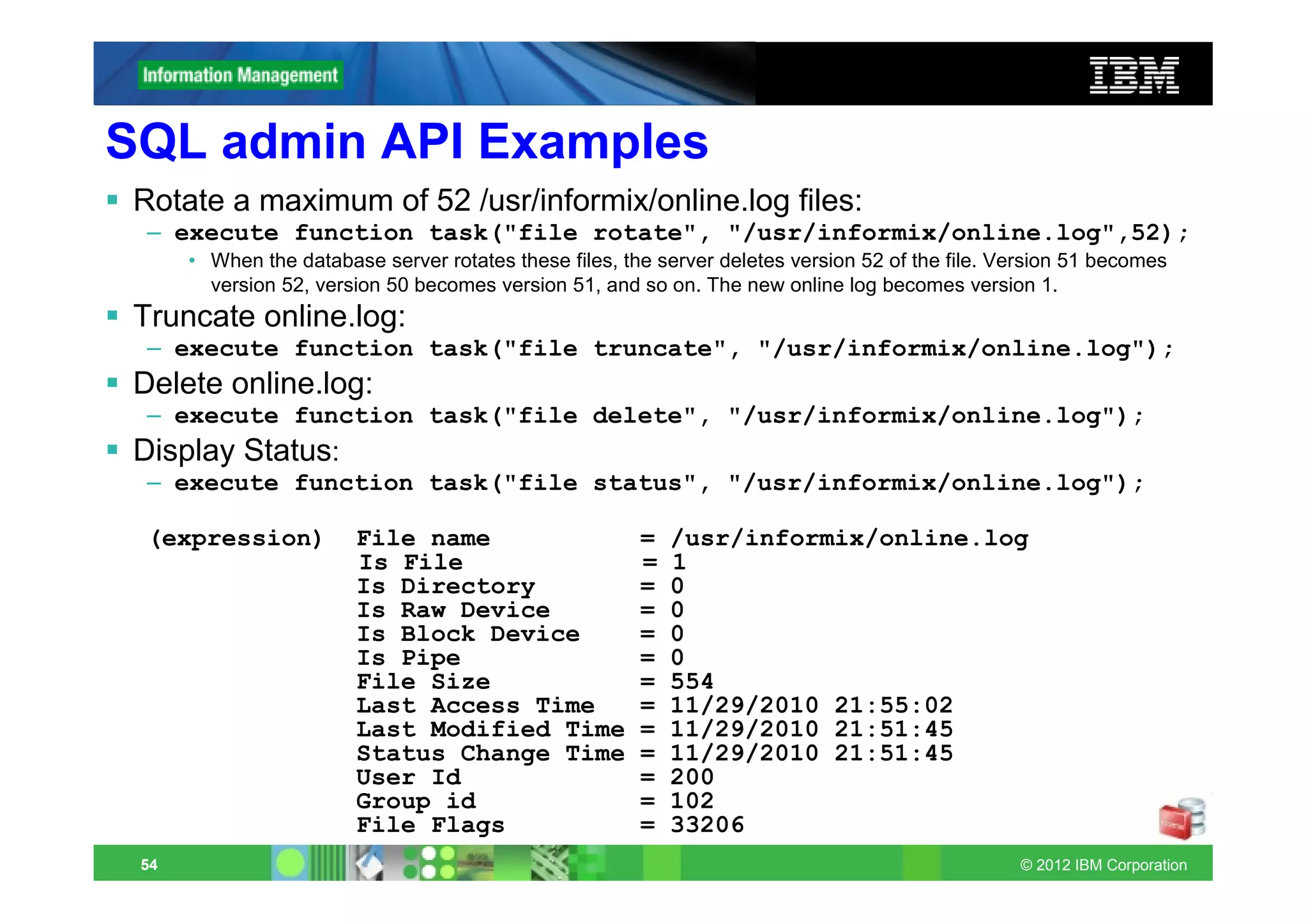
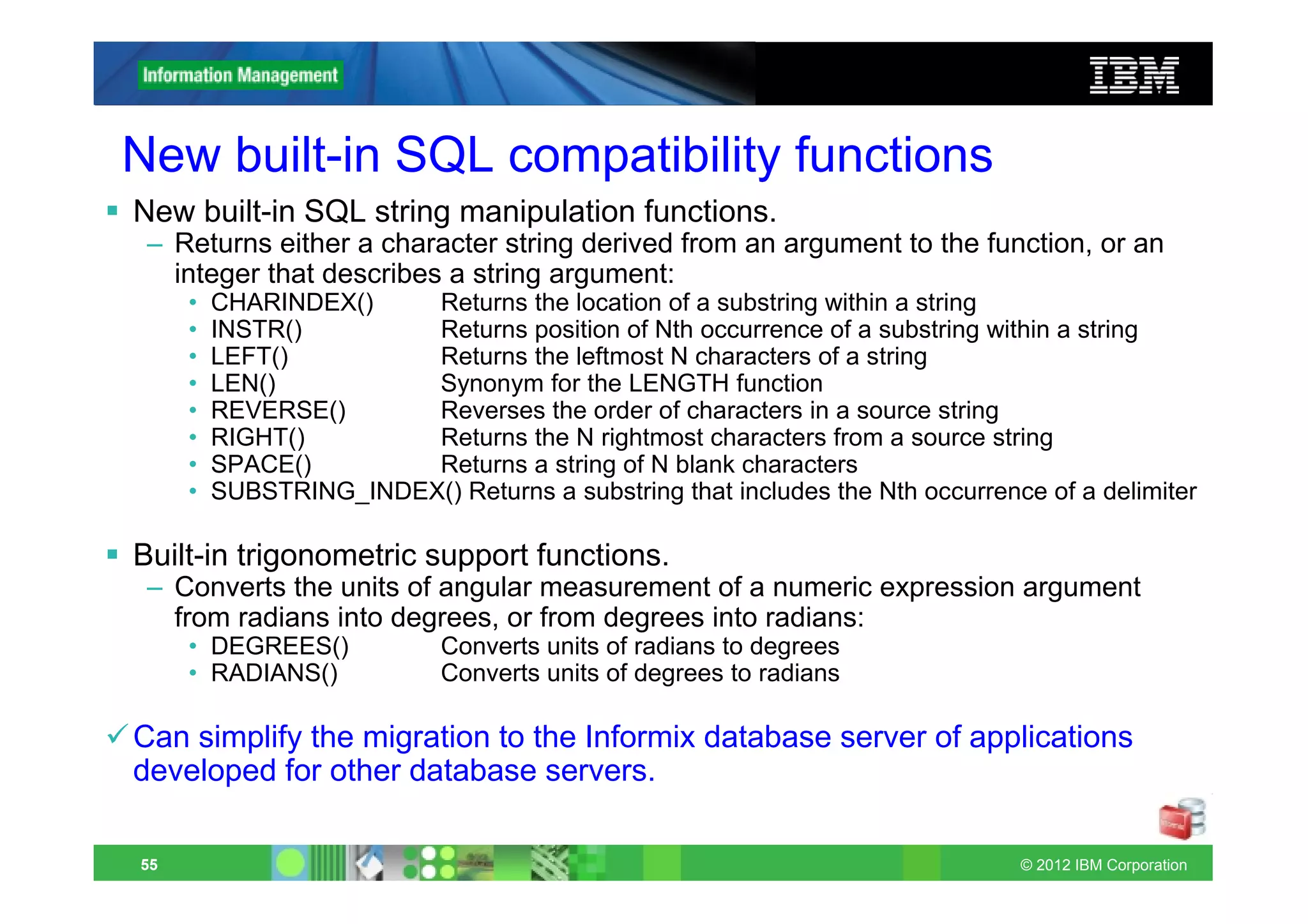
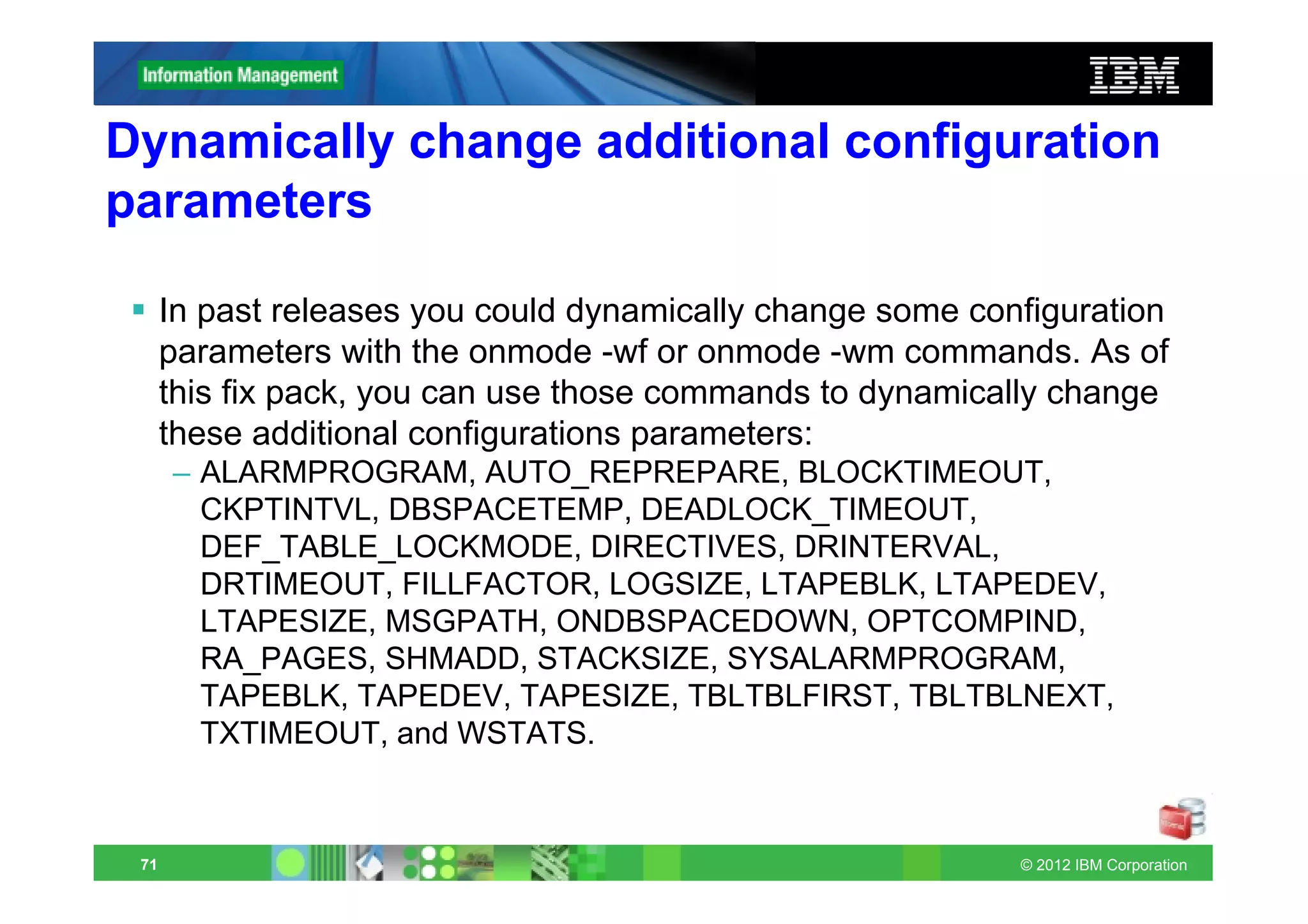
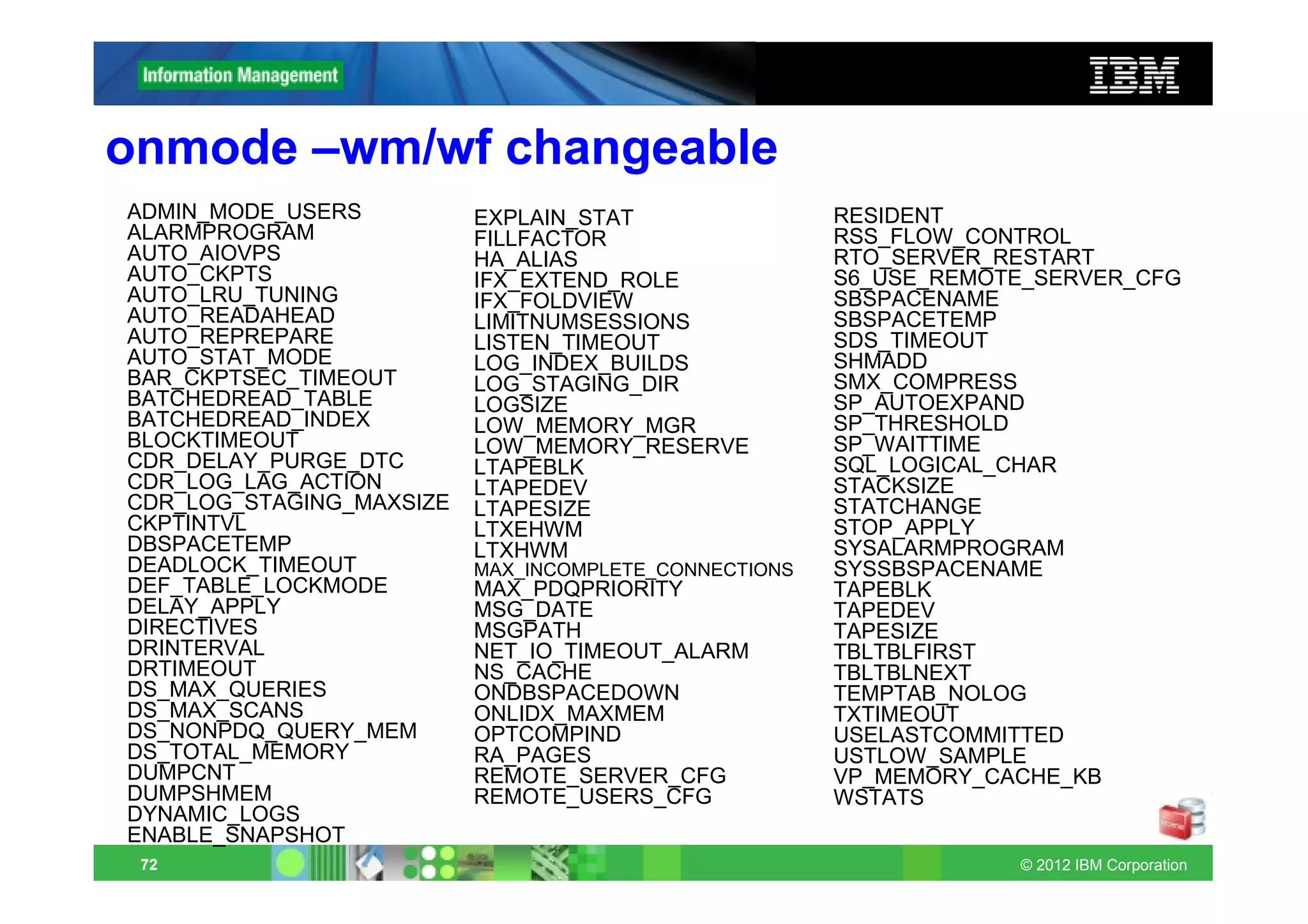
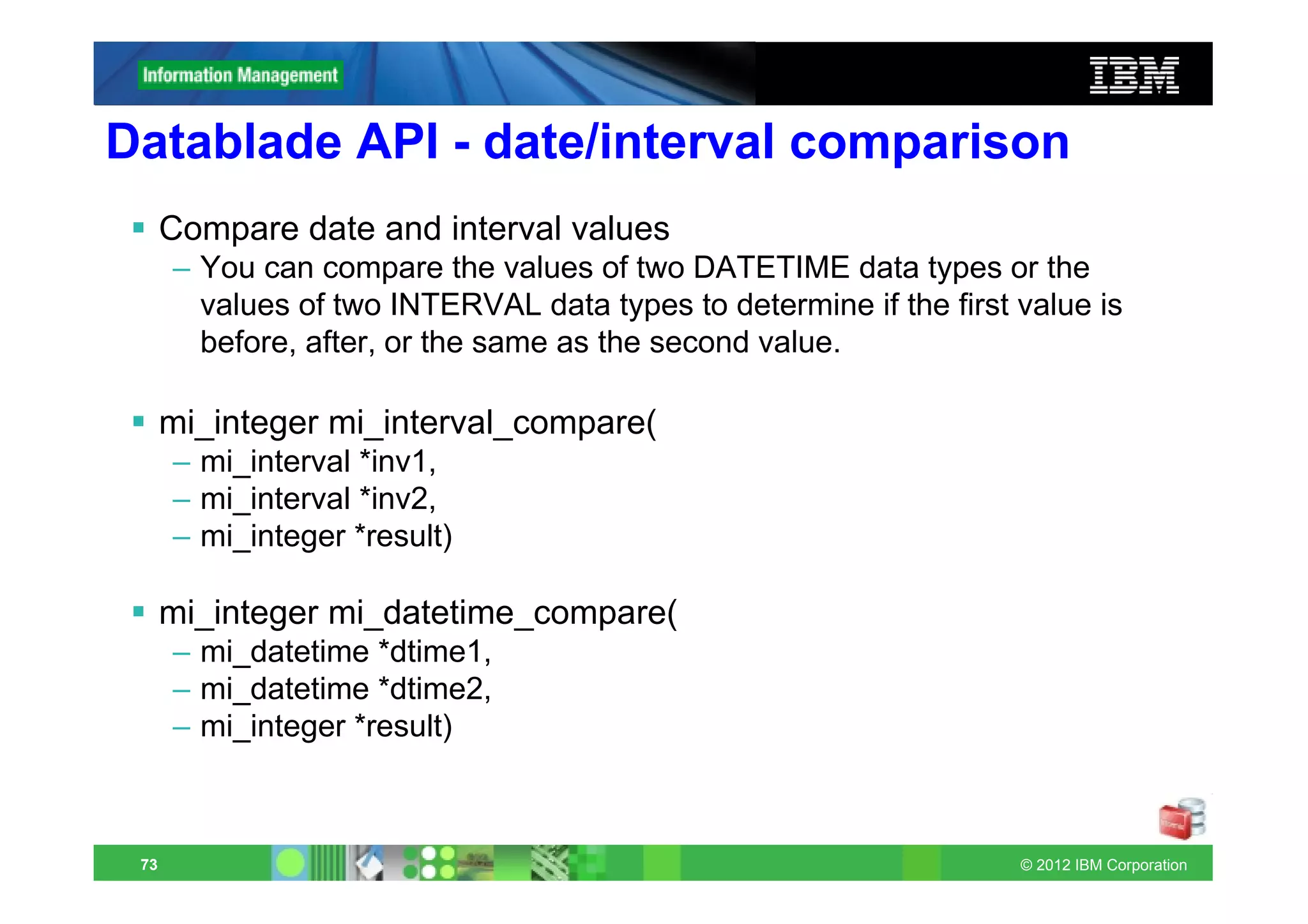
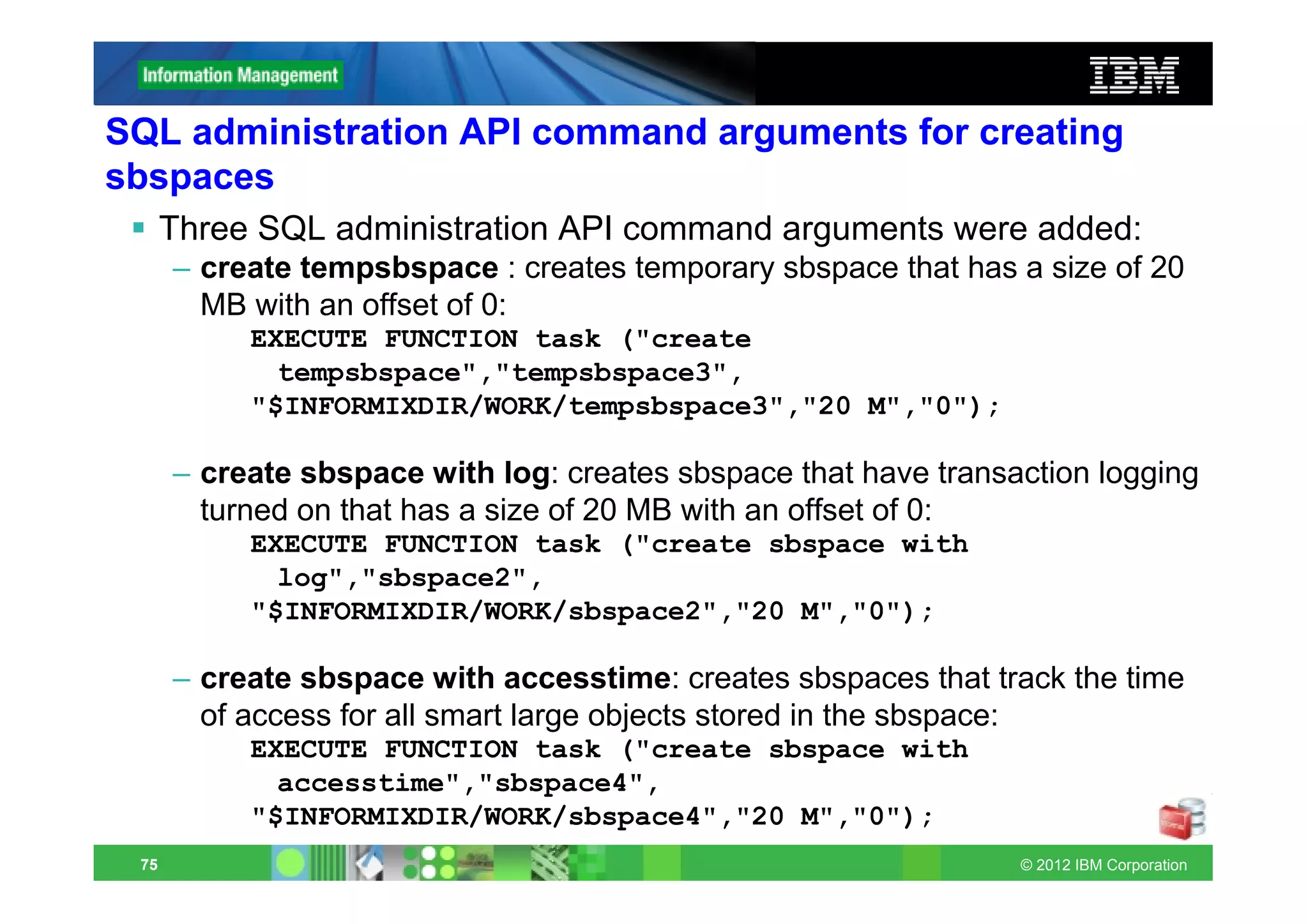
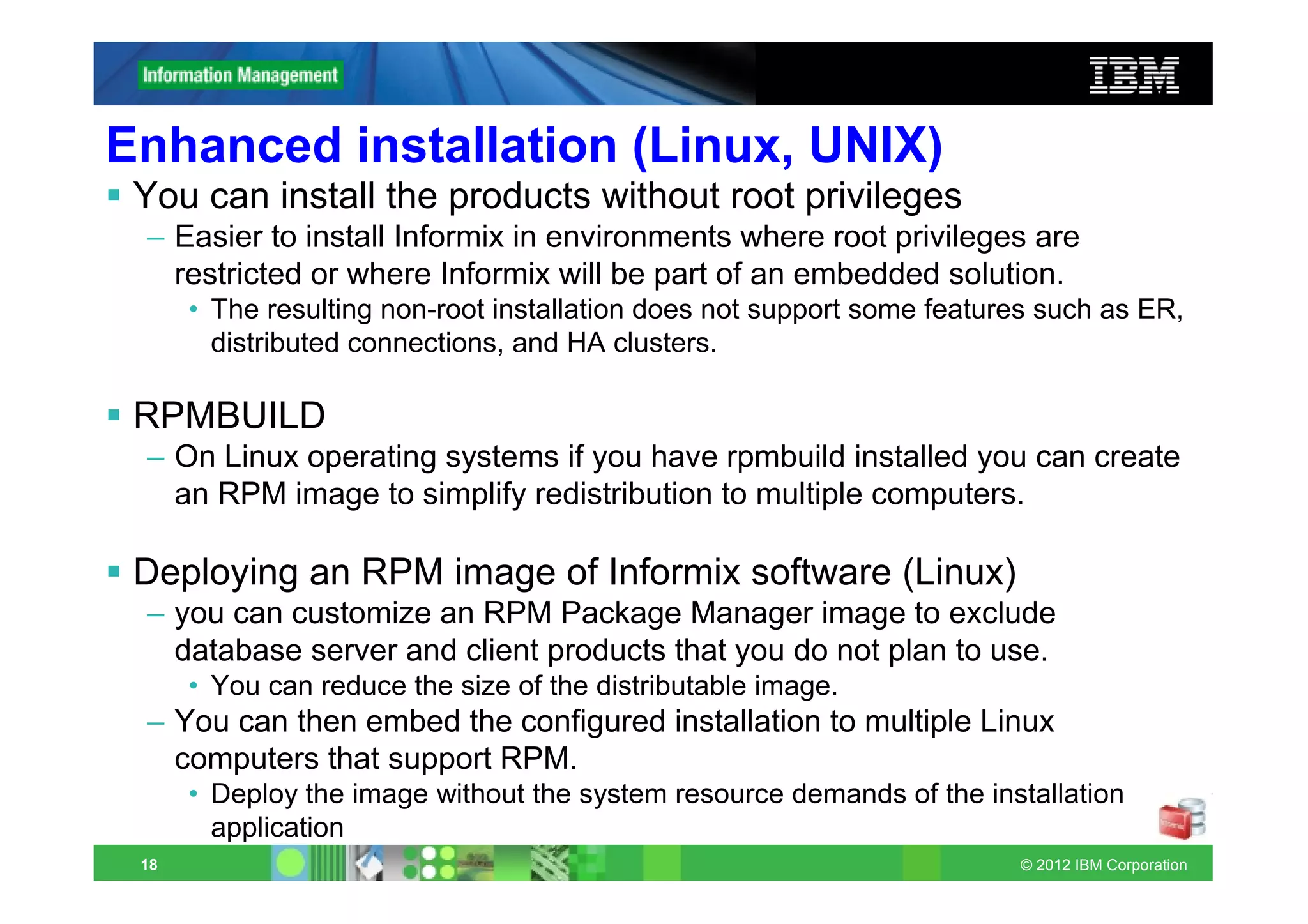
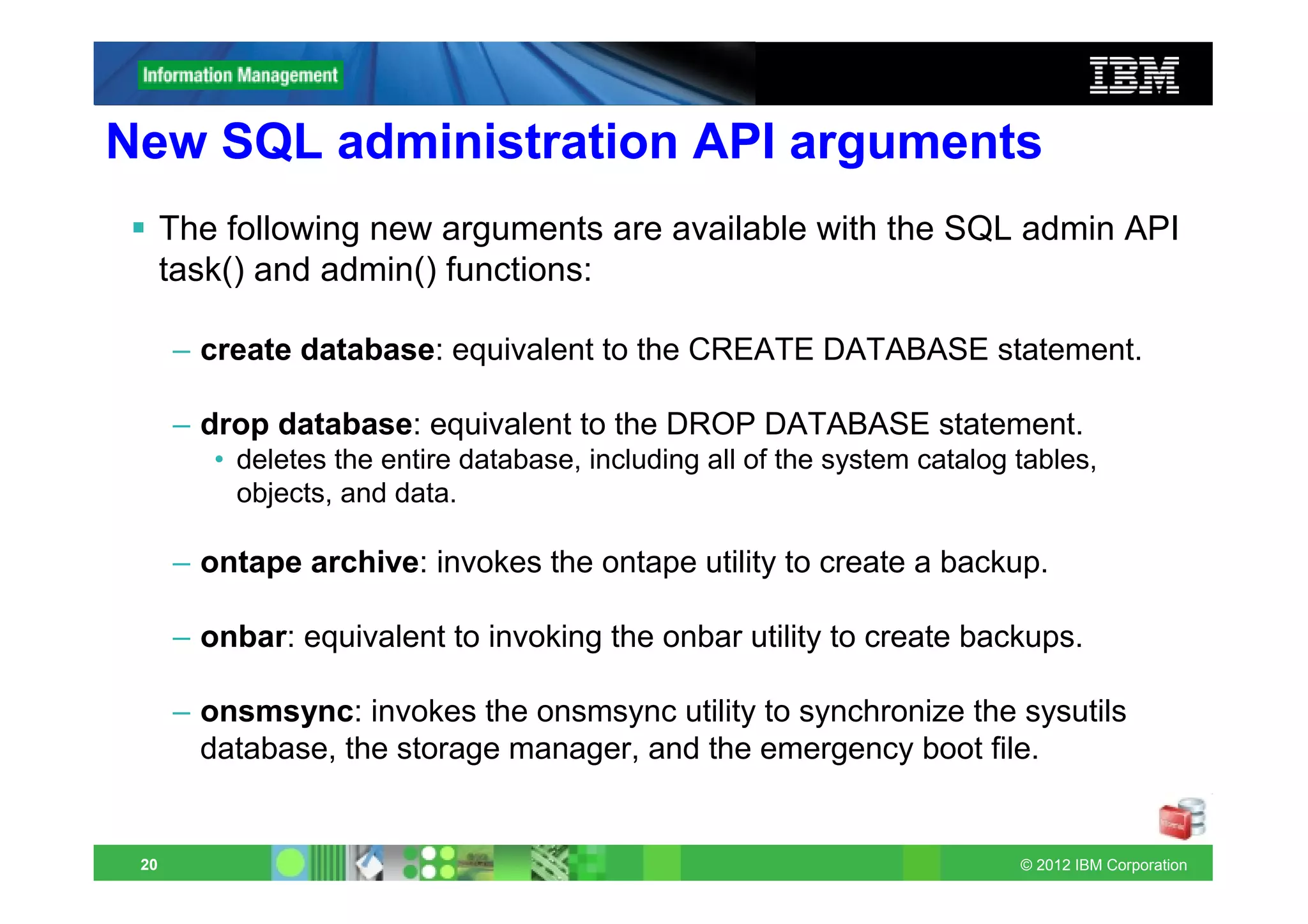
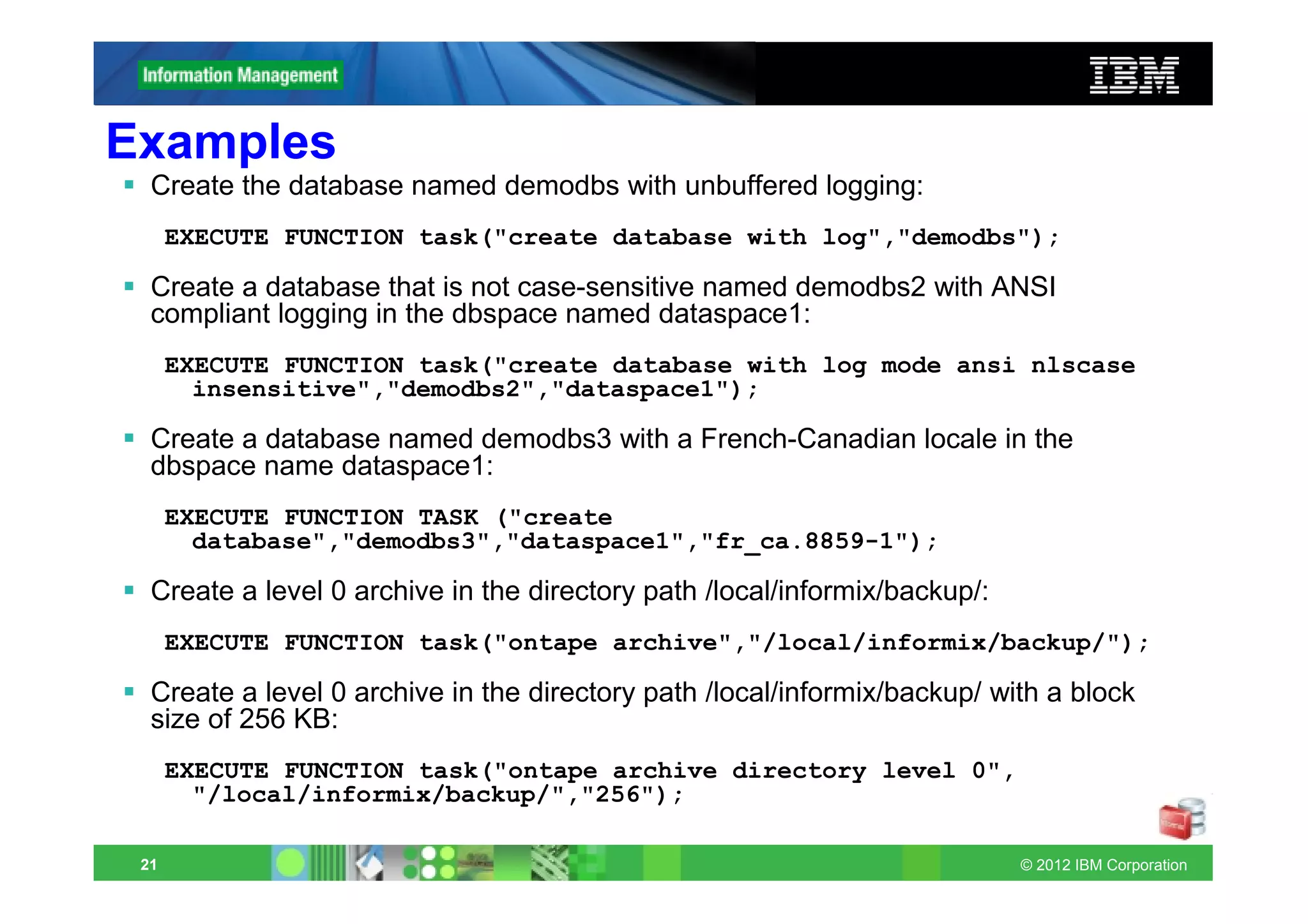
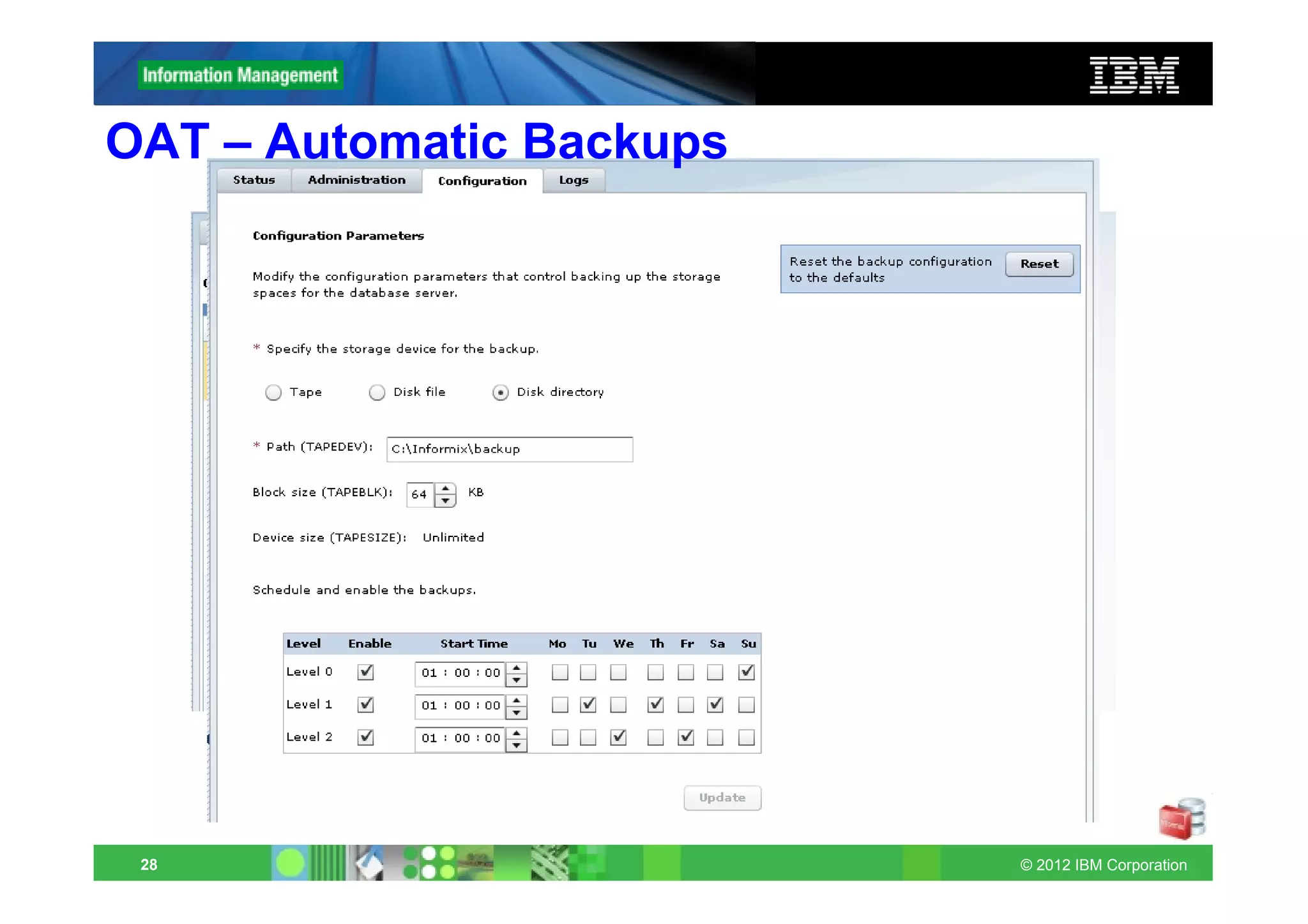
