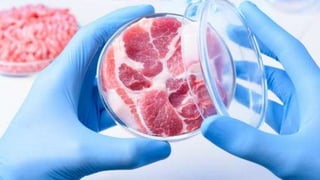
This document provides an overview of in vitro meat production. It begins with introducing meat and the large number of land animals killed annually for consumption. It then defines in vitro cultured meat as meat produced through tissue engineering techniques rather than slaughter. The history of the concept is traced back to the 1950s. Key ingredients for production include stem cells, culture media, bioreactors and scaffolds. Main techniques include scaffolding, self-organizing approach, organ printing, biophotonics and nanotechnology. Advantages include avoiding animal slaughter and reducing environmental impacts, though high production costs currently limit scale. In conclusion, cultured meat could potentially be healthier while eliminating many issues with conventional meat production.














![REFERENCE
Zandonella C. 2003. Tissue engineering: The beat goes on. Nature, 421, 884–886.
Fox J L. 2009. Test tube meat on the menu? Nature Biotechnology, 27, 873.
Catts O, Zurr I. 2002. Growing semi-living sculptures: The tissue culture project. Leonardo, 35, 365–
370.
Van Eelen W F, van Kooten W J, Westerhof W. 1999. Industrial production of meat from in vitro cell
cultures. WO/1999/031223: Patent Description. [1999-6-24].
http://www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/wo.jsp?wo=1999031223
Invitro meat production – NCBI-NIH
Zuhaib Fayaz Bhat , Sunil Kumar, Hina Fayaz. Division of Biotechnology, University of Kashmir, Srinagar
190006, India. In vitro meat production: Challenges and benefits over conventional meat production,
ScienceDirect.
29/3/2021 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/culturedmeatppt-210405150419/85/In-vitro-meat-ppt-16-320.jpg)
