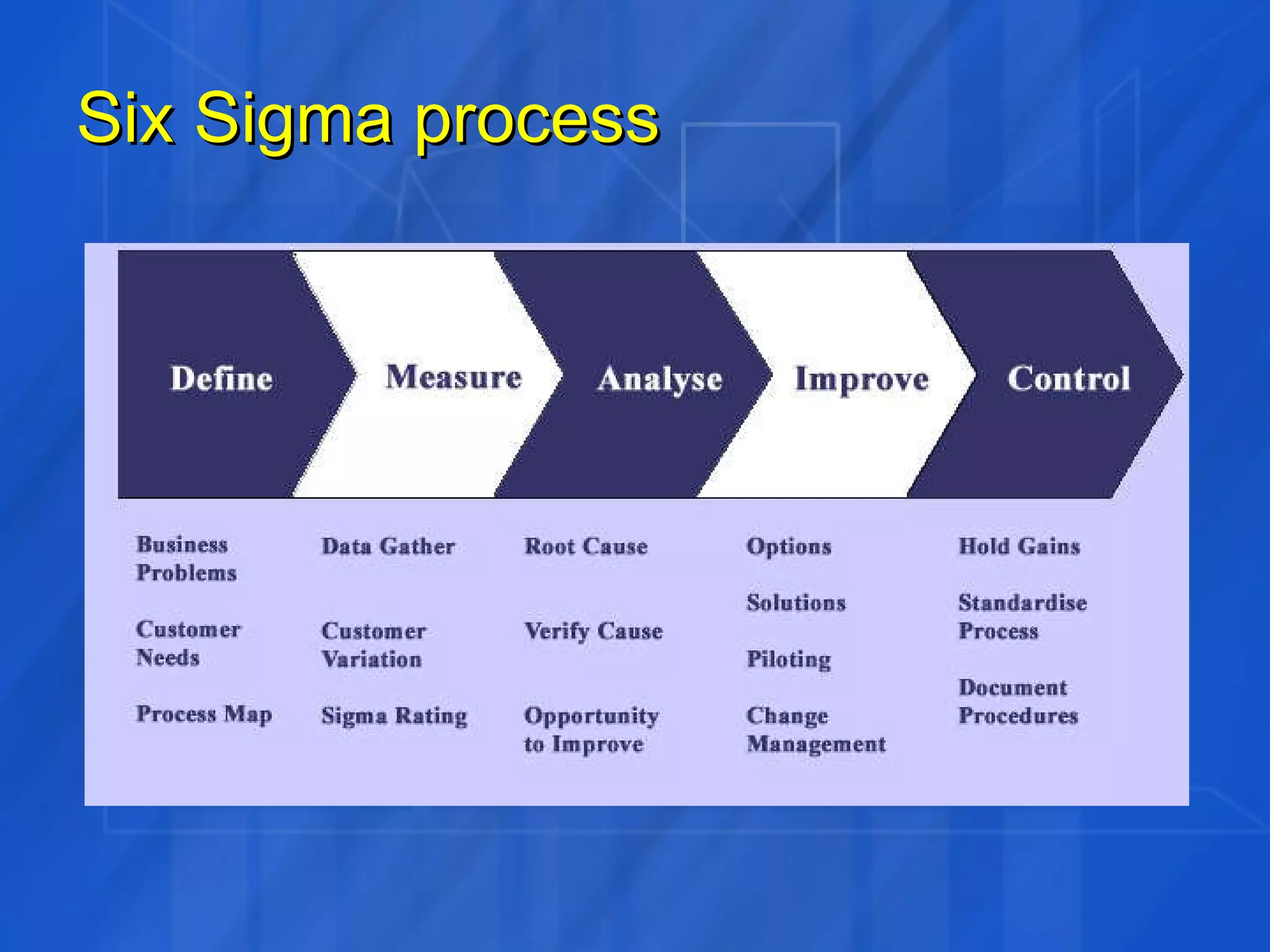
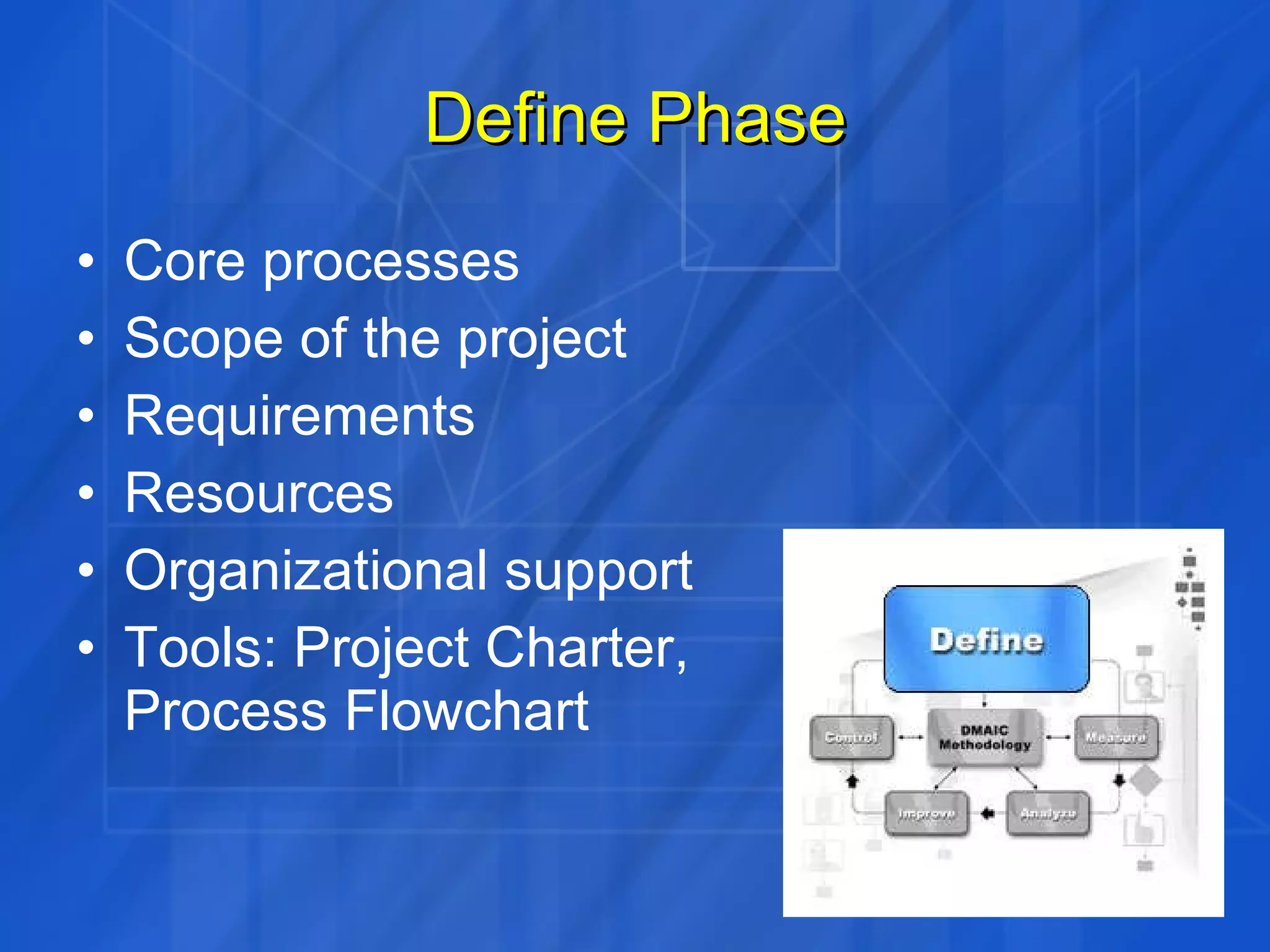
