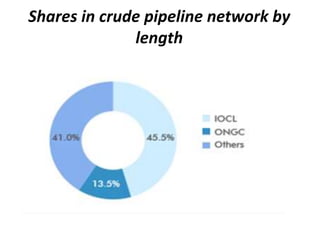
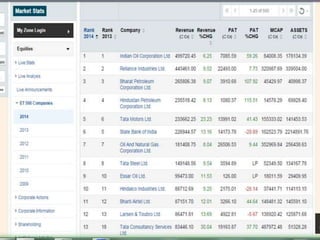
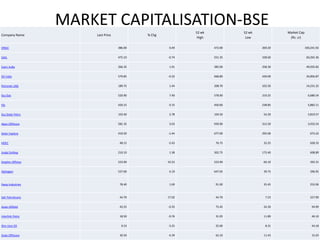
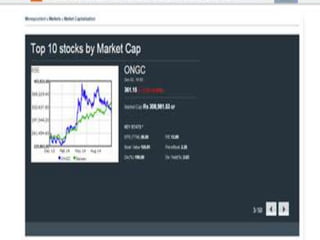
The oil and gas industry originated in India in the 19th century with the first oil strike in 1889. The government established oil as a core sector and established public sector companies like ONGC and OIL to control production and exploration. Private companies now also operate in the industry. Key players include ONGC, IOC, BPCL and Reliance with opportunities for MBA studies and jobs in the growing but also challenging industry. Strengths include growing demand but weaknesses include prices and infrastructure while opportunities exist in LNG and private investment but competition and policies pose threats.