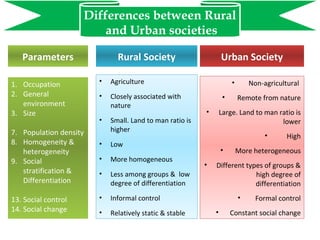
The document discusses the characteristics and differences between Indian rural and urban societies, highlighting that rural societies are primarily agricultural, small in size, and have close-knit relationships, while urban societies are larger, more diverse, and have complex social structures. Despite their differences, both societies are interconnected and influence one another, suggesting that understanding them requires examining their relationship rather than viewing them in isolation. Ultimately, the distinction between rural and urban societies is more theoretical than practical.