This document provides release notes for Informix Update 11.70.xC1+. It discusses new features for installation, migration, high availability, administration, application development, embeddability, enterprise replication, security and performance in the 11.70.xC1 release. It also briefly mentions new enhancements in the 11.70.xC2 release related to installation, administration, application development and embeddability. The document provides examples of using some of the new SQL administration API arguments and table/column aliases in DML statements.





![11.70.xC1 Features - 3
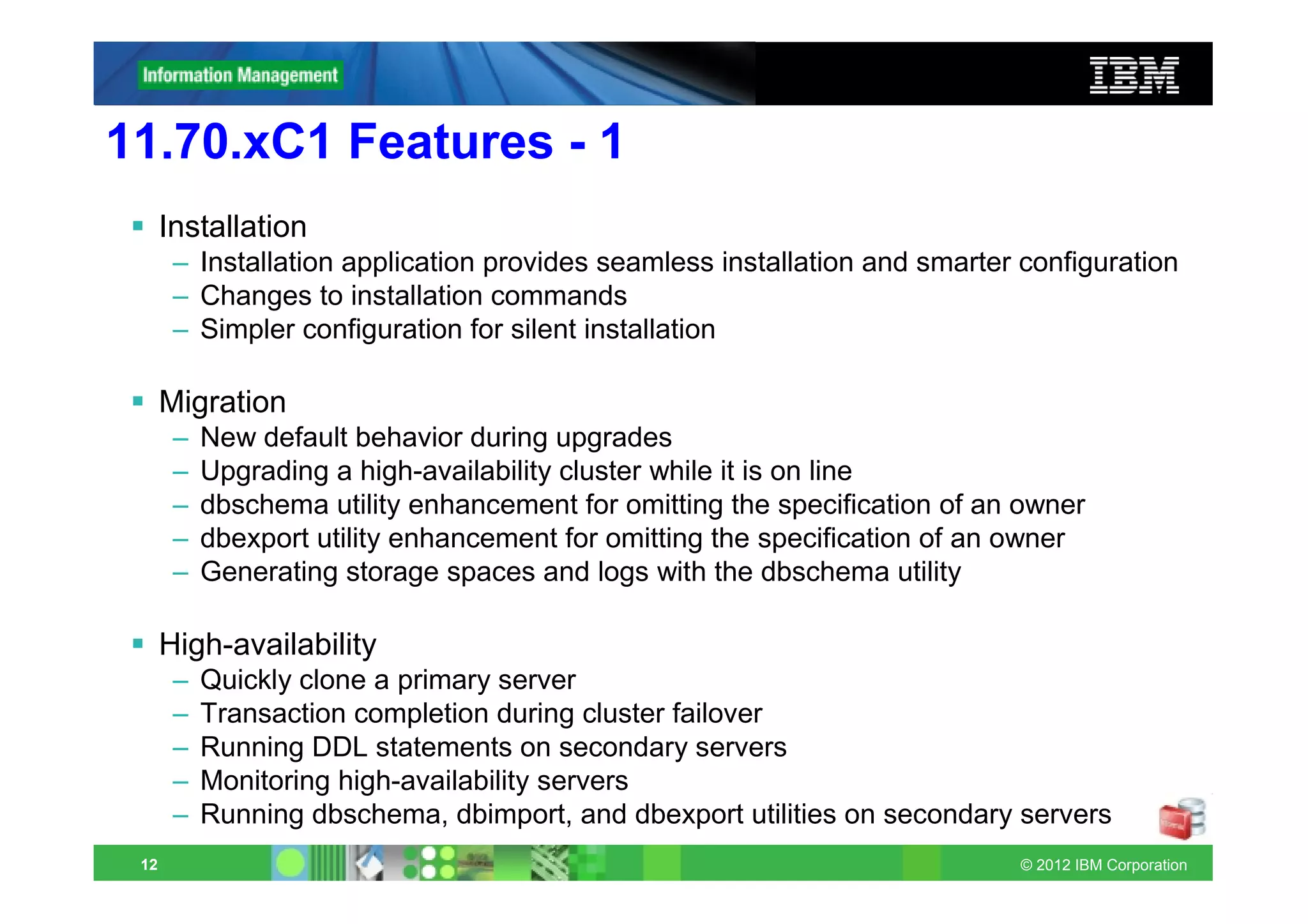
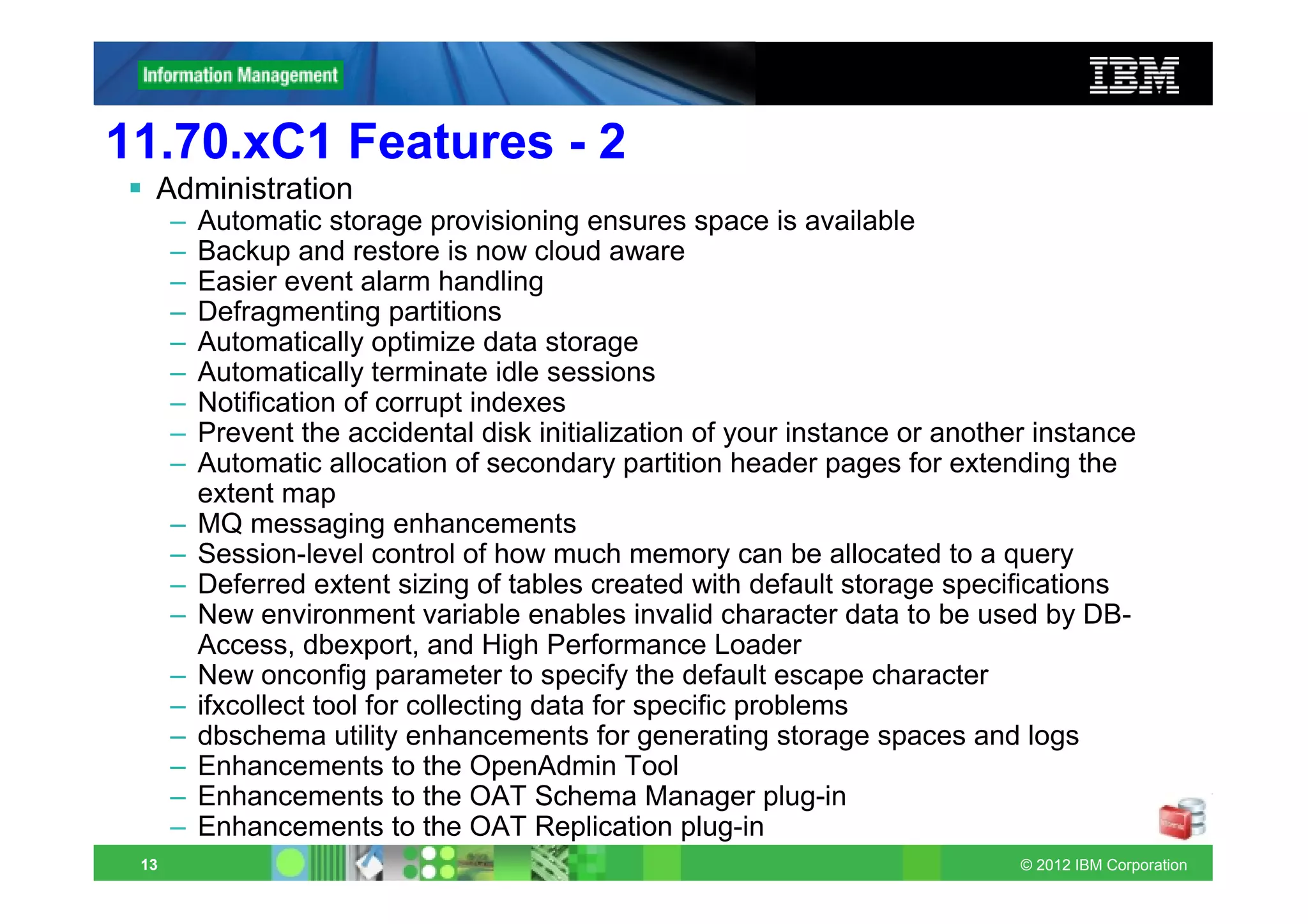
Application Development
– Database extensions are automatically registered
– Spatial data type and functions are built in and automatically registered
– Time series data types and functions are built-in and automatically registered
– Setting the file seek position for large files
