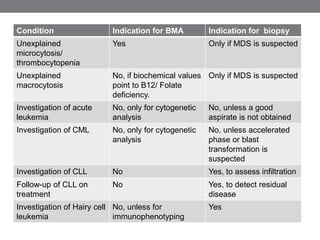
Bone marrow examination is an important diagnostic tool for evaluating hematological diseases. A bone marrow aspiration is usually sufficient to make a diagnosis but a trephine biopsy is needed in some cases to assess cellularity, detect focal lesions, or study bone marrow architecture. The decision to perform a biopsy depends on the condition being investigated. For example, a biopsy is indicated for suspected myelodysplastic syndrome or lymphoma to detect abnormal cell distribution, but not for acute leukemia where cytogenetics can be done on aspirated cells. A biopsy is also critical for investigating diseases like granulomatous disorders where aspirates often fail.