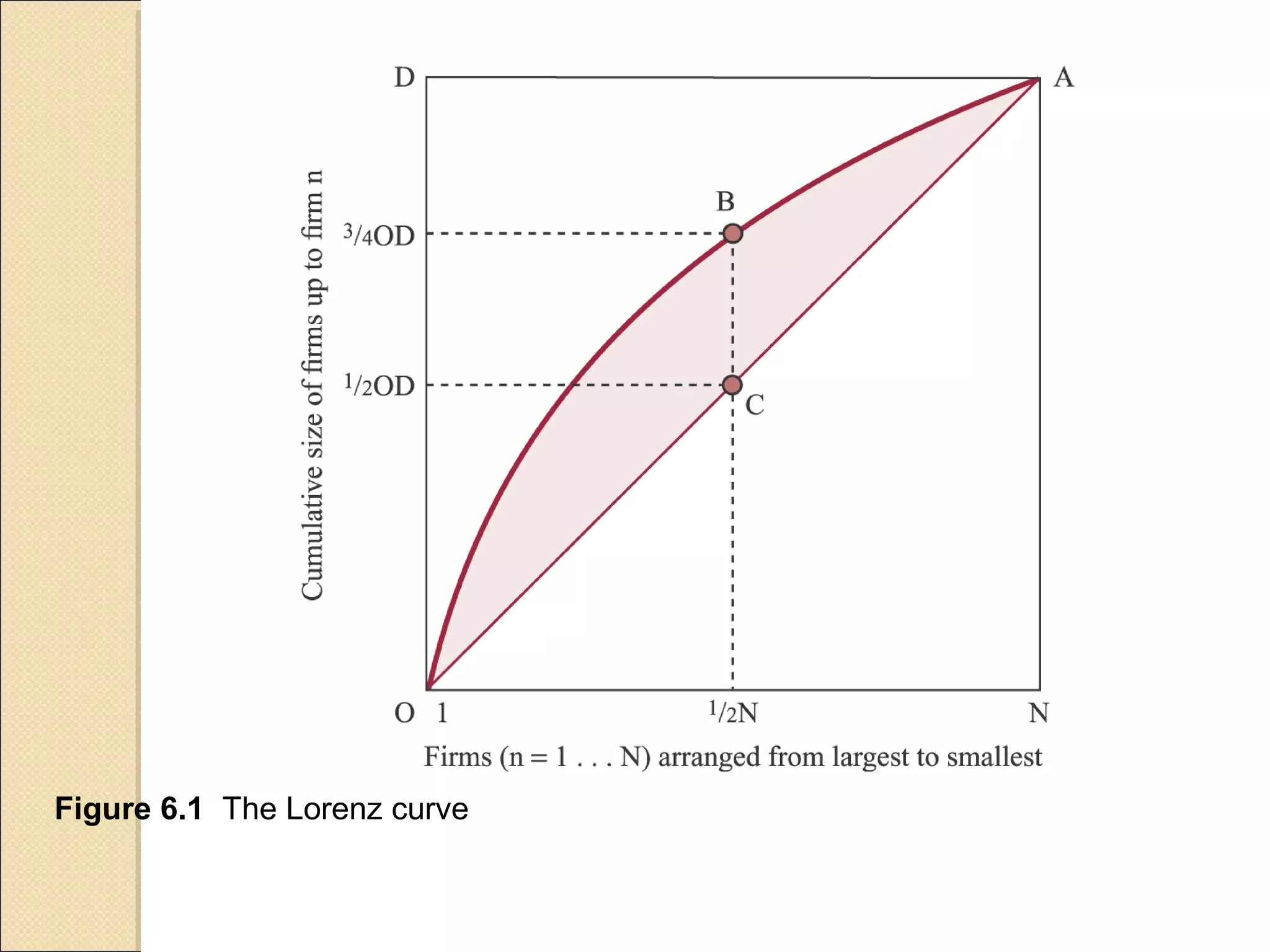
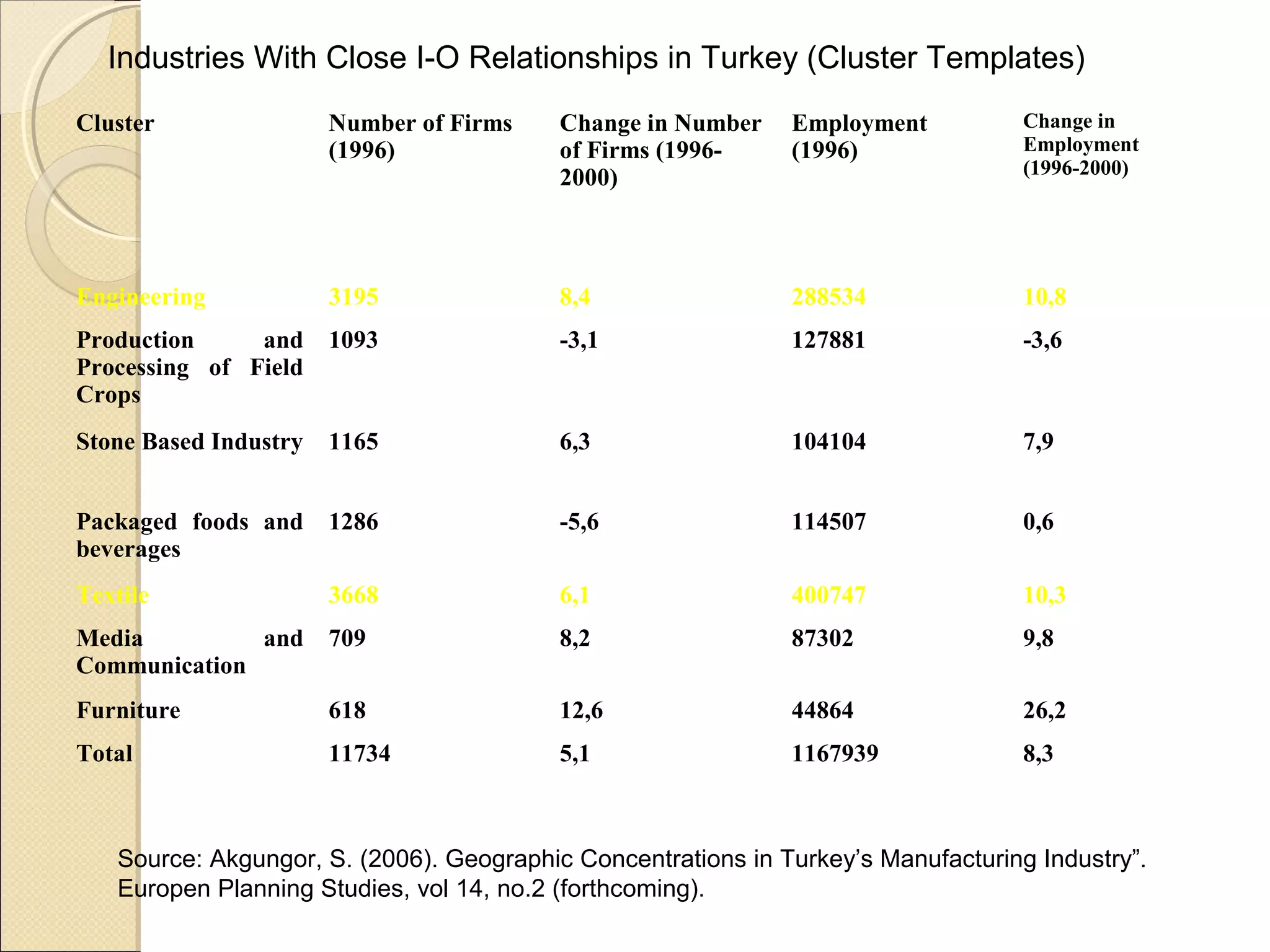
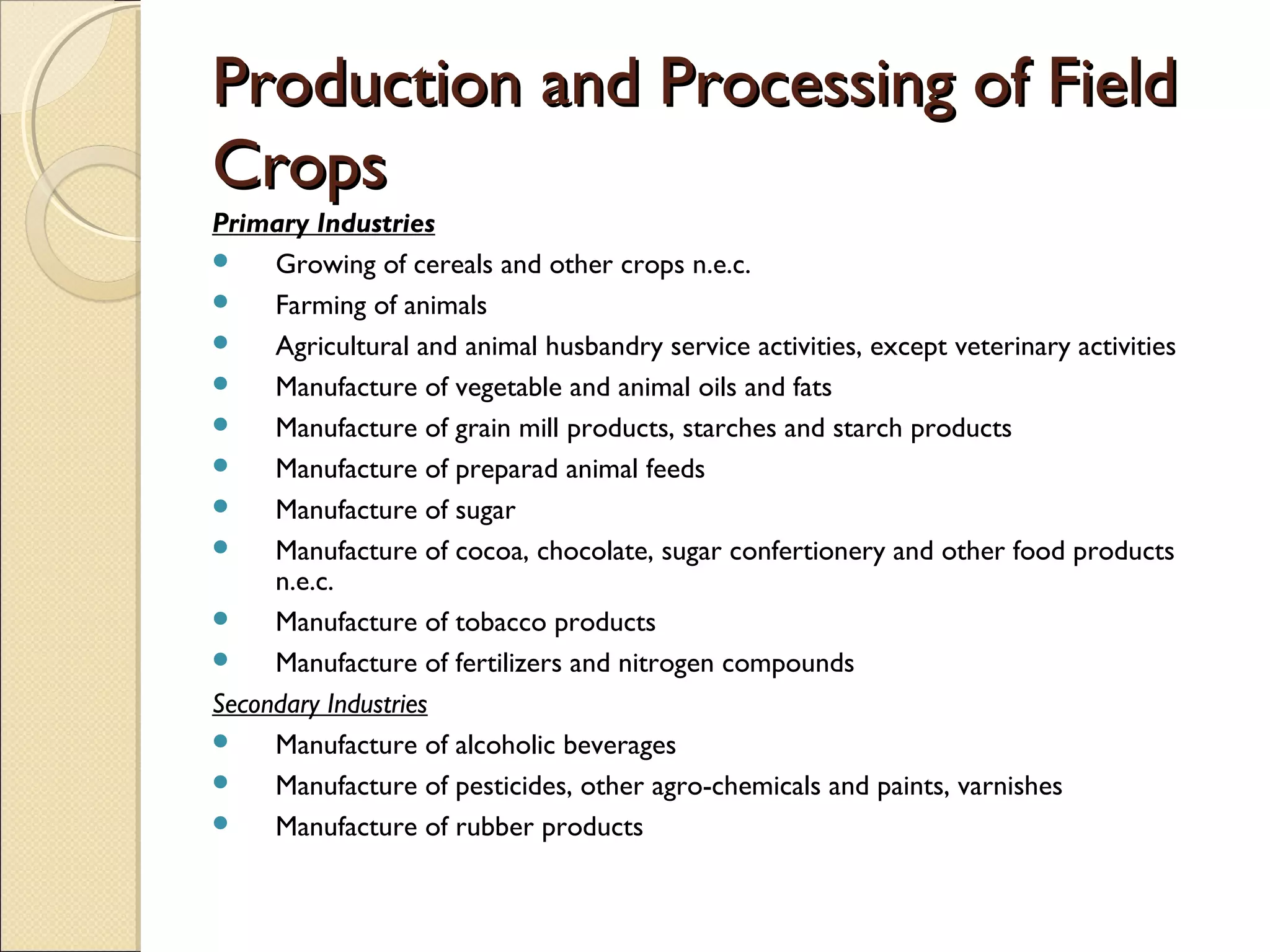
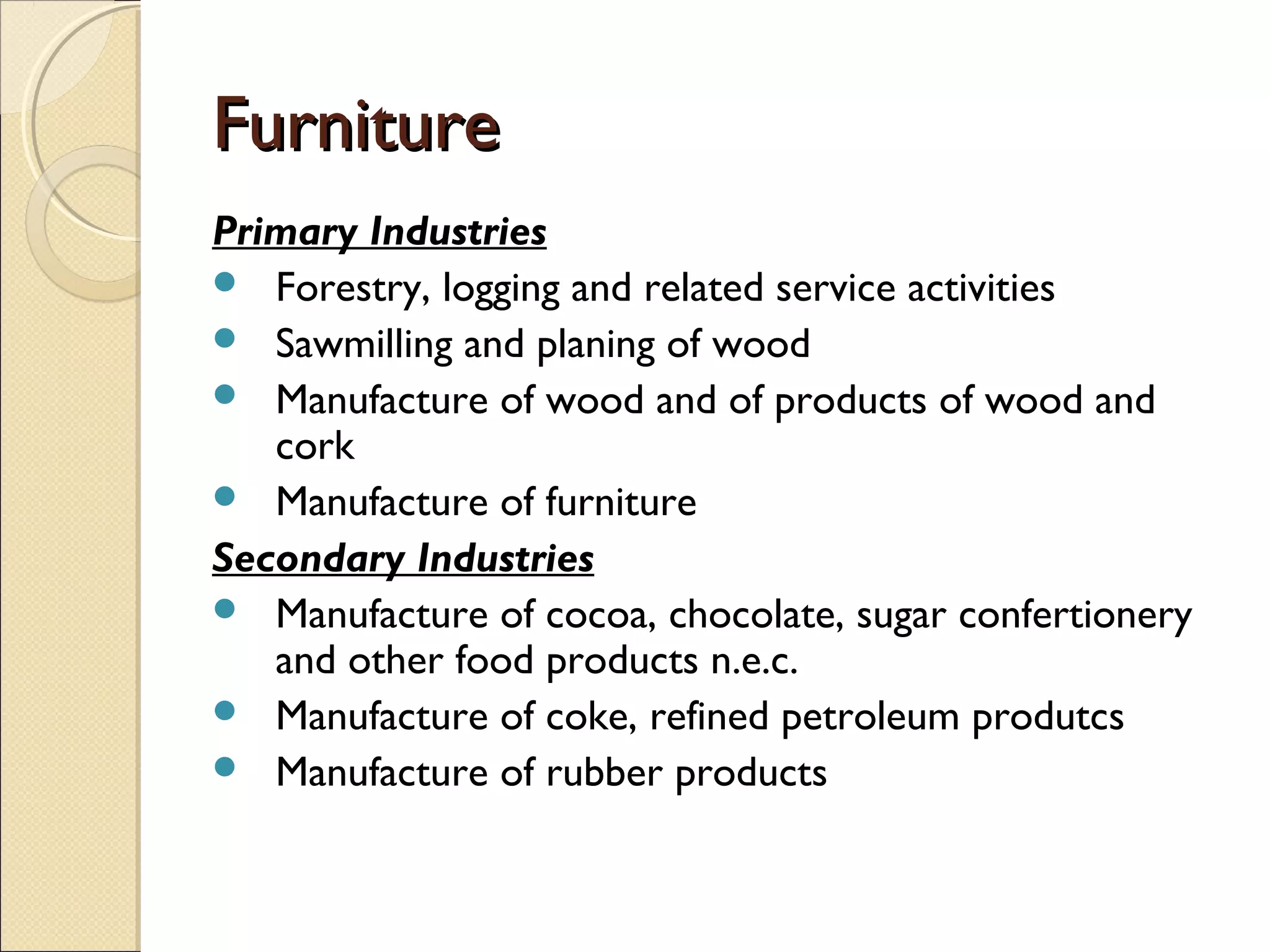
