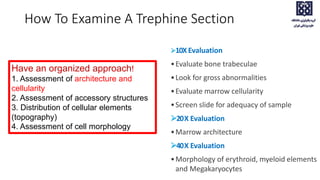
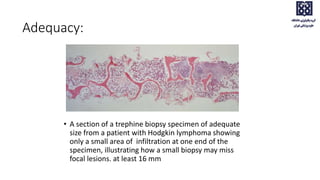
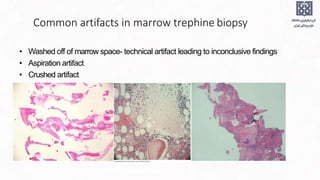
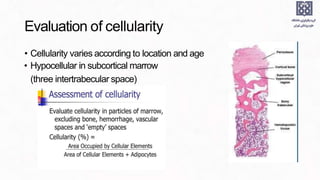
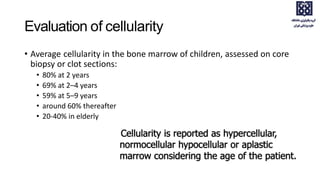
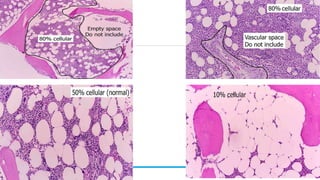
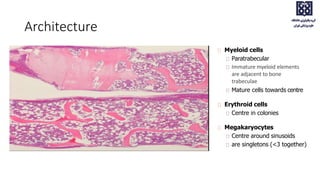
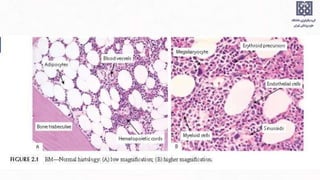
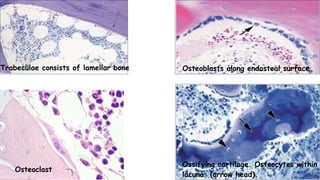
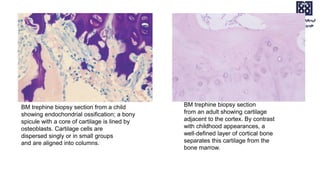
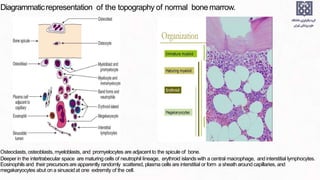
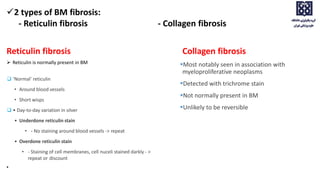
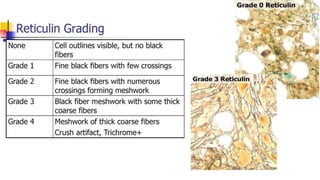
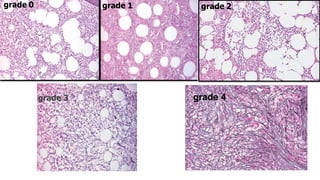
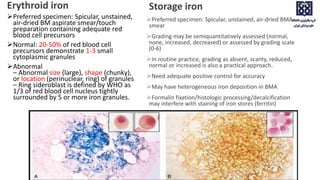
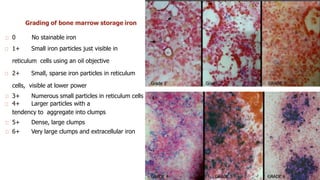
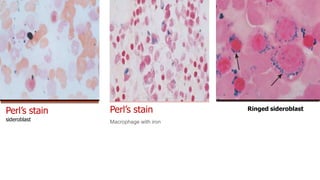
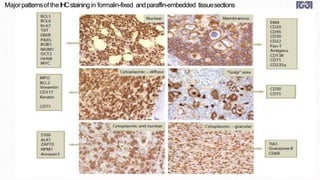
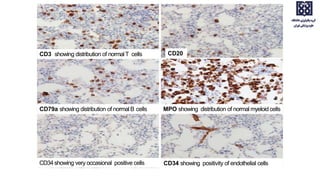
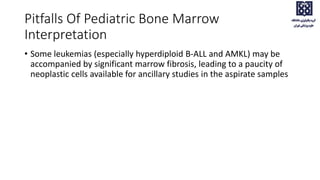
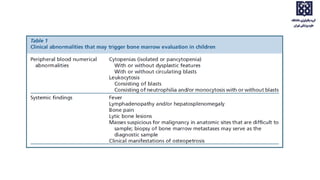
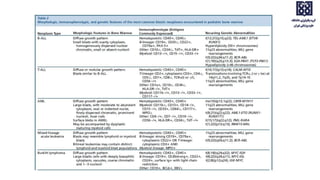
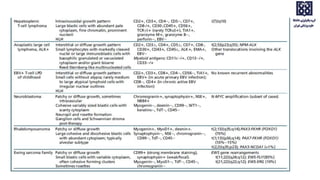
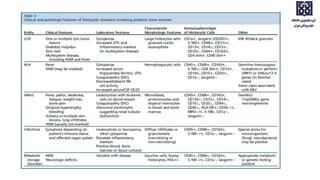
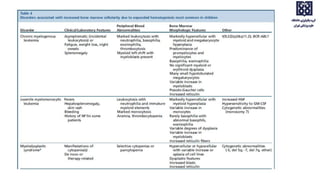
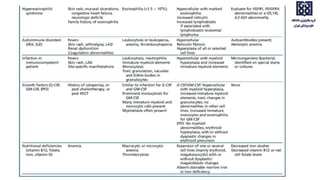
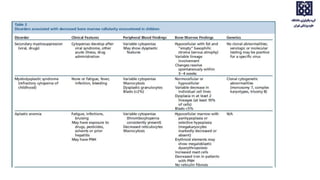
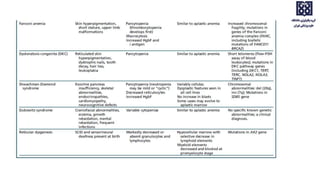
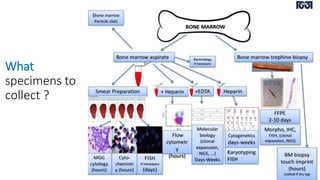
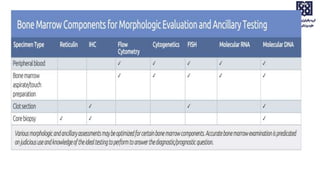
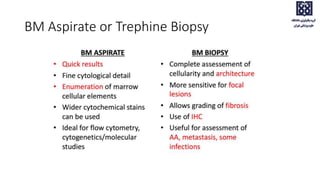
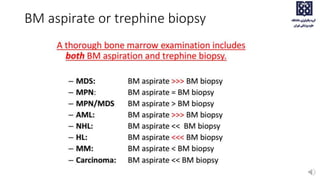
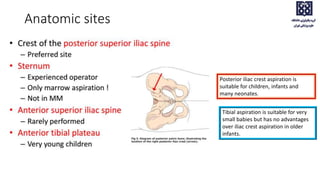
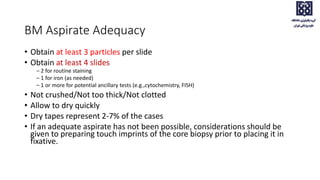
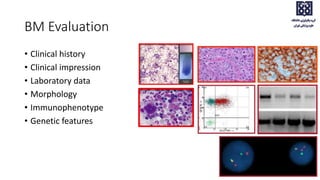
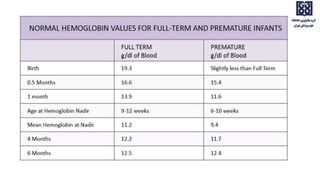
