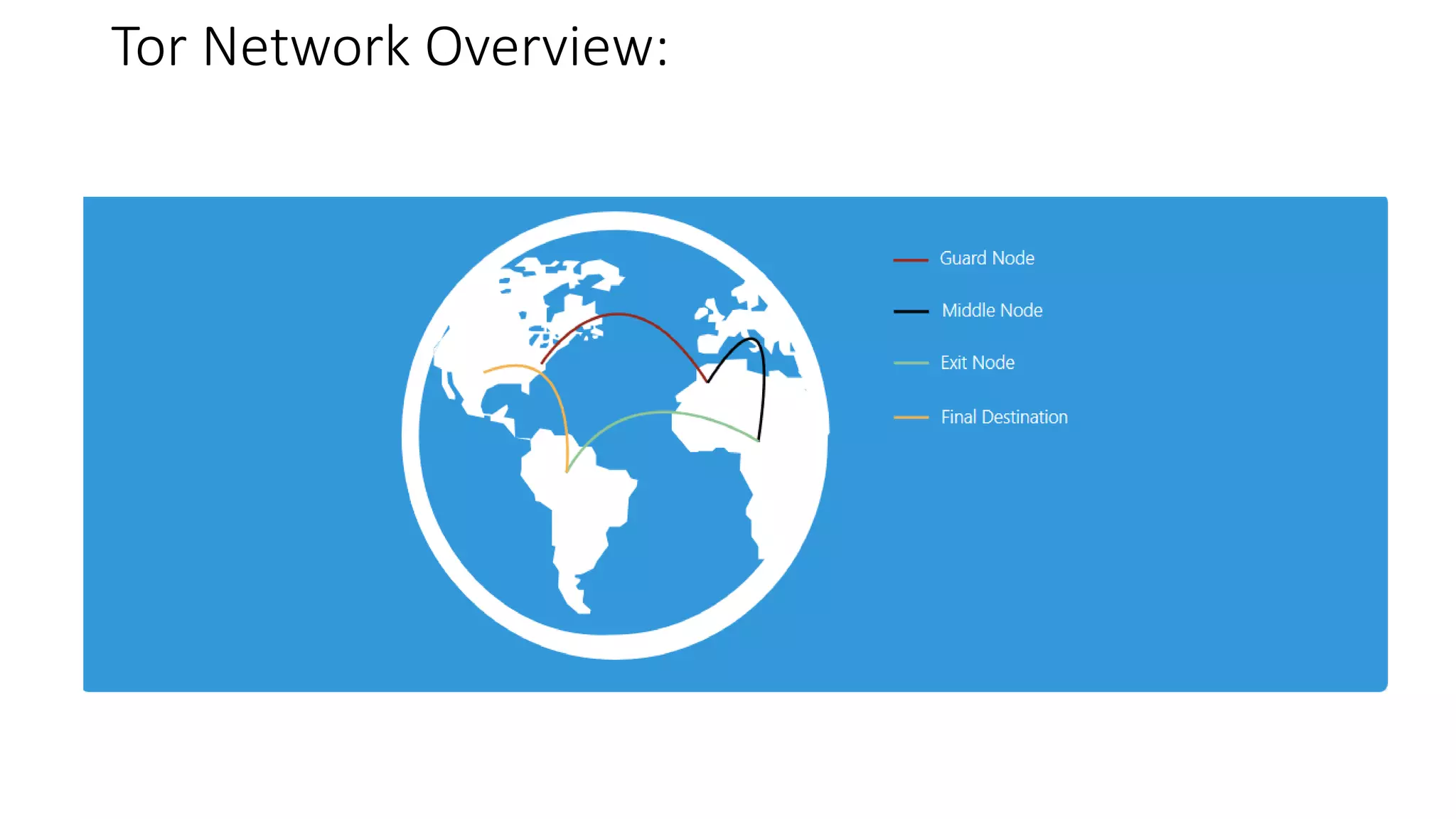
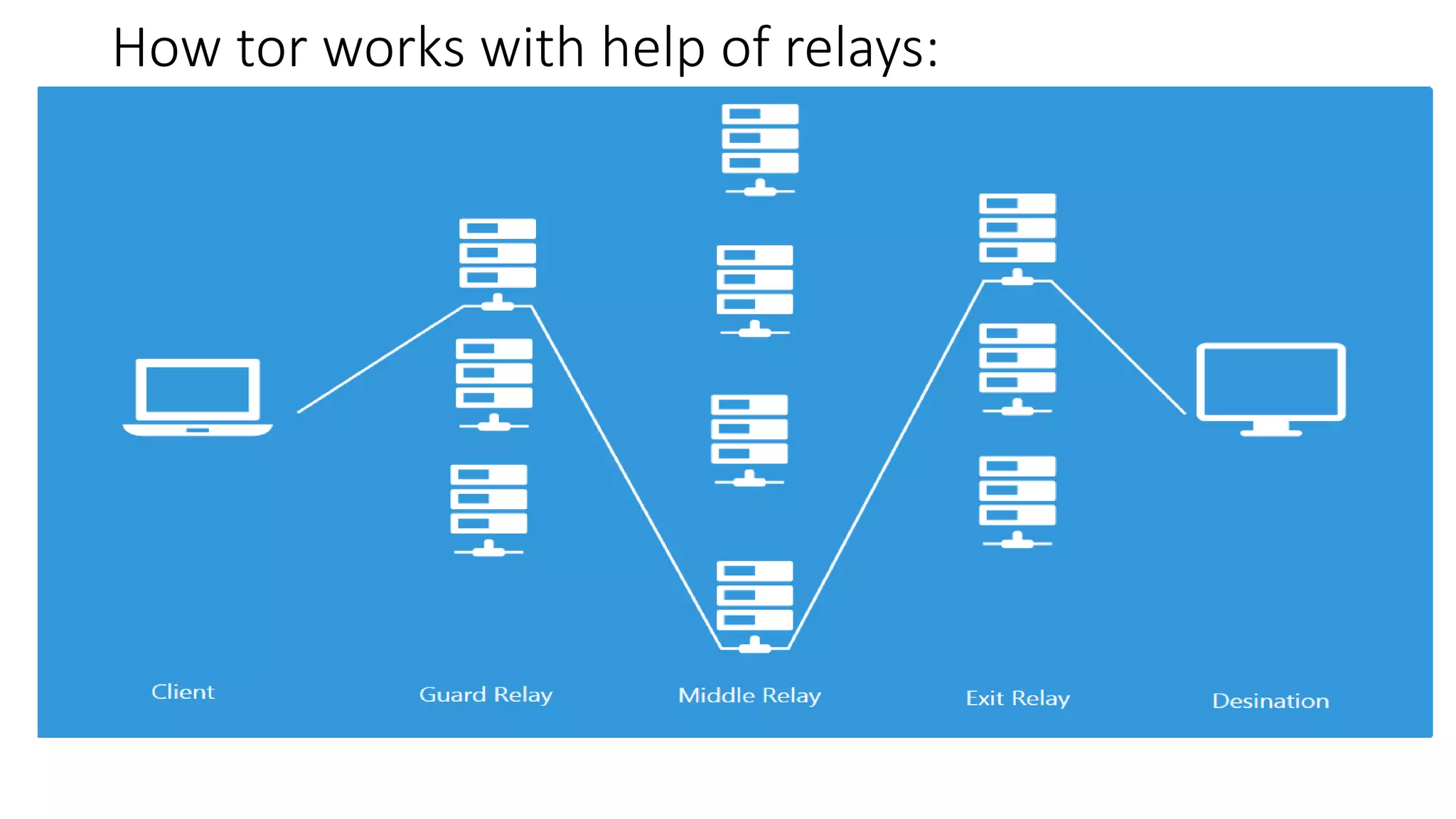
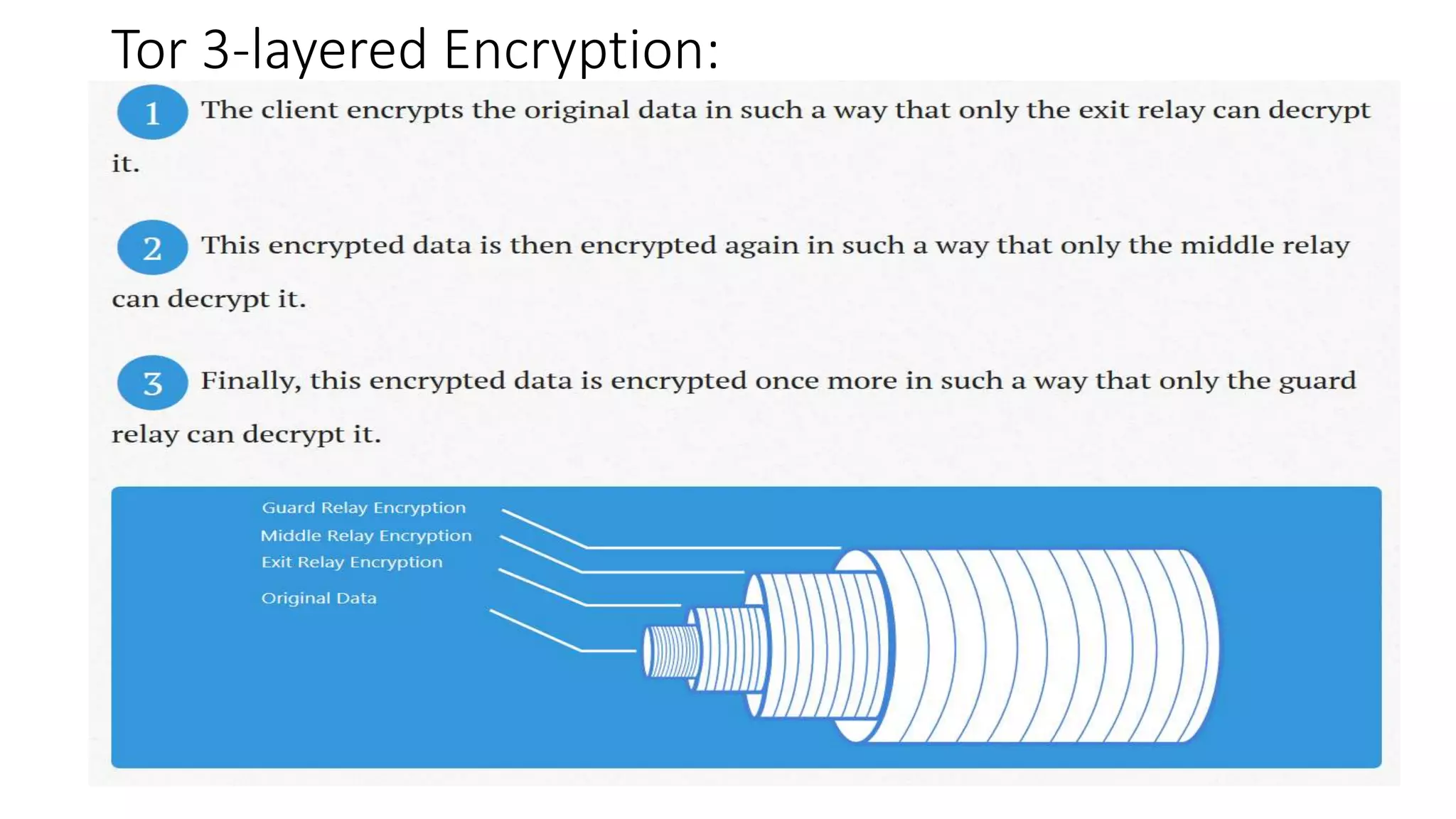
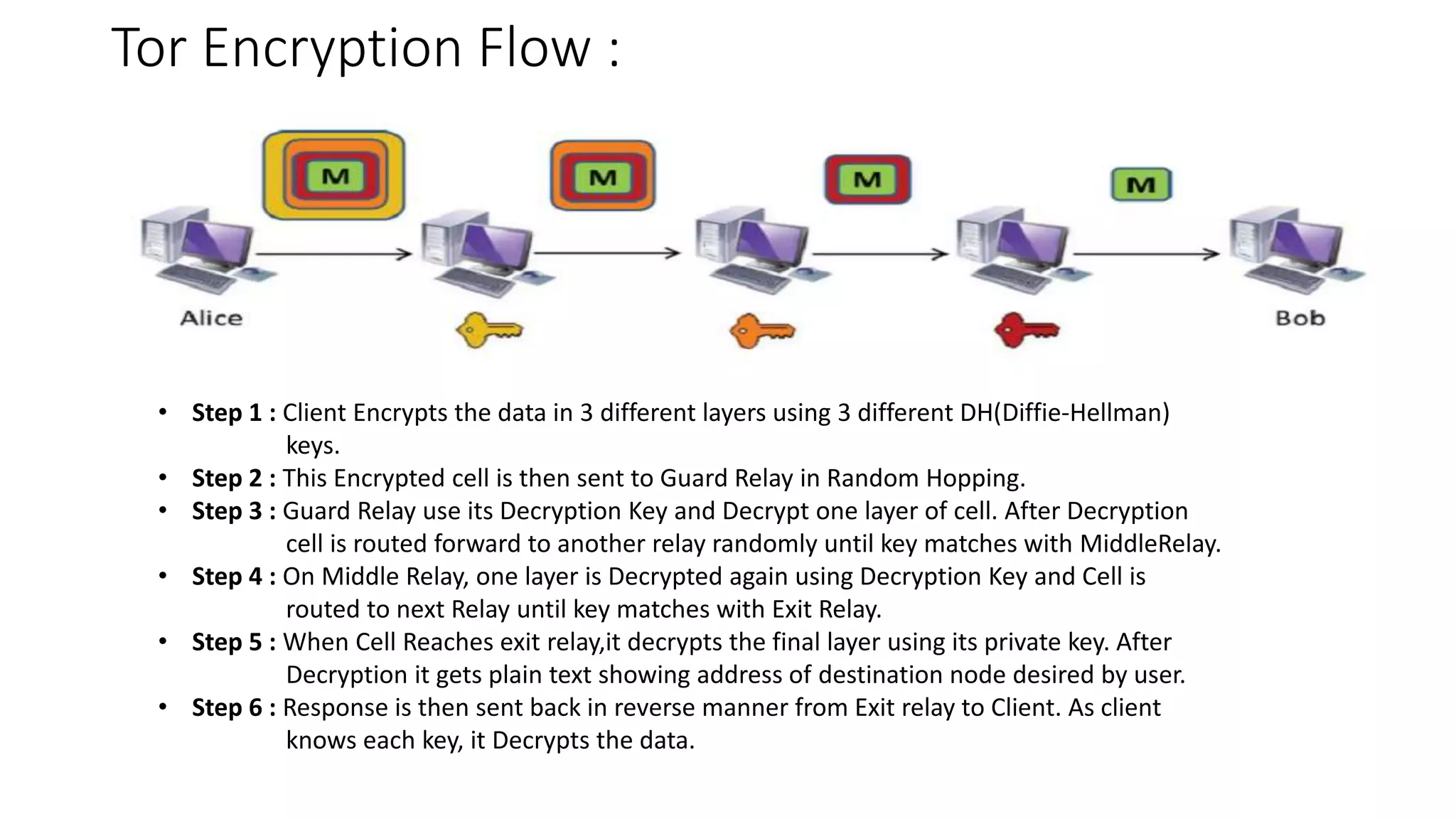
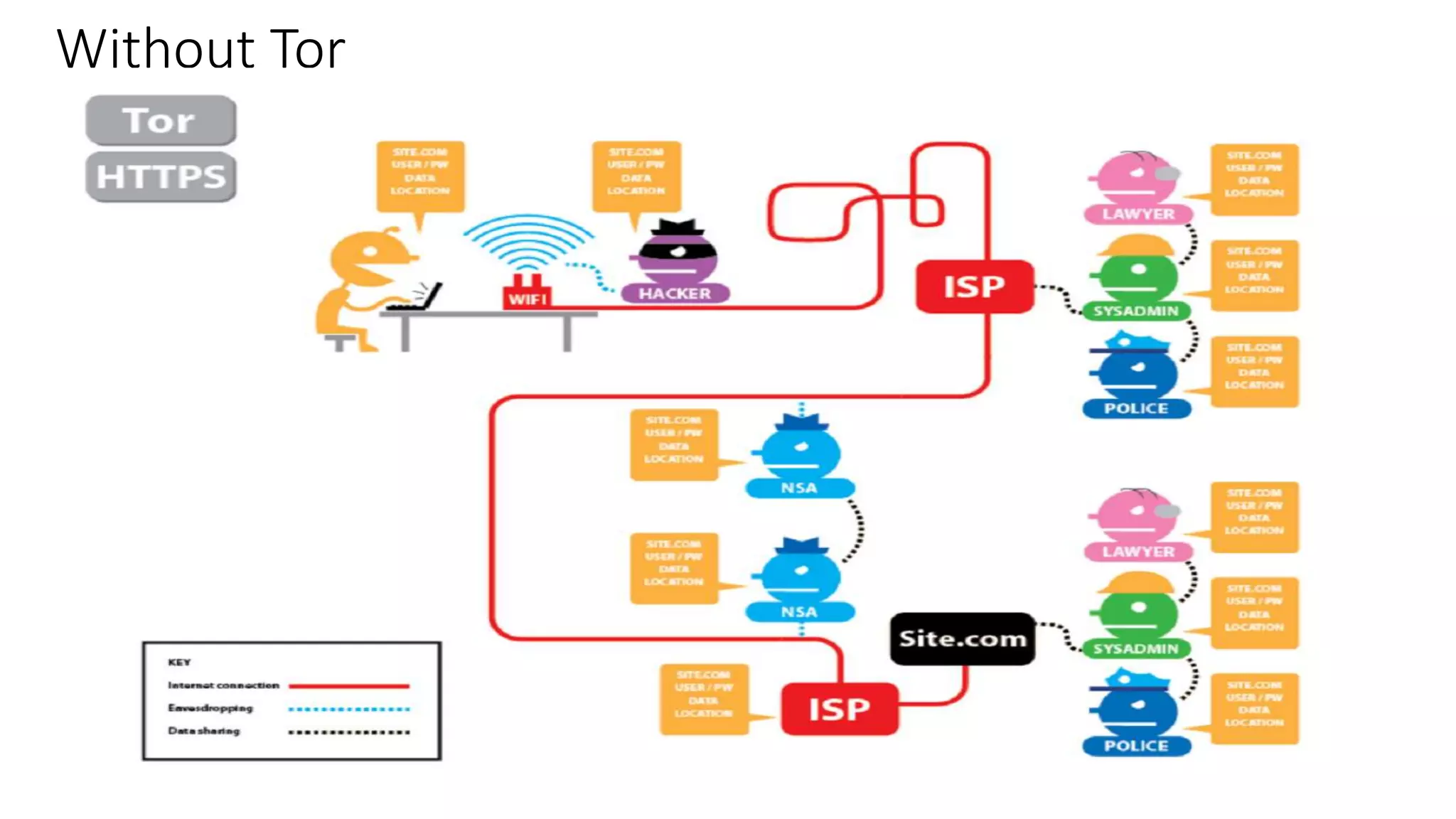
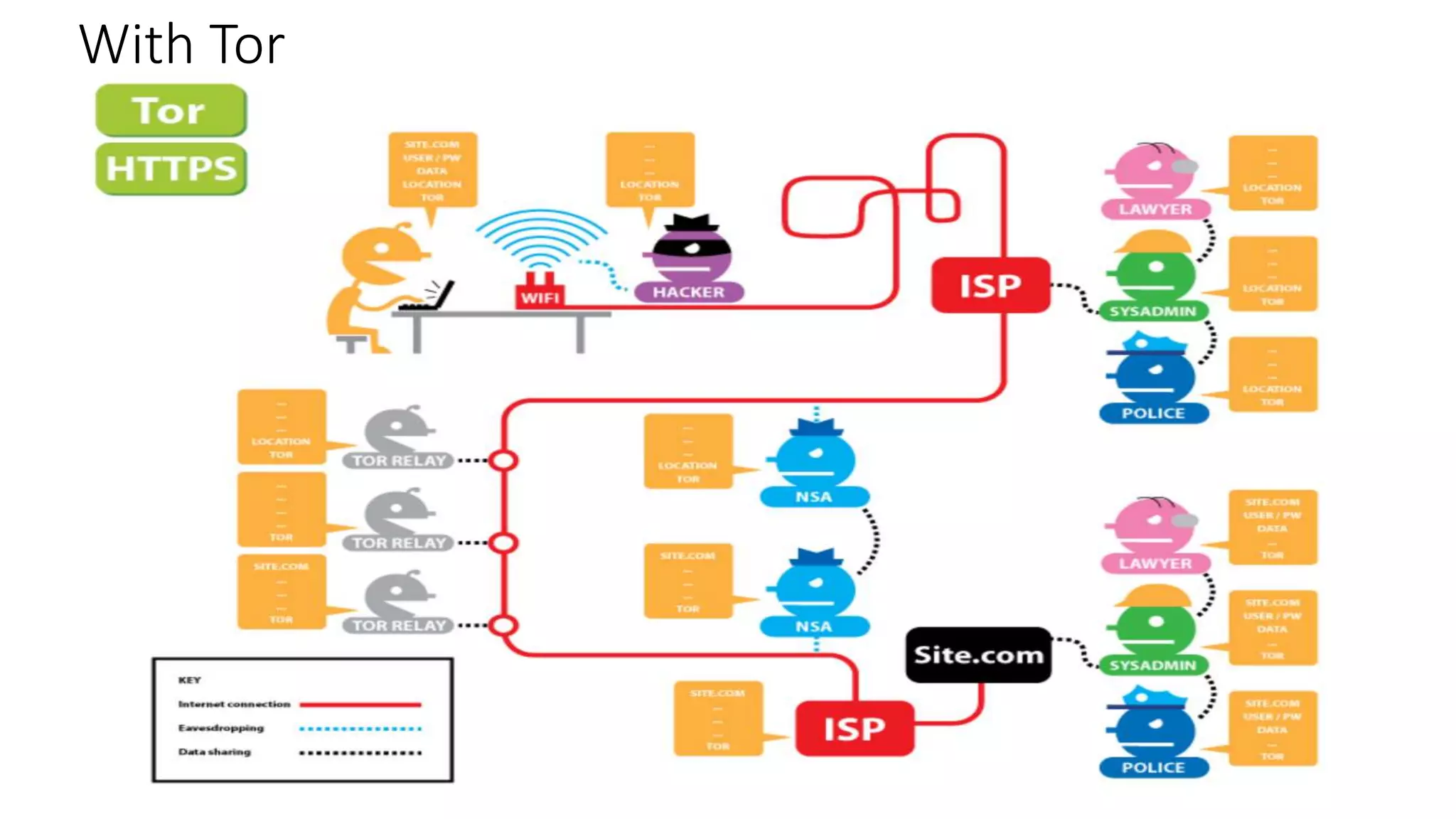
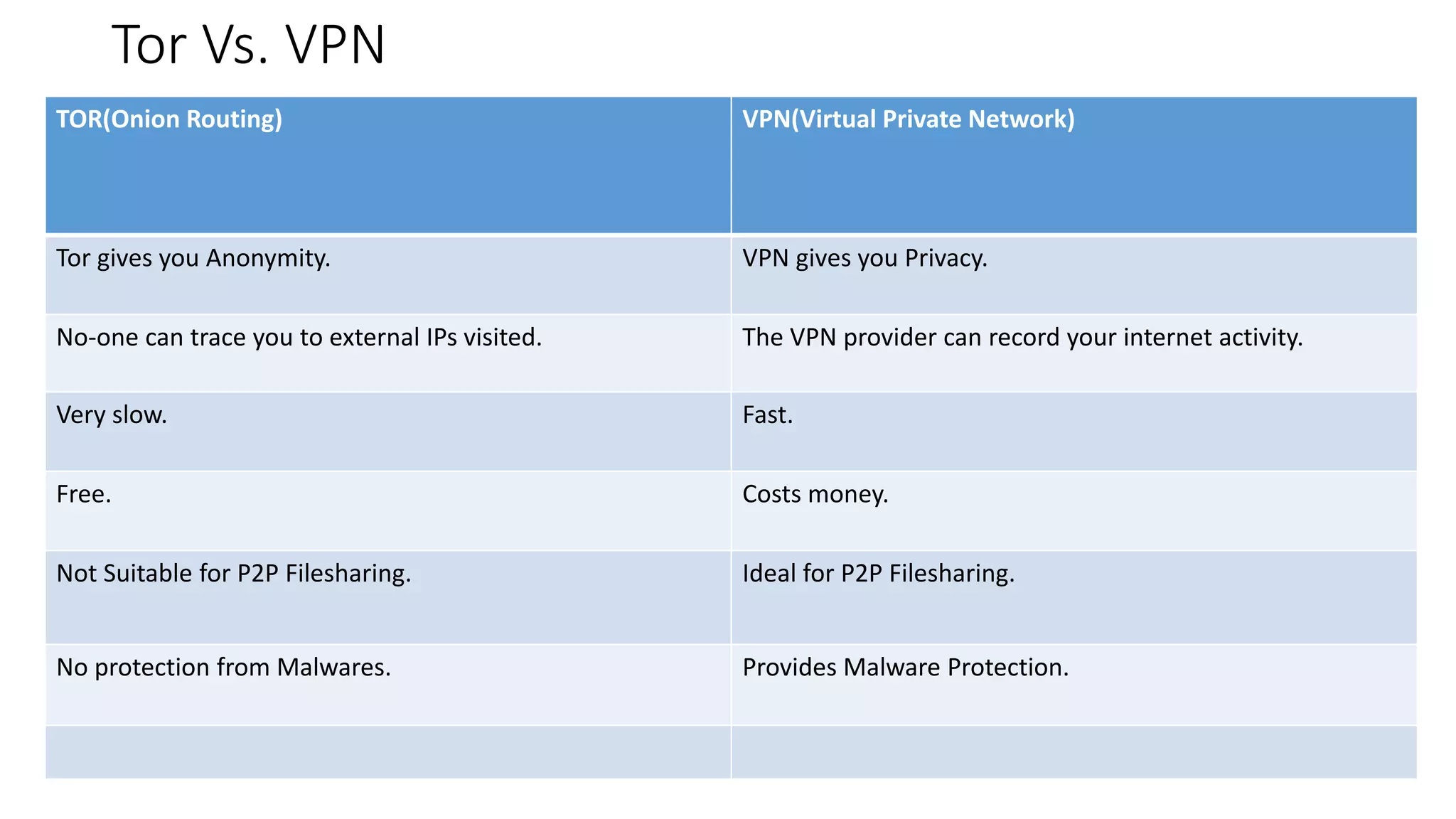