– Faster basic text searches on multiple columns
– Virtual processor is created automatically for XML publishing
– SQL expressions as arguments to the COUNT function
– Specifying the extent size when user-defined indexes are created
– Syntax support for DDL statements with IF [NOT] EXISTS conditions
– Simplified SQL syntax for defining database tables
– Debugging Informix SPL routines with Optim Development Studio
Embeddability
– Information about embedding Informix instances
– Enhanced utility for deploying Informix instances
– Tutorial to deploy and embed Informix
– Deployment assistant simplifies snapshot capture and configuration
– Enhanced ability to compress and to extract compressed snapshots
– Improved return codes for the oninit utility
– Sample scripts for embedding IBM Informix 11.70 database servers
14 © 2012 IBM Corporation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informixupdate-new11-70features-120604065119-phpapp02/75/Informix-Update-New-Features-11-70-xC1-10-2048.jpg)

![BTS Analyzers
Analyzers:
– cjk: Processes Chinese, Japanese, and Korean text. Ignores surrogates.
– cjk.ws: Processes Chinese, Japanese, and Korean text. Processes surrogates.
– esoundex: Processes text into pronunciation codes.
– keyword: Processes input text as a single token.
– simple: Processes alphabetic characters only without stopwords.
– snowball: Processes text into stem words.
– snowball.language: Processes text into stem words in the specified language.
– soundex: Processes text into four pronunciation codes.
– standard: Default. Processes alphabetic characters, special characters, and
numbers with stopwords.
– stopword: Processes alphabetic characters only with stopwords.
– udr.udr_name: The name of a user-defined analyzer.
