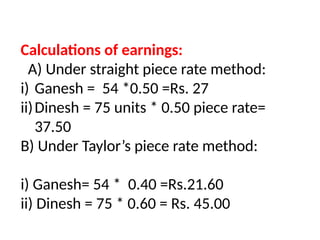
The document discusses various incentive schemes for workers, specifically focusing on Taylor's differential piece rate system, Halsey plan, and Rowan plan. Taylor's system rewards efficient workers with higher piece rates and penalizes slower workers, but lacks minimum wage guarantees and fairness for those just below the standard. The Halsey and Rowan plans also provide guaranteed wages with bonuses for time saved, offering different calculations for wages based on output performance.