Tor is an anonymity network that allows users to access the internet anonymously. It works by routing connections through a series of volunteer relays run by other Tor users, making it difficult to trace the connection back to the original user. There are three types of relays - entry/guard relays, middle relays, and exit relays. Data is encrypted multiple times and sent through the relays, with each relay decrypting one layer of encryption. This prevents any single relay from knowing both the IP address of the user and the destination they are connecting to. Tor provides anonymity but is slower than a VPN. A VPN provides privacy by masking the user's IP address but does not provide the same level of anonymity as Tor since






![References :
[1]. TorBridge Discovery: Extensive Analysis and Large - scale Empirical Evaluation Zhen Ling, Junzhou
Luo, WeiYu,Ming Yang,and Xin wenFu
[2]. TorWard: Discovery, Blocking, and Traceback of Malicious Traffic Over Tor Zhen Ling, Junzhou Luo,
Member,IEEE, Kui Wu, Senior Member, IEEE, Wei Yu, and Xinwen Fu
[3]. How to Find Hidden Users :A Survey of Attacks on Anonymity Networks Esra Erdin,Chris Zachor ,and
Mehmet HadiGunes
[4]. http://jordan-wright.com/blog/2015/02/28/how-tor-works-part-one/
[5]. The Tor Project, Inc. (2015). Tor: Anonymity Online. [Online]. Available : https://www.torproject.org/
[6]. https://thetinhat.com/tutorials/darknets/tor-vpn.html
[7]. http://lifehacker.com/what-is-tor-and-should-i-use-it-1527891029](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationsecurityusingonionroutingtor-210224143425/75/Information-security-using-onion-routing-tor-15-2048.jpg)