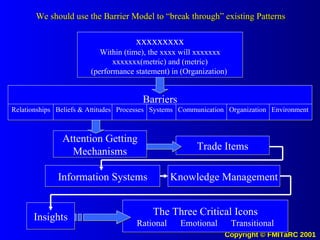
1. The document discusses how providing access to information and knowledge management systems can be used to positively influence human behavior and drive desired organizational values and outcomes. It argues that information accessibility encourages transparency, honesty, adherence to values and measurable performance.
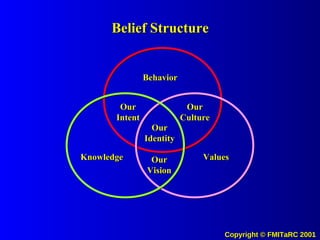
2. Key points made include that knowledge directly shapes beliefs, identity, vision and drives behavior and values. The quality of decisions can be improved by equipping people with better information streams.
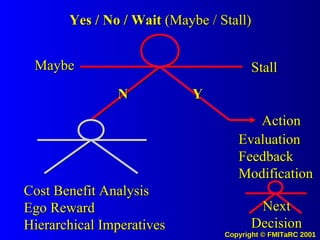
3. When information is fully distributed and knowledge management systems are used, it allows understanding of all decision factors and comparison of behaviors, which encourages transparency, honesty and adherence to shared values and goals.




























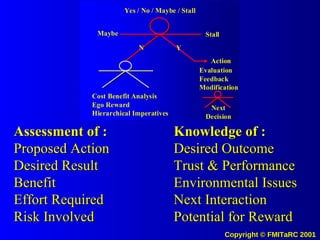












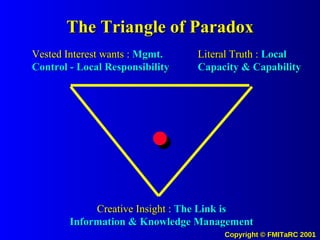









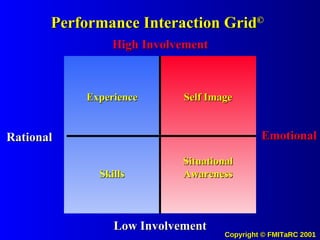
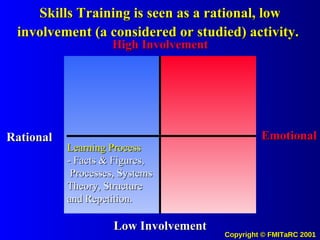
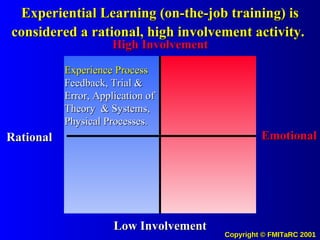
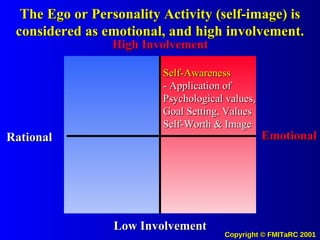
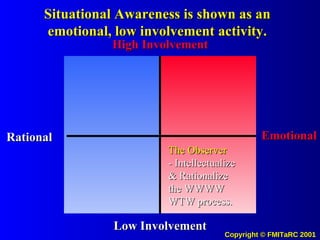








![The Potential Use of Information Systems and Knowledge Management to drive Desired Values and Behaviors in People Systems (to Achieve Measurable Outputs with Performance Based Metrics) [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationkmattitudechangemodel00-090622204628-phpapp02/85/Information-Km-Attitude-Change-Model-00-71-320.jpg)