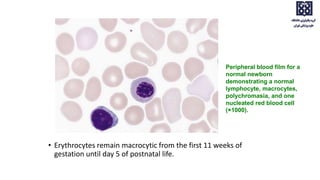
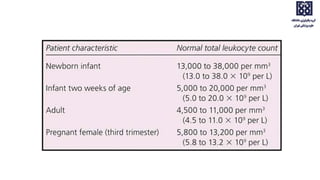
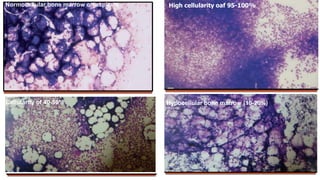
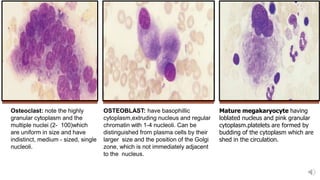
Bone marrow examination is indicated for investigating unexplained blood abnormalities, diagnosing hematopoietic neoplasms, infectious disease workup, evaluating storage disorders, and staging lymphomas or other cancers. An adequate bone marrow aspirate requires at least 3 particles per slide and 4 slides total, while an adequate trephine biopsy is at least 1.6 cm long. Bone marrow specimens are evaluated for cellularity, morphology of cells, immunohistochemistry, cytogenetics, and iron staining as needed. Cell distributions and accessory structures like osteoblasts are also assessed.









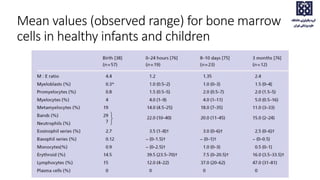


![95% Range Mean[12] Mean[11]
Myeloblasts 0–3 1.4 0.4
Promyelocytes 3–12 7.8 13.7[*]
Myelocytes (neutrophil) 2–13 7.6 –
Metamyelocytes 2–6 4.1 –
Neutrophils 22–46 32.1M; 37.4W 35.5
Myelocytes (eosinophil) 0–3 1.3 1.6
Eosinophils 0.3–4 2.2 1.7
Basophils 0–0.5 0.1 0.2
Lymphocytes 5–20 13.1 16.1
Monocytes 0–3 1.3 2.5
Plasma cells 0–3.5 0.6 1.9
Erythroblasts[†] 5–35 28.1M; 22.5W 23.5
Megakaryocytes 0–2 0.5
Macrophages 0–2 0.4 2.0
Normal ranges for differential counts on aspirated bone marrow (500 cells should be counted)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bmevaluationpart1pbsbma-231223041249-22f30be9/85/Bone-Marrow-evaluation-EVALUATION-PBS-BMA-pptx-29-320.jpg)