– whitespace: Creates tokens based on whitespace only
– or create your own analyzer
The Snowball analyzer is similar to the Standard analyzer except that is
converts words to stem words: different words are indexed with the same
stem word:
– accept [accept]
– acceptable [accept]
– acceptance [accept]
23 © 2012 IBM Corporation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informixupdate-new11-70features-120604065119-phpapp02/75/Informix-Update-New-Features-11-70-xC1-19-2048.jpg)


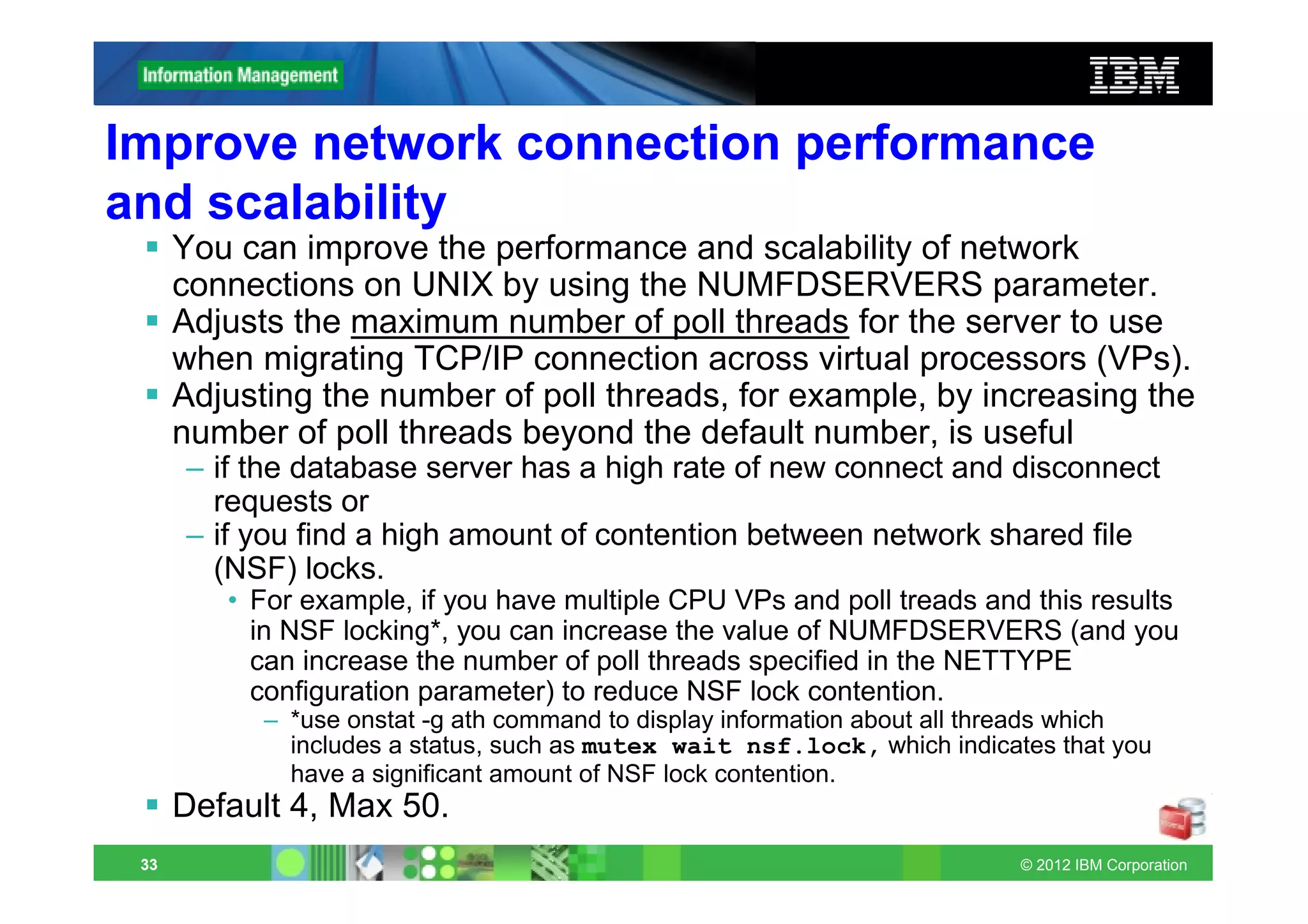

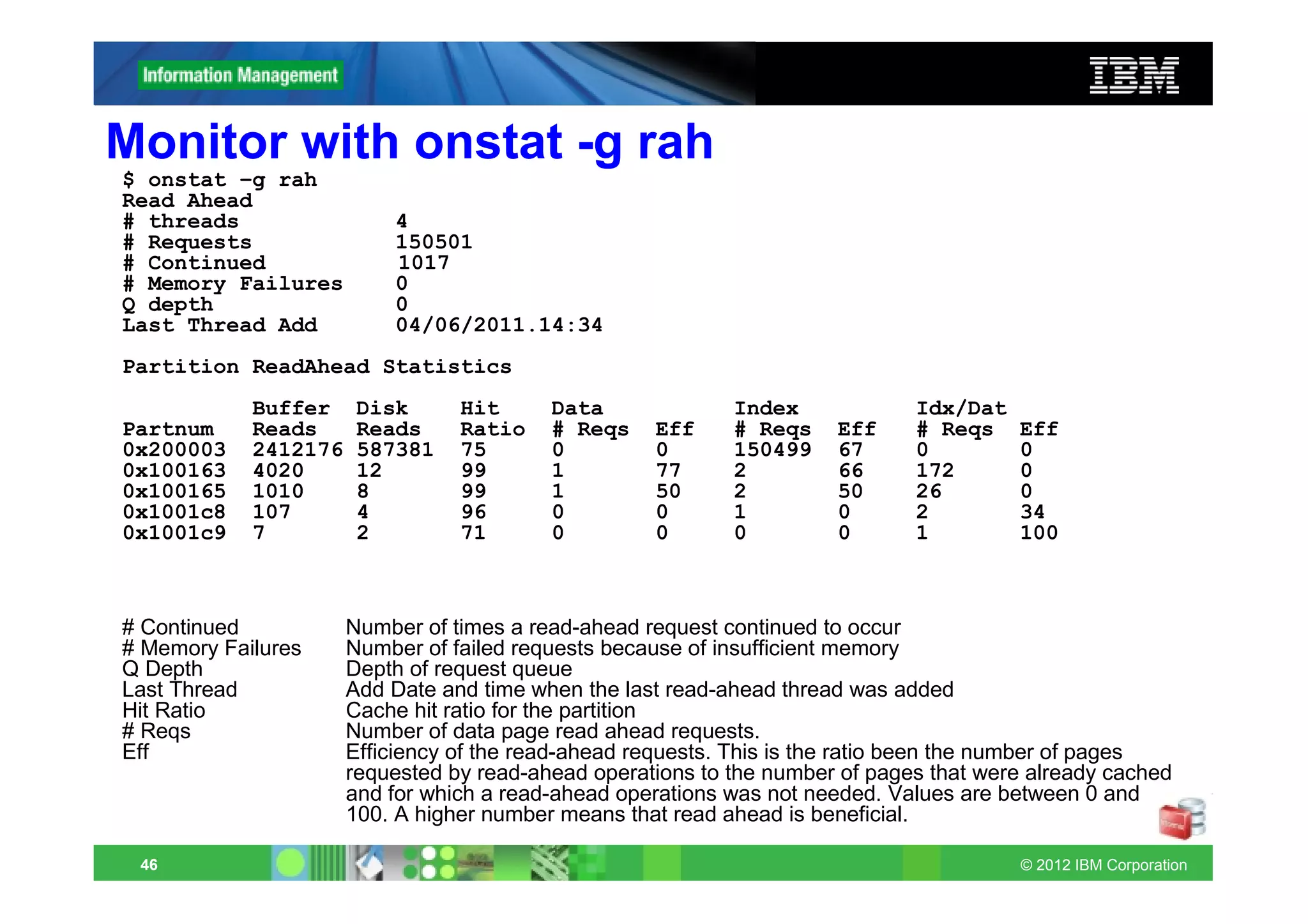
![Automatic read-ahead operations
Asynchronous page requests can improve query performance by
overlapping query processing with the processing necessary to
retrieve data from disk and put it in the buffer pool.
Avoids read-ahead if data cached in bufferpool
Set up and administration of automatic read-ahead
– ONCONFIG: AUTO_READAHEAD mode[,readahead_cnt]
– Environment: SET ENVIRONMENT AUTO_READAHEAD mode
– onmode –wm/fm AUTOREADAHEAD=mode
Value/Mode Comments
2 Enable automatic requests aggressive mode
1 Default: Enable requests in standard mode
0 Disable automatic read-ahead requests
readahead_cnt Optional: Read ahead pages
AUTO_READAHEAD deprecates ONCONFIG parameters RA_PAGES
and RA_THRESHOLD!
44 © 2012 IBM Corporation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informixupdate-new11-70features-120604065119-phpapp02/75/Informix-Update-New-Features-11-70-xC1-40-2048.jpg)