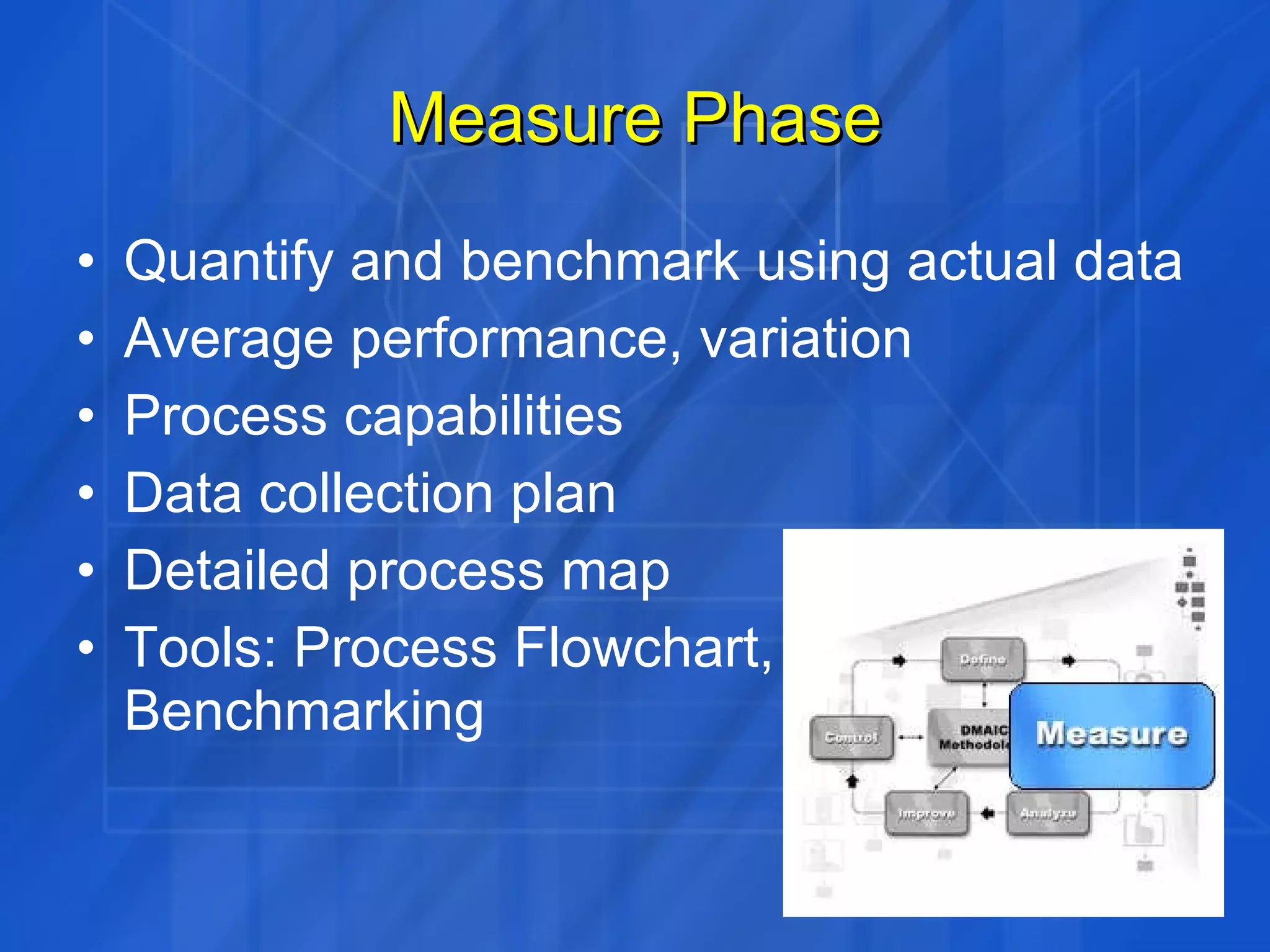
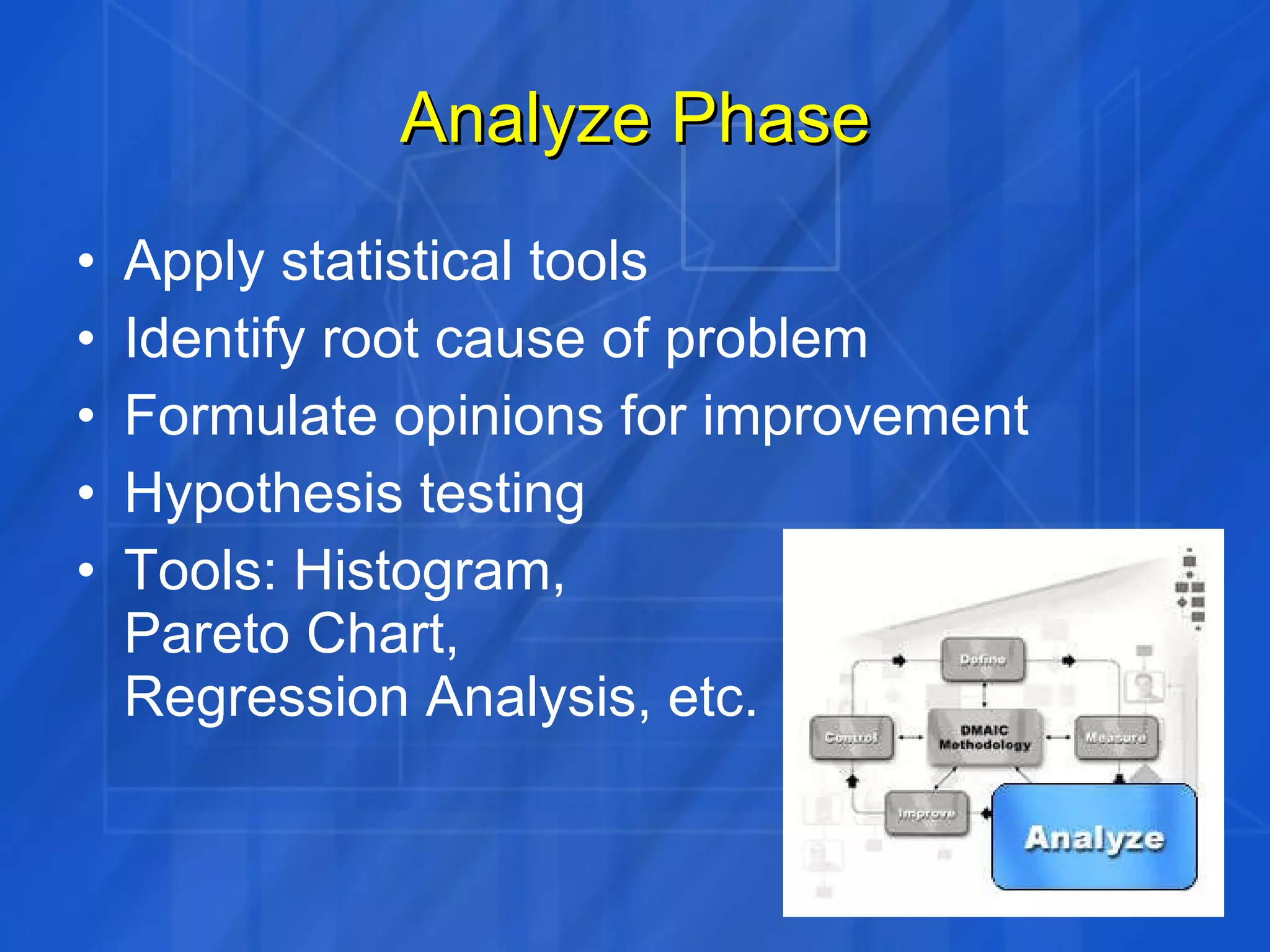
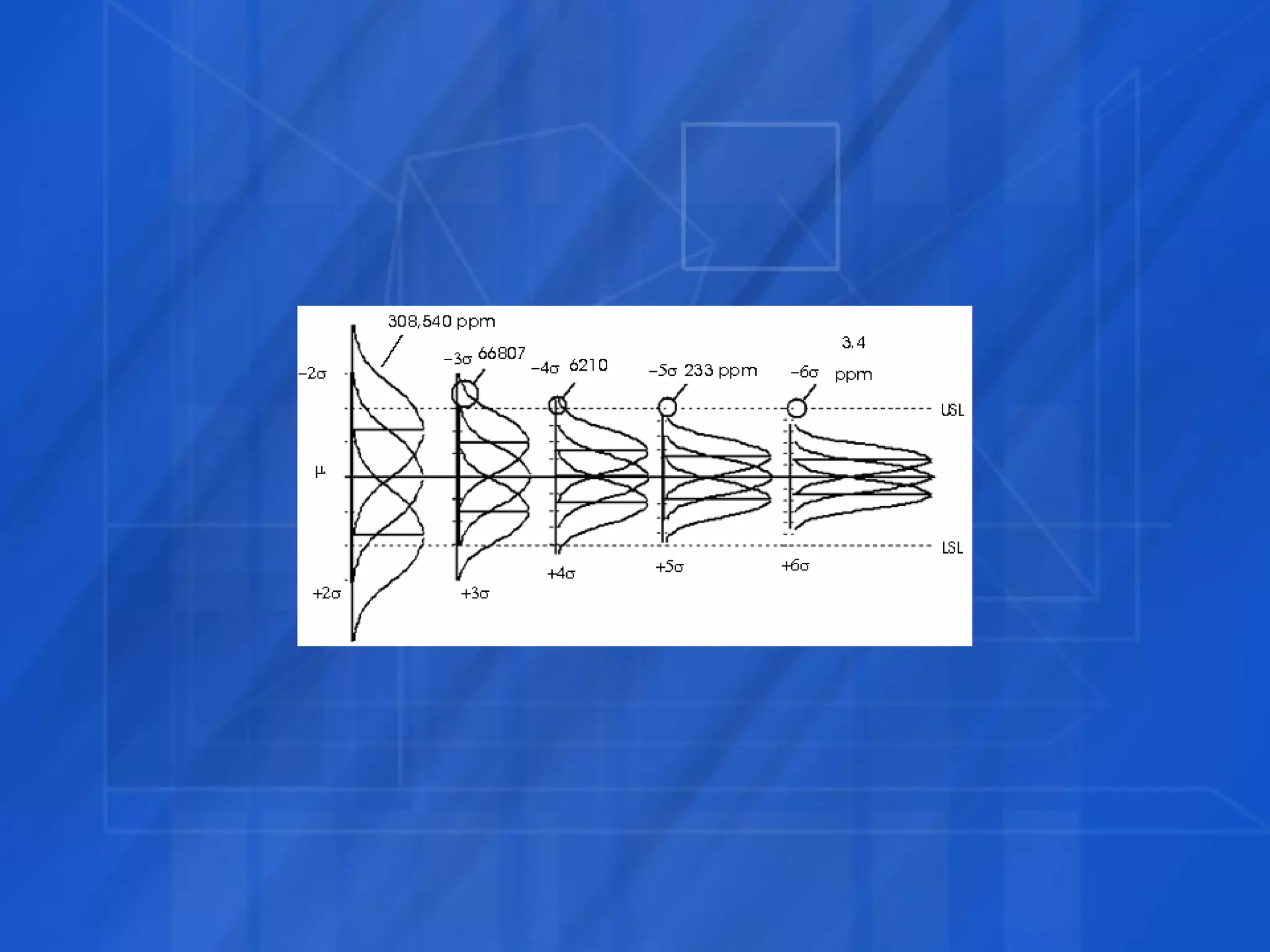
