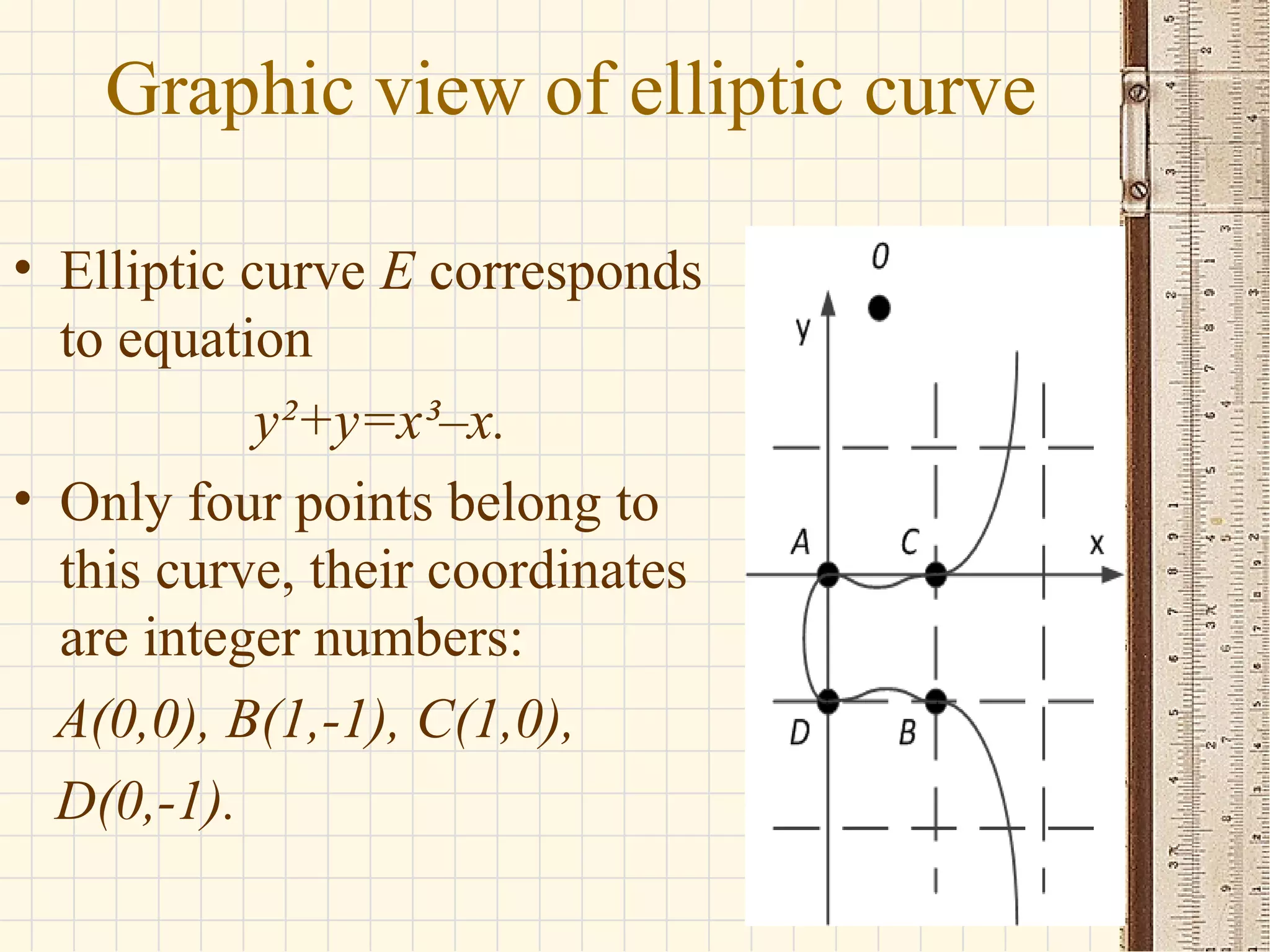
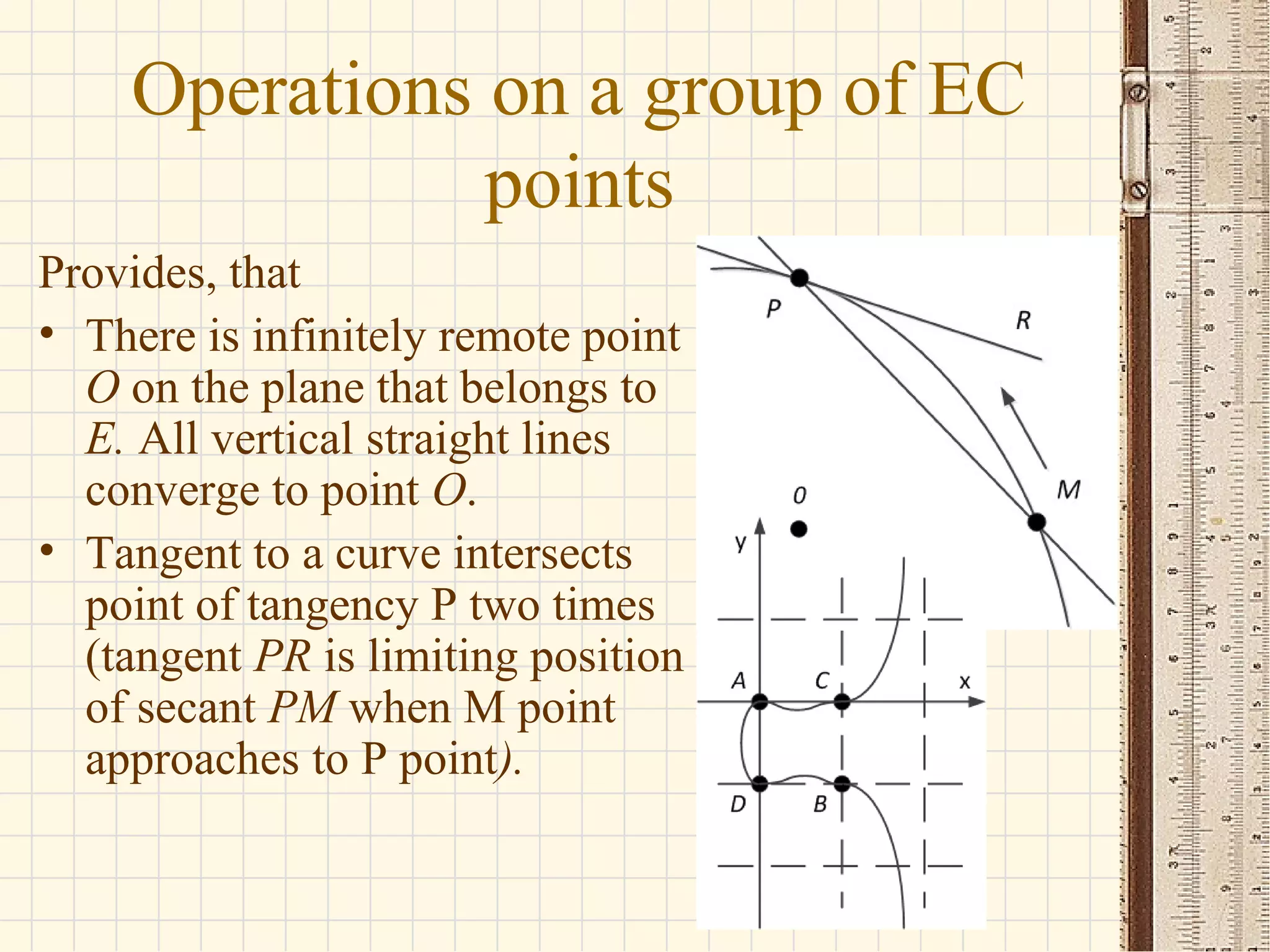
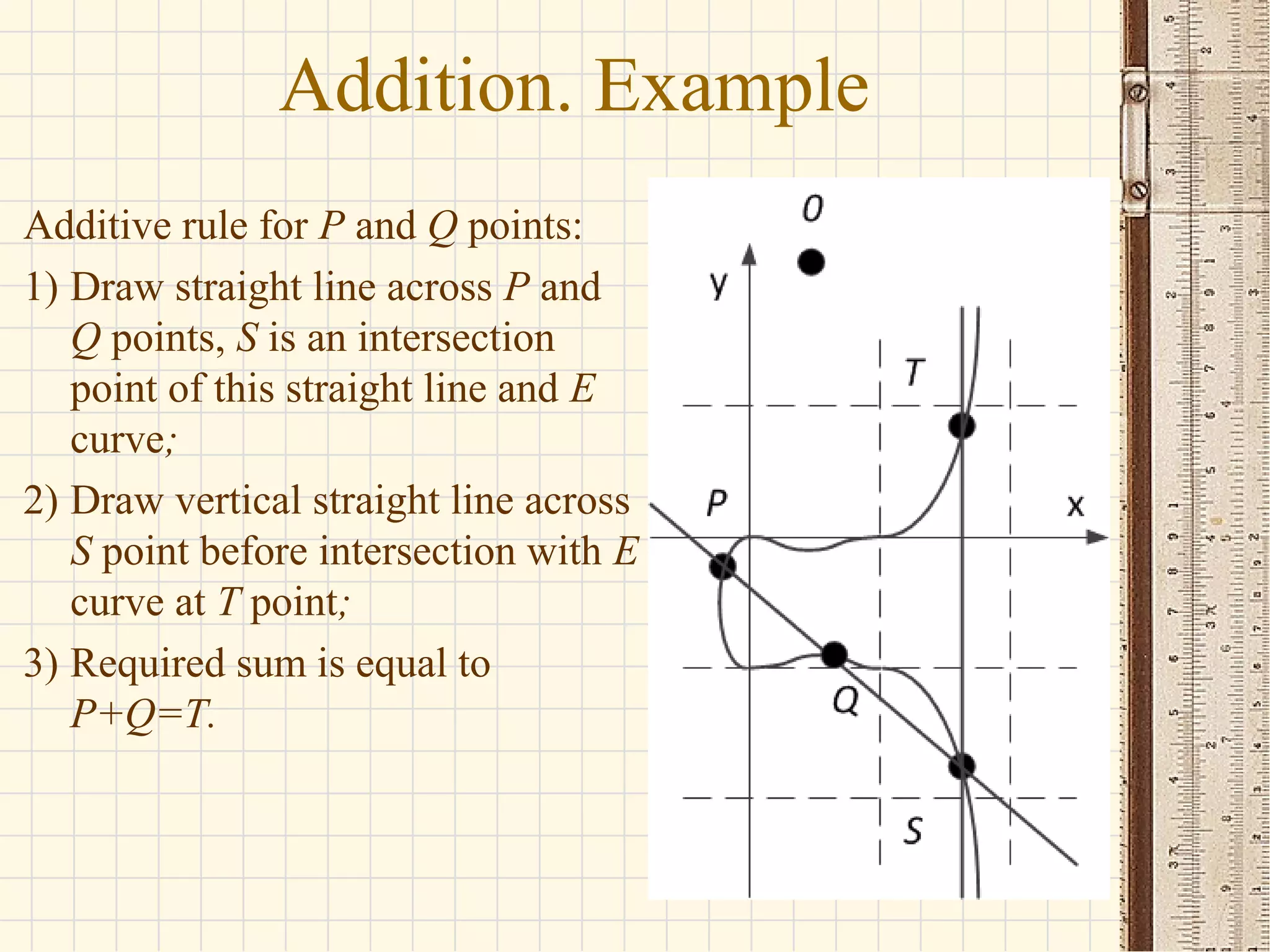
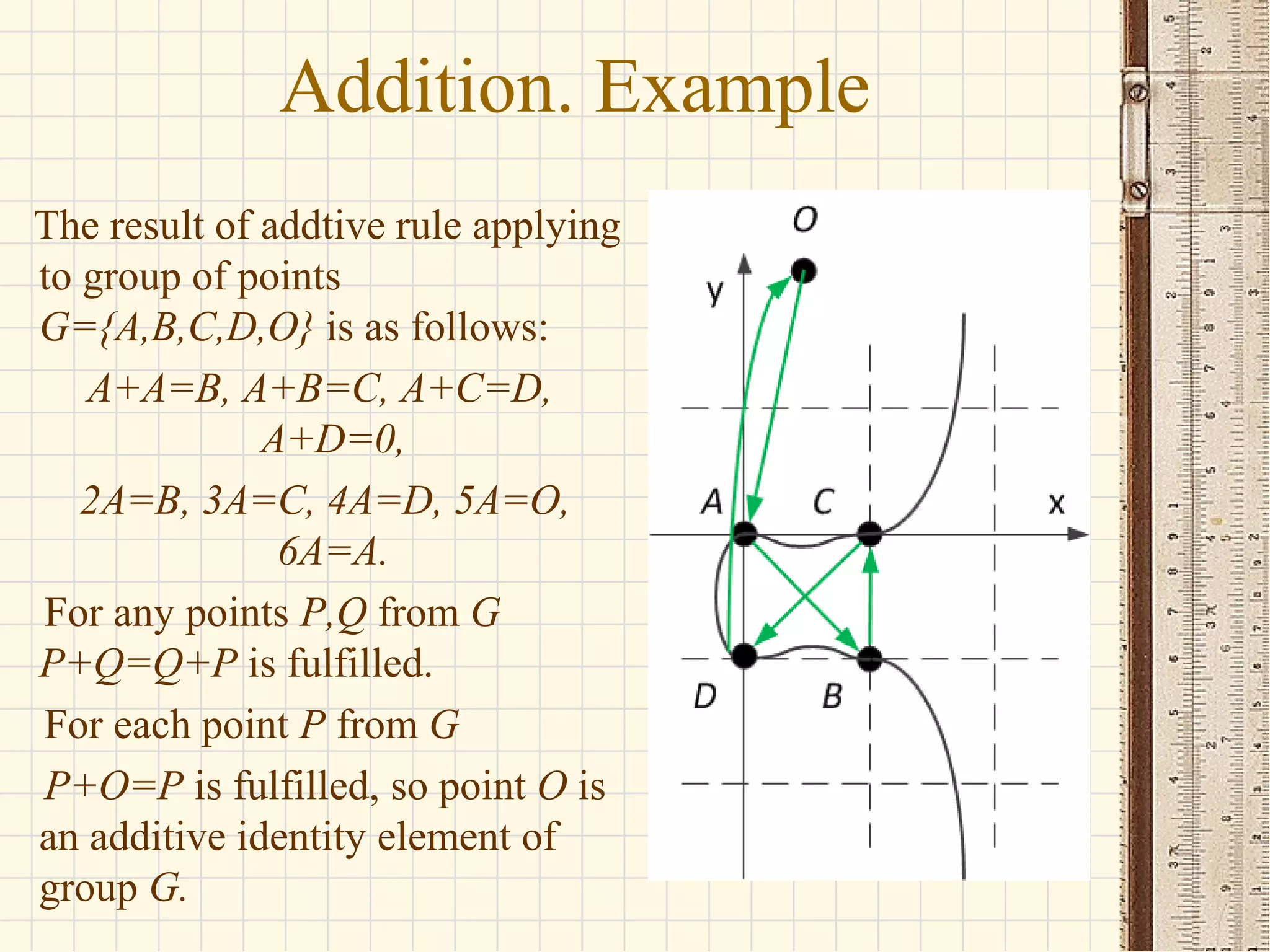