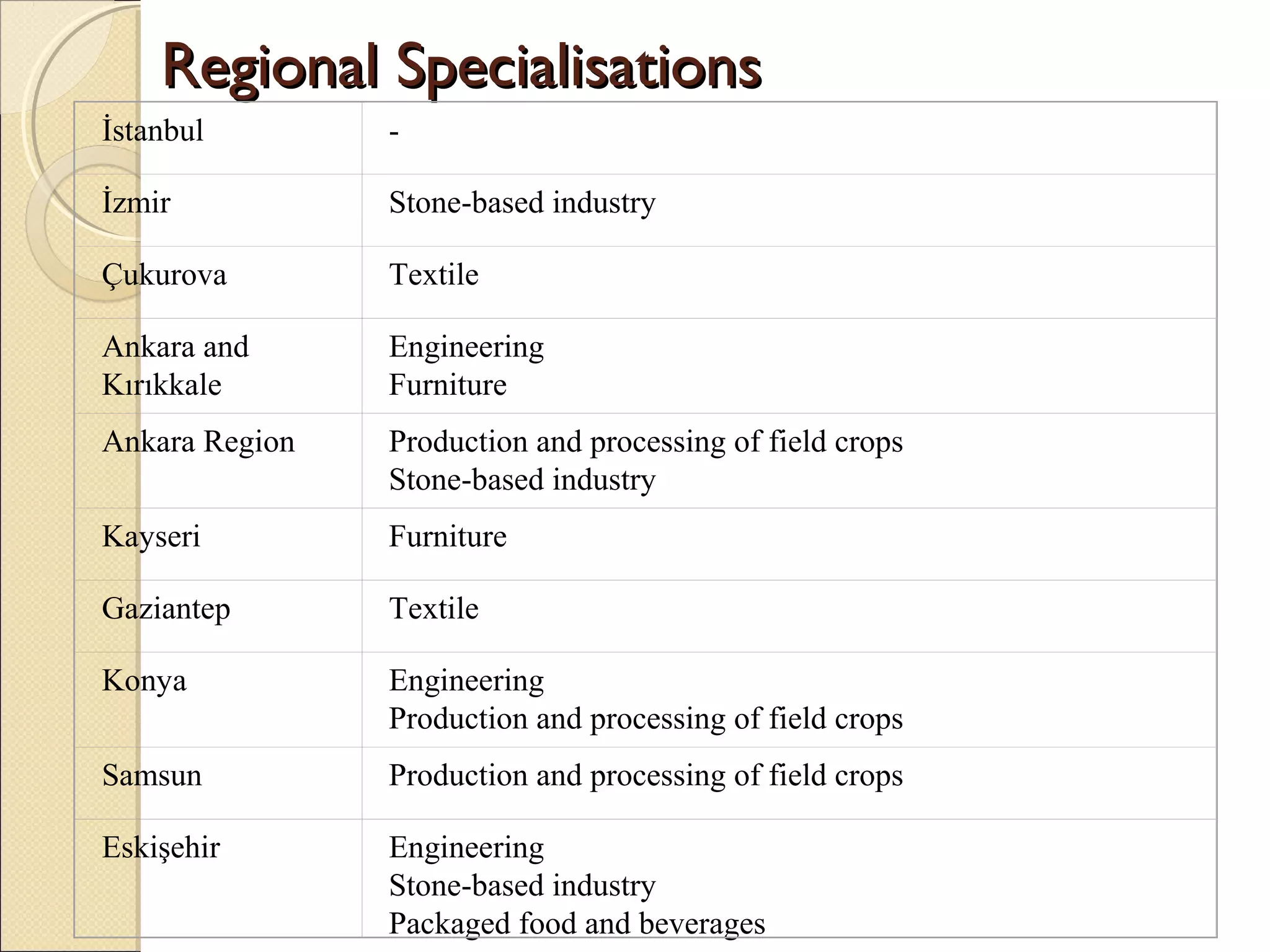
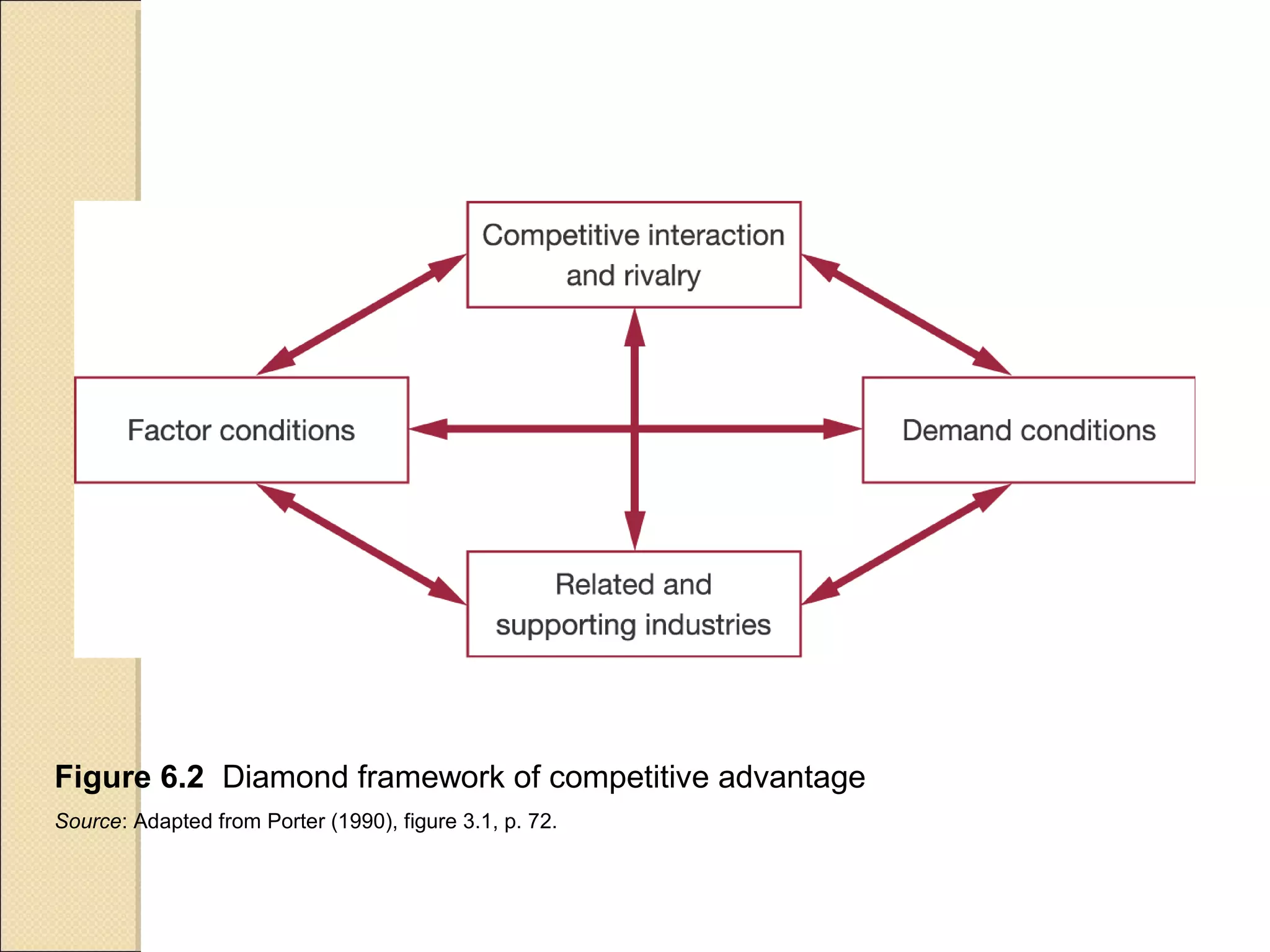
This document discusses industry concentration and trends. It begins by defining key elements for analyzing industry structure, including the number and size of firms and seller concentration. It also defines product and geographic dimensions for market and industry definition. Several common measures of seller concentration are described, including concentration ratios and the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index. The document presents data on trends in European manufacturing concentration and discusses industry clusters. It provides examples of industry cluster templates for key clusters in Turkey, including engineering, food production, textiles and others. It concludes by discussing regional specialization patterns across Turkey.