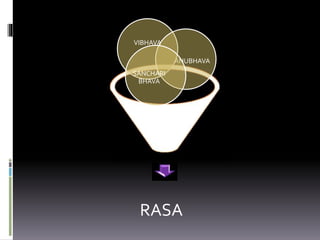
Indian aesthetics encompasses many areas including poetry, music, architecture, painting, and sculpture. Key texts that shaped Indian aesthetics include the Natya Shastra, Dhwanyaloka, and Abhinavabharati. Indian aesthetics views art as a means to experience the Absolute. Nine rasas or aesthetic emotions are described including love, humor, compassion, anger, terror, disgust, wonder, heroism, and peace. Natya Shastra outlines the origin and purpose of Indian drama. Rasa is realized through vibhavas, anubhavas, and sancaribhavas interacting to arouse the sthayibhava or dominant emotion. Major schools of thought on rasa include