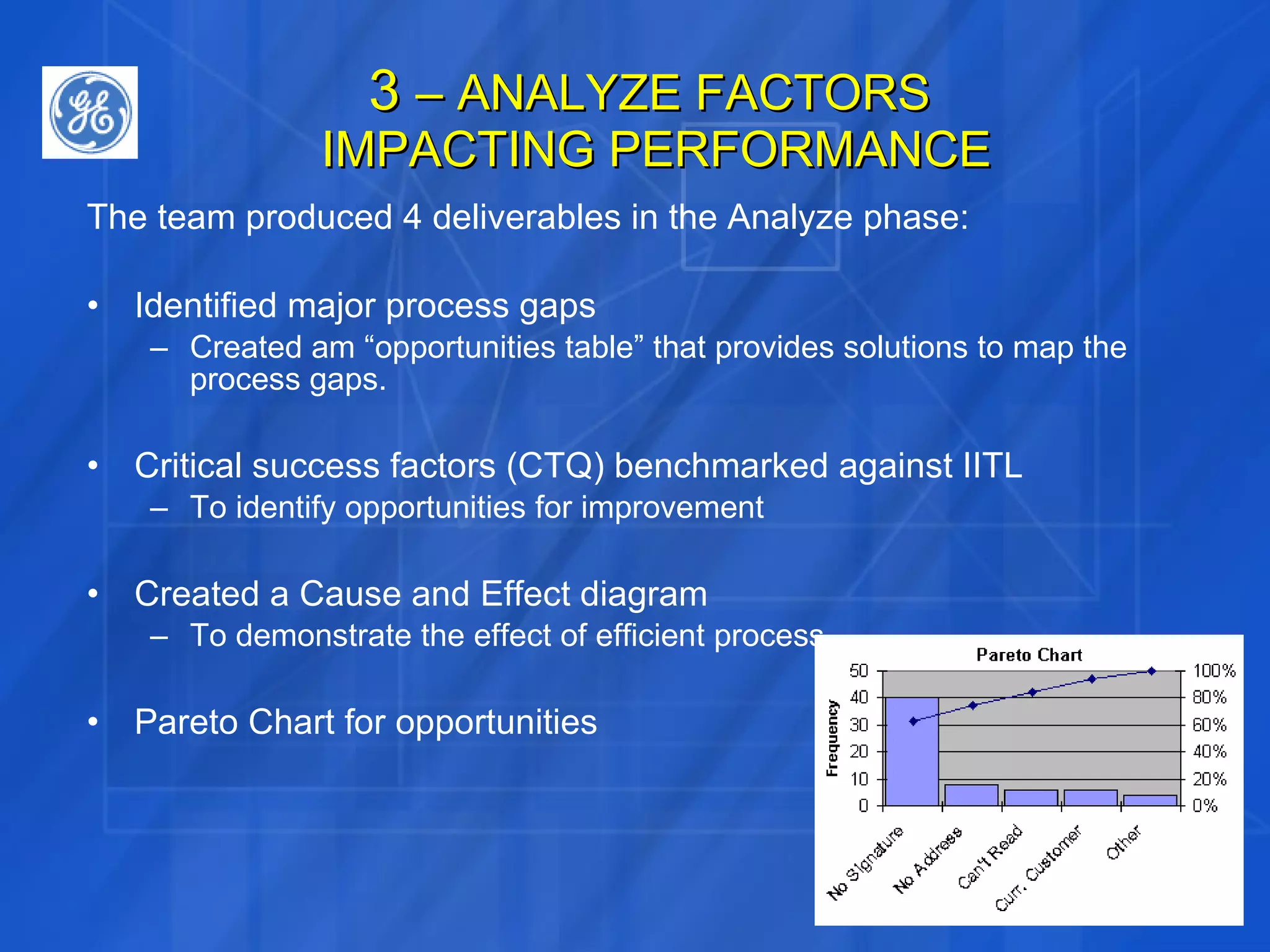
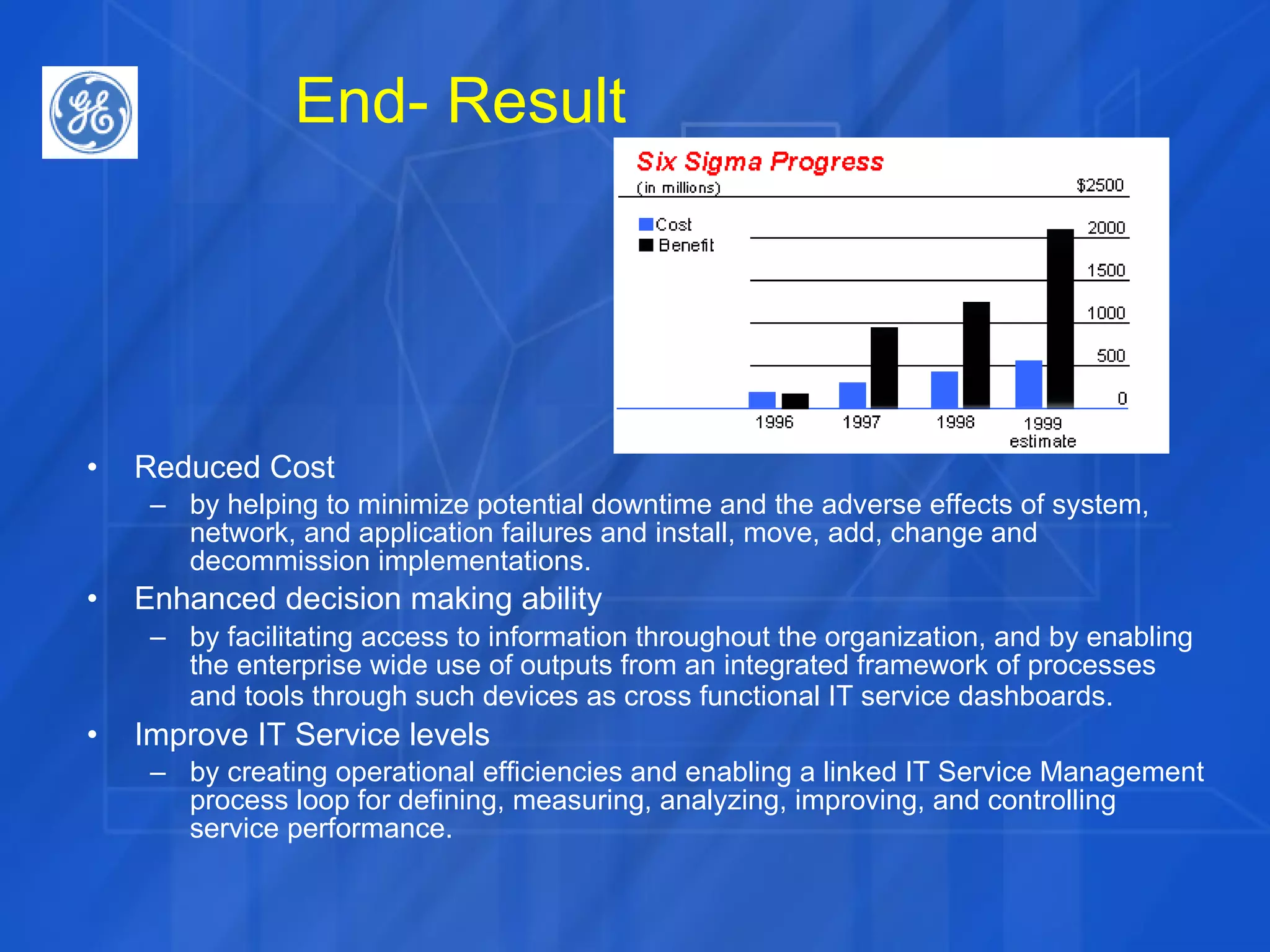
