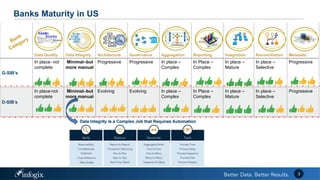
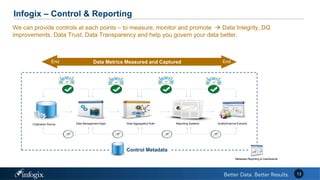
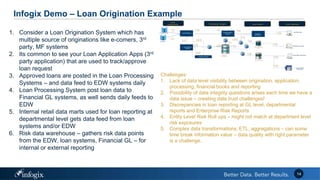
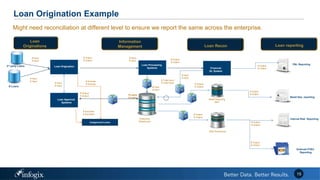
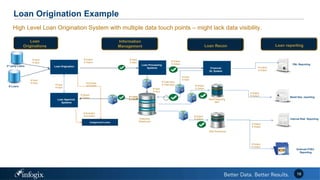
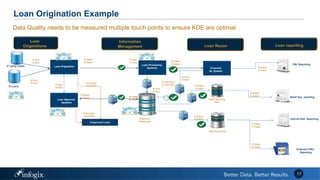
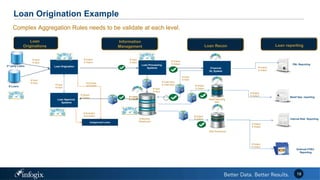
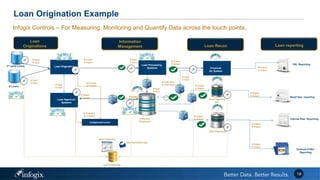
The document discusses the challenges banks face in implementing BCBS 239 regulations regarding data governance, risk aggregation, and reporting, highlighting issues with data quality, integration, and architecture. It emphasizes the need for improved metadata management, operational metrics, and automation processes to enhance data trust and compliance. Key recommendations include building a comprehensive inventory of risk data, leveraging analytics for monitoring data issues, and establishing clear ownership for data integrity.