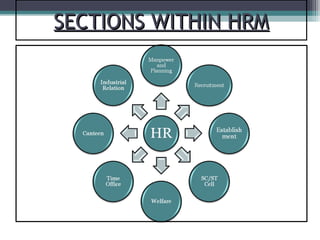
The document provides an overview of Air India's history, focusing on its managerial hierarchy and human resource functions, including recruitment and employee welfare. It addresses dispute resolution within the organization, the role of special cells for marginalized communities, and describes the industrial relations mechanisms in place, such as conciliation and adjudication. Key recommendations highlight the need for better data management and streamlining processes to enhance efficiency.