Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times

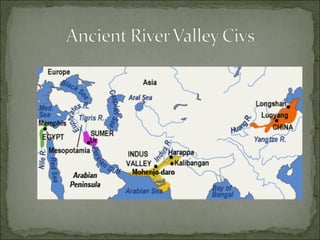
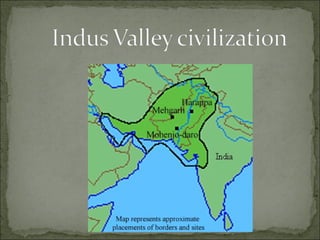









The Indus Valley civilization flourished around 2,500 B.C. in modern-day Pakistan and western India along the Indus River valley. The largest and most familiar archaeological site of this civilization is Mohenjo Daro. The Indus Valley civilization was one of the four ancient urban civilizations but was not discovered until the 1920s, and much of its ruins remain unexcavated. It developed sophisticated cities, an early form of writing that has yet to be deciphered, and extensive trade networks.