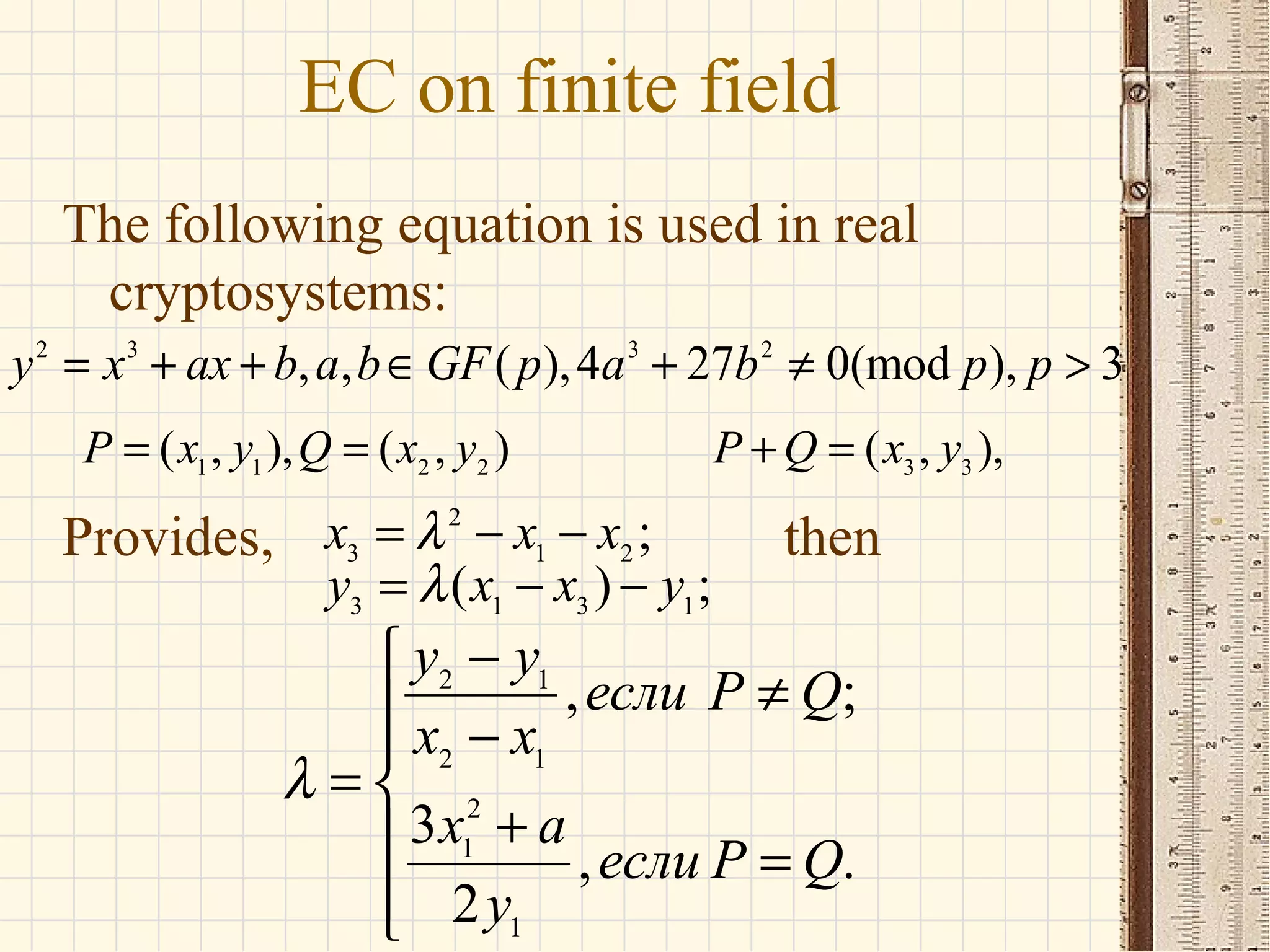
- Elliptic curves are algebraic structures used in cryptography and defined by cubic equations over finite fields. They form groups where the group operation is point addition.
- A digital signature algorithm can be based on elliptic curves by using the discrete logarithm problem over elliptic curve groups.
- The seminar discusses definitions of groups, elliptic curves, and their use in cryptography including defining the group operation of point addition on elliptic curves and calculating parameters like the group order.