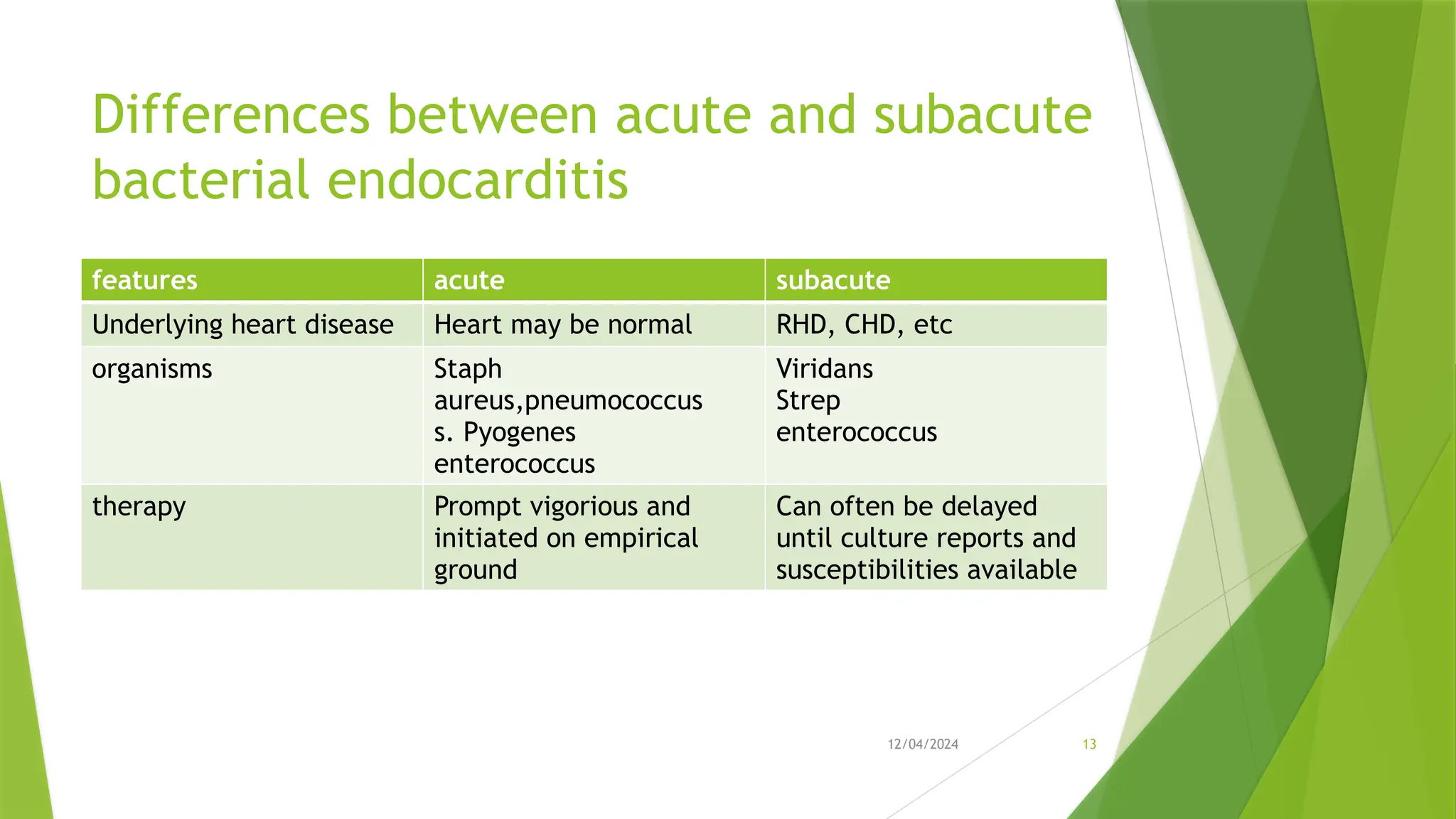
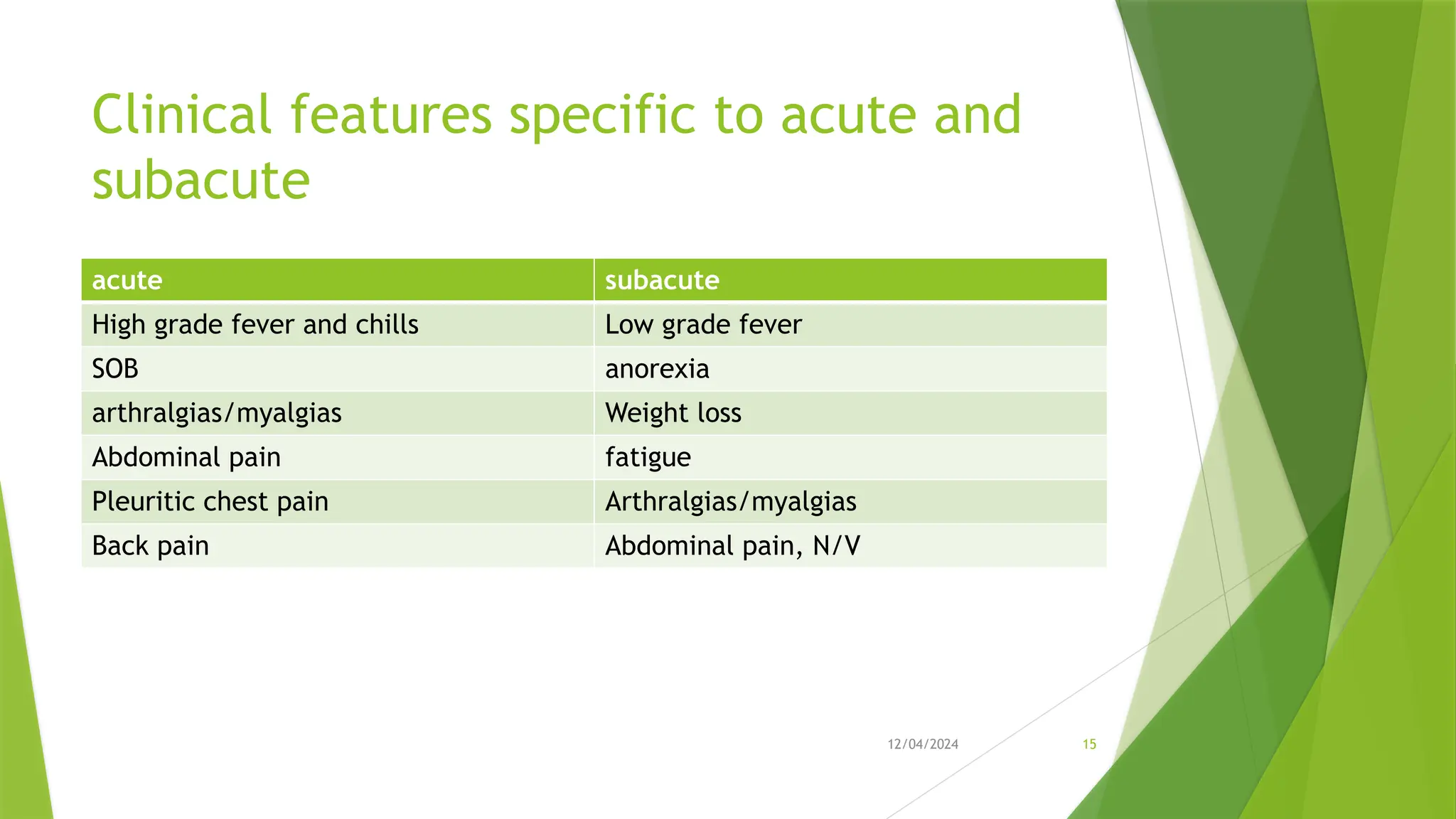
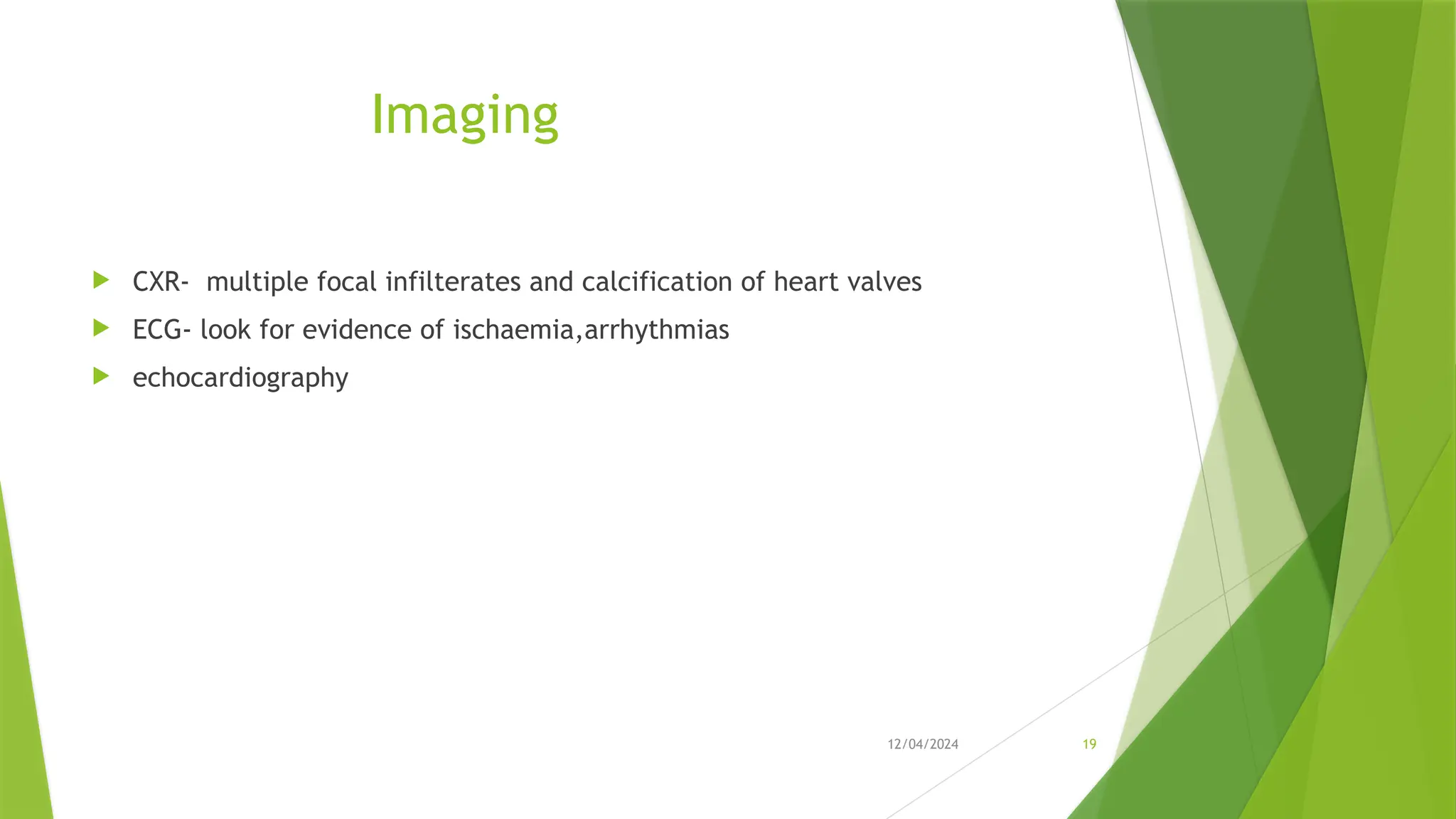
Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a serious heart infection, primarily affecting the endocardium and heart valves, linked to high morbidity and mortality rates. The disease can be classified into native and prosthetic valve infections, with risk factors including dental procedures, intravenous drug use, and prior heart conditions. Diagnosis relies on clinical features and laboratory tests, with treatment typically involving prolonged antibiotic therapy and possible surgical intervention for complications.