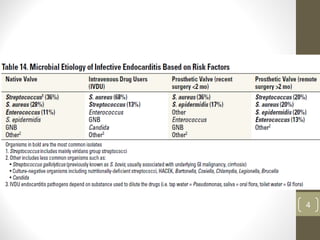
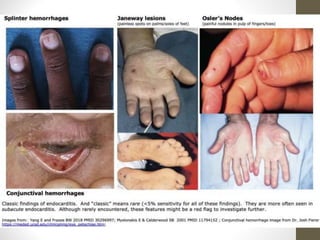
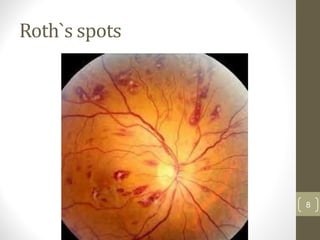
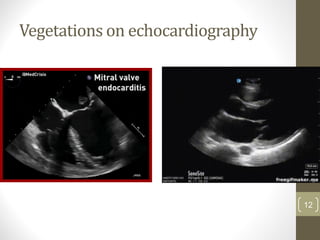
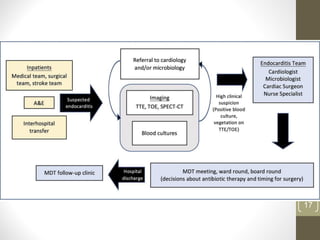
This document provides an overview of infective endocarditis. It defines infective endocarditis as a cardiac valve infection caused by platelet-fibrin vegetations containing bacteria and white blood cells. Risk factors include pre-existing heart conditions and procedures that cause bacteremia. Symptoms include fever, heart murmurs, heart failure, embolic events, and immunological findings. Diagnosis is based on modified Duke criteria using blood cultures, echocardiography, and clinical features. Treatment involves antibiotics targeted to the identified organism with consideration of surgery for complications or refractory infection. Prognosis depends on patient and infection factors with higher mortality for prosthetic valves and complications.