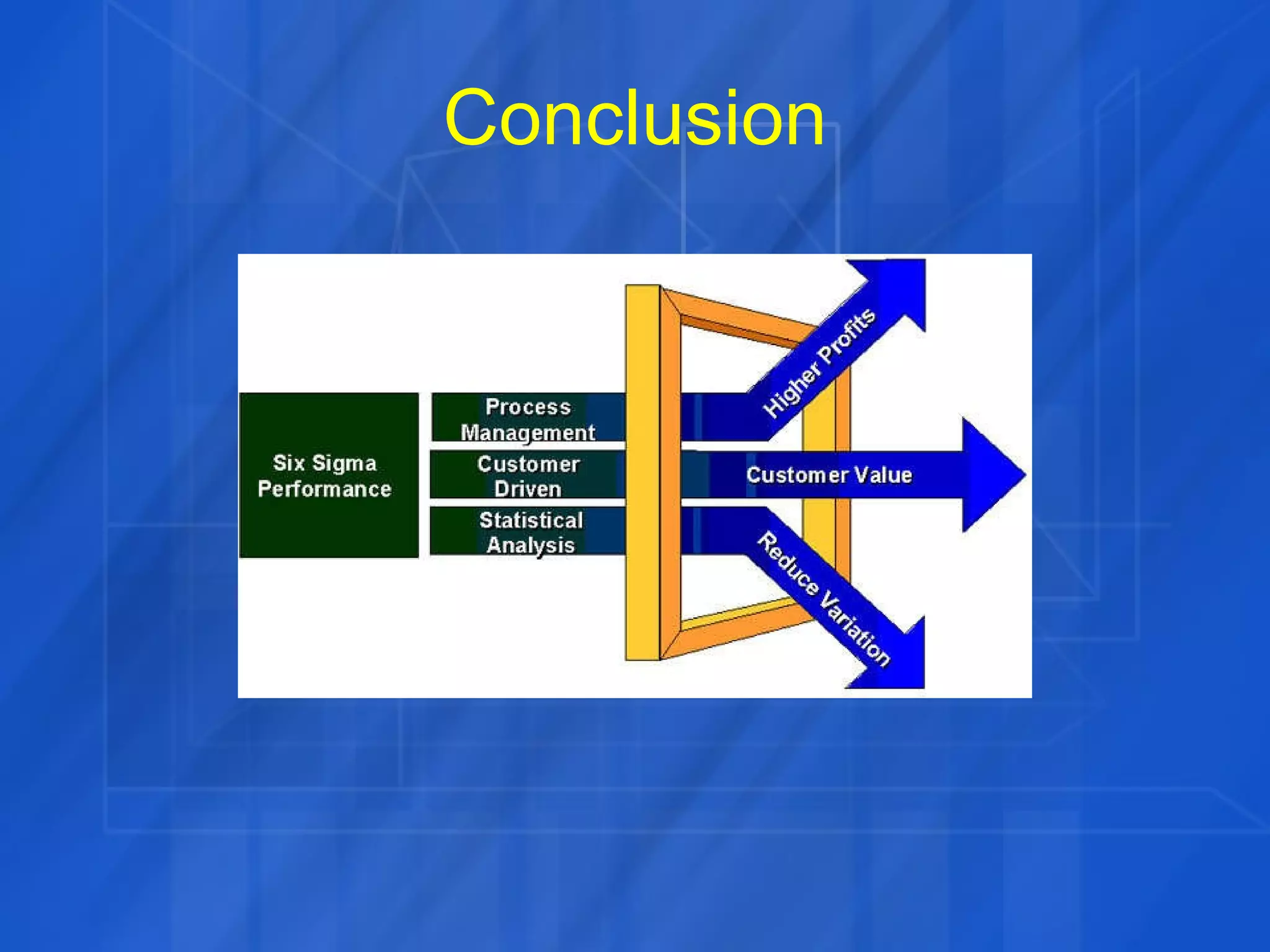
This document discusses how Six Sigma process and IT Service Management (ITSM) can be combined to improve IT application services. It outlines the Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control (DMAIC) process of Six Sigma and how each phase was applied in a case study at GE. The case study showed combining Six Sigma and ITIL reduced costs, enhanced decision making, and improved IT service levels through operational efficiencies and a linked service management process.