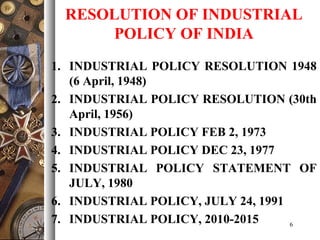
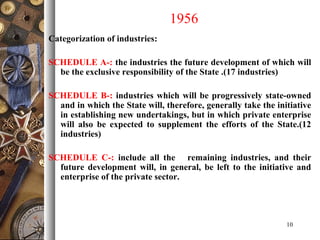
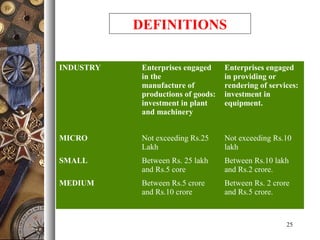
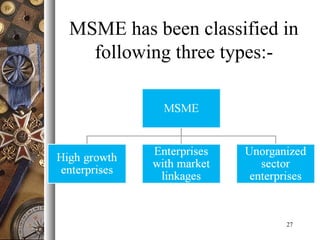
The document provides an overview of India's industrial policies from 1948 to 2010. It discusses the key objectives and provisions of various policy resolutions and statements over time. Some of the major policies covered include the Industrial Policy Resolutions of 1948, 1956, 1973, 1977, and 1980 as well as the new industrial policies of 1991 and 2010-2015. The document also defines different industry classifications and provides details on policies related to micro, small, and medium enterprises in India.