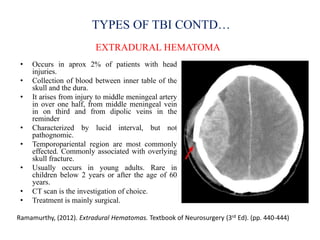
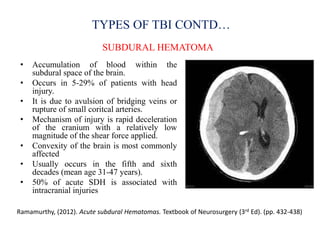
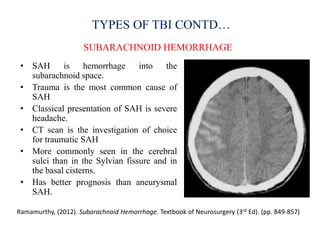
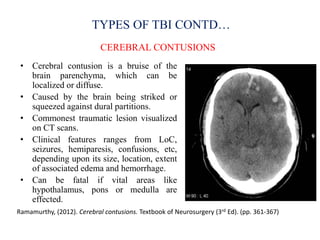
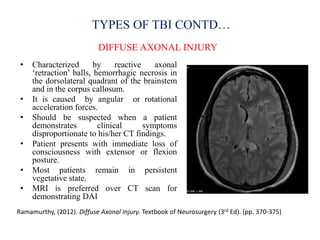
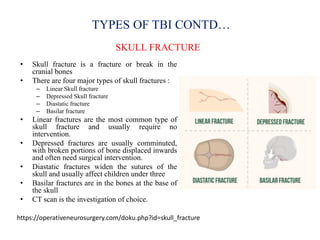
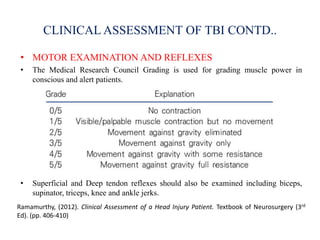
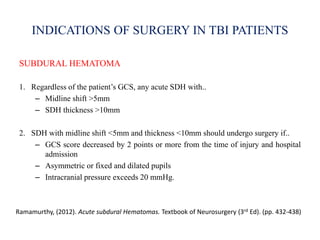
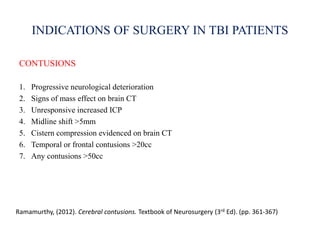
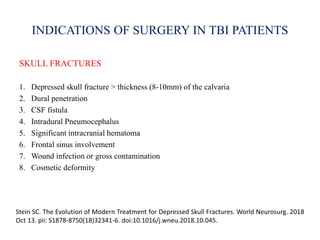
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is defined as injury to the brain caused by an external force. It is a leading cause of death and disability in India, often caused by road accidents, falls, and violence. The severity of TBI can range from mild concussions to severe injuries involving loss of consciousness for over 24 hours. Common clinical features include headache, vomiting, confusion, and seizures. The pathology involves primary injury at impact and secondary injury from processes like ischemia and inflammation. Types of TBI include concussions, extradural hematomas, subdural hematomas, subarachnoid hemorrhage, contusions, diffuse axonal injury, and skull fractures. Clinical assessment focuses on consciousness, pupillary